redis(1)
NoSQL 技术
泛指非关系型的数据库,NoSQL数据库的产生就是为了解决大规模数据集合多重数据种类带来的挑战,尤其是大数据应用难题。它是基于内存的数据库,并且提供一定的持久化功能。
Redis和MongoDB是当前使用最广泛的NoSQL,而就Redis技术而言,它的性能十分优越,可以支持每秒十几万此的读/写操作,其性能远超数据库,并且还支持集群、分布式、主从同步等配置,原则上可以无限扩展,让更多的数据存储在内存中,更让人欣慰的是它还支持一定的事务能力,这保证了高并发的场景下数据的安全和一致性。
Redis
Redis 是一个开源(BSD许可)的,内存中的数据结构存储系统,它可以用作数据库、缓存和消息中间件。 它支持多种类型的数据结构,如字符串(strings), 散列(hashes), 列表(lists), 集合(sets), 有序集合(sorted sets) 与范围查询, bitmaps, hyperloglogs 和 地理空间(geospatial) 索引半径查询。 Redis 内置了 复制(replication),LUA脚本(Lua scripting), LRU驱动事件(LRU eviction),事务(transactions) 和不同级别的 磁盘持久化(persistence), 并通过 Redis哨兵(Sentinel)和自动 分区(Cluster)提供高可用性(high availability)。
Linux安装Redis
1)在redis根目录下执行: make 指令
2)安装:make install
3)reids 启动校验:redis -server
4)解决控制台启动redis后不能在执行其它指令
在redis根目录下执行:vim redis.conf
4.1:取消ip绑定

4.2:关闭保护模式
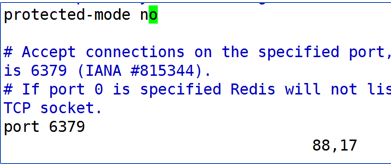
4.3:开启后台启动

spring管理redis
1.序列化工具类
/** * 需要将json串与对象实现互转 */ public class ObjectMapperUtil { private static final ObjectMapper MAPPER = new ObjectMapper(); public static String toJSON(Object obj) { String json = null; try { json = MAPPER.writeValueAsString(obj); } catch (JsonProcessingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException(e); } return json; } //将json串转化为对象 public static <T> T toObject(String json,Class<T> targetClass) { T obj = null; try { obj = MAPPER.readValue(json, targetClass); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException(e); } return obj; } }
2.编辑properties文件
redis.host=192.168.175.129
redis.port=6379
3.编辑配置类
@Configuration //标识配置类 @PropertySource("classpath:/properties/redis.properties") public class RedisConfig { @Value("${redis.host}") private String host; @Value("${redis.port}") private Integer port; @Bean @Scope("prototype") //设置为多例 当用户使用时创建 public Jedis jedis() { return new Jedis(host, port); } }
4.业务实现
/** * 步骤: * 1.先查询缓存 确定key的写法 * 2.如果缓存中没有数据.说明用户第一次查询. * 先查询数据库,将数据转化为JSON.保存到redis中. * 3.如果缓存中有数据.说明不是第一次查询.从redis中 * 获取数据.需要将json转化为对象. */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") @Override public List<EasyUITree> findItemCatCache(Long parentId) { List<EasyUITree> treeList = new ArrayList<>(); String key = "ITEMCAT::"+parentId; String json = jedis.get(key); //判断数据是否为null if(StringUtils.isEmpty(json)) { //用户第一次查询 treeList = findItemCatByParentId(parentId); String itemCatJSON = ObjectMapperUtil.toJSON(treeList); jedis.set(key, itemCatJSON); System.out.println("用户第一次查询数据"); }else { //说明用户不是第一次查询 treeList = ObjectMapperUtil.toObject(json, treeList.getClass()); System.out.println("用户查询缓存!!!!"); } return treeList; }
5.控制层实现
@RequestMapping("/list")
public List<EasyUITree> findItemCatByParentId
(@RequestParam(value = "id",defaultValue = "0") Long parentId){
//return itemCatService.findItemCatByParentId(parentId);
//先查询缓存,如果缓存中没有数据,则查询数据库
return itemCatService.findItemCatCache(parentId);
}
AOP实现缓存查询
1.自定义注解@Target(ElementType.METHOD) //对方法生效 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //运行时有效 public @interface CacheFind { //1.key可以动态获取. 类名.方法名::第一个参数值 //2.key也可以自己指定. String key() default ""; int seconds() default 0; //用户数据不超时 }
2.定义切面
@Component //将类交给容器管理 @Aspect //标识切面 public class CacheAspect { @Autowired private Jedis jedis; //如果是环绕通知,则参数必须写ProceedingJoinPoint,必须位于第一位 @Around("@annotation(cacheFind)") public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint,CacheFind cacheFind) { Object obj = null; String key = getKey(joinPoint,cacheFind); //1.先查询缓存数据 String result = jedis.get(key); try { if(StringUtils.isEmpty(result)) { //第一次查询数据 obj = joinPoint.proceed(); //执行目标方法 //将数据保存到redis中 String json = ObjectMapperUtil.toJSON(obj); //判断用户是否传递超时时间 if(cacheFind.seconds()==0) jedis.set(key, json); else jedis.setex(key, cacheFind.seconds(), json); System.out.println("执行数据库查询"); }else { //数据不为null,将缓存数据转化为对象 Class returnType = getType(joinPoint); obj = ObjectMapperUtil.toObject(result,returnType); System.out.println("执行AOP缓存!!!!"); } } catch (Throwable e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException(e); } return obj; } /** * 目的:获取方法的返回值类型 * 提示:利用方法对象获取返回值类型 * @param joinPoint * @return */ private Class getType(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) { MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature(); return signature.getReturnType(); /* * Object[] objs = joinPoint.getArgs(); Class[] argsClass = new * Class[objs.length]; for (int i=0; i<objs.length;i++) { argsClass[i] = * objs[i].getClass(); } * * joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getMethod(name, parameterTypes); */ } //判断用户是否传递参数, 如果用户传参使用用户自己的key. //如果用户没有指定参数,使用动态生成的. private String getKey(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, CacheFind cacheFind) { //获取当前方法的名称 类名.方法名 String className = joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName(); String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); String key = cacheFind.key(); if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(key)) { //以用户的数据为准 return className+"."+methodName+"::"+key; }else {//动态拼接参数 //类名.方法名::第一个参数值 Object args0 = joinPoint.getArgs()[0]; return className+"."+methodName+"::"+args0; } } }
Redis命令
1.启动命令:redis-server redis.conf
2.进入客户端 : redis-cli -p 6379
3.查看客户端详细信息:info replication
4.关闭reids:redis-cli -p 6379 shutdown
如果是默认端口 redis-cli shutdown
退出:ctrl+c、exit、quit

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号