scrapy的一个简单小项目
使用scrapy抓取目标url下所有的课程名和价格,并将数据保存为json格式url=http://www.tanzhouedu.com/mall/course/initAllCourse
观察网页并分析该网页:
是一个ajax加载的页面,每次数据变化,但是url不变化,
通过查看headers中的信息,得到每次点击下一页时真正请求的链接url
观察发现每次翻页,请求变化的是offset的数值和时间戳
1.创建项目
使用命令:scrapy startproject 'project_name'得到对象的项目文件夹,里面包含scrapy的一些必要组件
如下:

具体文件含义,参见链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/pythoner6833/p/9012292.html
2.明确抓取目标。
编辑items.py文件,定义好需要抓取的数据字段名
代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define here the models for your scraped items # # See documentation in: # https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html import scrapy class TanzhouItem(scrapy.Item): # define the fields for your item here like: # name = scrapy.Field() """ 定义爬取的目标,本案例中只爬取标题和价格两个内容 所以定义两个字段 """ # 课程金额 money = scrapy.Field() # 课程名称 title = scrapy.Field()
3.编辑爬虫。
进入spiders文件夹下,创建爬虫文件,命令:scrapy genspider 'spider_name' "start_url"
就会得到一个以spider_name命名的文件,在里面编写爬虫的逻辑
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ 抓取:http://www.tanzhouedu.com/mall/course/initAllCourse 下的所有课程名称和价格,并保存为json格式 网页分析: 是一个ajax加载的页面,每次数据变化,但是url不变化, 通过查看headers中的信息,得到每次点击下一页时真正请求的链接url 观察发现每次翻页,请求变化的是offset的数值和时间戳 1.首先创建一个爬虫项目。 使用命令:scrapy startproject 'pro_name' # pro_name是项目名称 输入命令后,会自动出现一个用pro_name的项目文件夹, 里面包含一个scrapy项目所必要的文件 2.明确爬取目标,编辑items.py文件,定义需要爬取的字段。 3.编辑爬虫。进入spiders文件夹下,创建爬虫文件。 使用命令:scrapy genspider 'spider_name' 'start_url' 生成一个爬虫,名字为spider_name,初始爬取url为start_url 会在spiders文件夹下生成一个spider_name.py的文件, 里面包含一个name=‘spider_name’, name是不同爬虫的唯一标识,不能重复 start_url是爬虫的第一个爬取链接(可修改),并返回一个response 解析response中的其他可用链接和数据 4.将爬取到的数据通过yield,丢给pipelines.py文件保存, 在pipelines.py文件中编写保存文件的逻辑 5.运行爬虫,使用命令:scrapy crawl "spider_name" 注:在配置文件中打开头信息和管道 """ import scrapy # 从items文件中导入已经写好的待爬取目标(money和title) from tanzhou.items import TanzhouItem import time class TzSpider(scrapy.Spider): name = 'tz' # 爬虫名称。区别于其他爬虫的唯一ID。 allowed_domains = ['tanzhouedu.com'] # 允许域名 # 爬虫的第一个爬取链接,启动爬虫就执行,并返回一个response交给parse函数 start_urls = ['http://www.tanzhouedu.com/mall/course/initAllCourse'] offset = 0 def parse(self, response): item = TanzhouItem() # 实例化。实例一个爬取字段的实例对象。 # 通过xpath解析response,并从中提取数据,得到xpath对象 node_list = response.xpath('//div[@id="newCourse"]/div/div/ul/li') for node in node_list: # extract_first() 是取对象的值,得到一个字符串 item['money'] = node.xpath('./div/span/text()').extract_first() item['title'] = node.xpath('./a/@title').extract_first() yield item # yield将item返回,scrapy_engine通过管道,将item交给pipelines # pipelines.py文件用于爬取结果的保存 if node_list == []: """ 下一页到最后时,xpath匹配到的是一个空列表 此时已没有可爬取页面,return结束程序。 """ return self.offset += 20 # 构造变化的offset,每次翻页增加20 # yield将新的请求丢给调度器,然后交给下载器,继续下载页面,得到response # callback回调parse函数,实现循环抓取 yield scrapy.Request(url="http://www.tanzhouedu.com/mall/course/initAllCourse?params.offset=" + str(self.offset) +"¶ms.num=20&keyword=&_=" + str(int(time.time() * 1000)), callback=self.parse)
4.编写保存数据的逻辑。
在pipelines.py文件中编写保存数据的逻辑
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define your item pipelines here # # Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting # See: https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html import json class TanzhouPipeline(object): """ 编写爬取到的数据保存的逻辑 """ def __init__(self): """ 可选择实现,对参数做一些初始化的处理 """ pass def open_spider(self, spider): """ 重写open_spider函数,该函数在爬虫启动时就自动执行 :param spider: :return: """ self.file = open("tz.json", 'w', encoding='utf-8') def process_item(self, item, spider): """ 将yield丢过来的数据进行一定的处理并保存 :param item: :param spider: :return: """ # 管道传过来的数据item是一个对象,将它转化为字典,然后存储 content = json.dumps(dict(item), ensure_ascii=False) + '\n' self.file.write(content) return item def close_spider(self, spider): """ 重写该函数,爬虫执行完毕后执行该函数 :param spider: :return: """ self.file.close()
5.运行爬虫。
使用命令:scrapy crawl "spider_name"
运行结果:
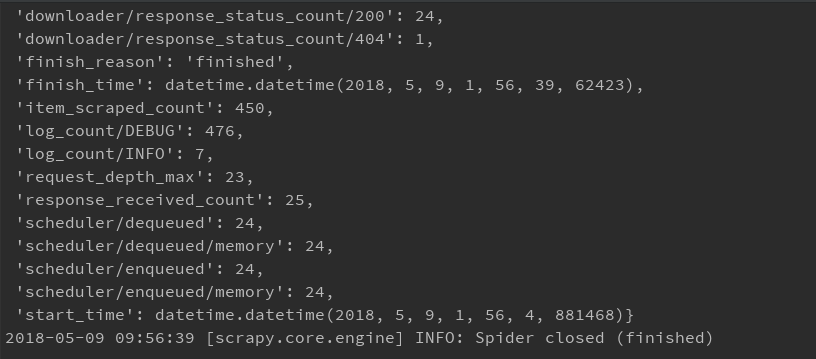
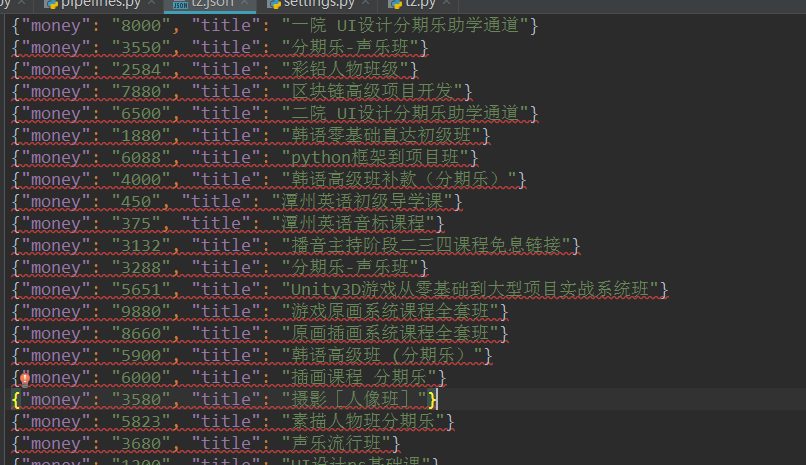
得到一个保存有抓取结果的json文件


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号