【Vue】Re17 Router 第四部分(参数传递,守卫函数)
一、案例搭建
新建Profile组件
组件写好内容后配置路由
{ path : '/profile', component : () => import('../components/Profile') }
二、参数配置
App.vue配置profile
我们可以使用对象对to的url进行封装
path属性就是url
query属性就是我们的请求数据【给地址的请求参数】
<template> <div id="app"> <router-link to="/home" tag="button" >去首页</router-link> <router-link to="/about" tag="button" >去关于</router-link> <router-link :to="/user/+username" tag="button" >用户管理</router-link> <router-link :to="ppp" tag="button" >profile</router-link> <!-- <button @click="toHome">首页</button>--> <!-- <button @click="toAbout">关于</button>--> <router-view></router-view> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'App', data() { return { username : 'aaa', ppp : { path : '/profile', query : { name : 'aaa', age : 22, gender : true } } } } // methods : { // toHome () { // this.$router.push('/home'); // }, // toAbout () { // this.$router.push('/about'); // } // } } </script> <style> #app { font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; -webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; -moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; text-align: center; color: #2c3e50; margin-top: 60px; } </style>
可以看到参数这样传递过来了
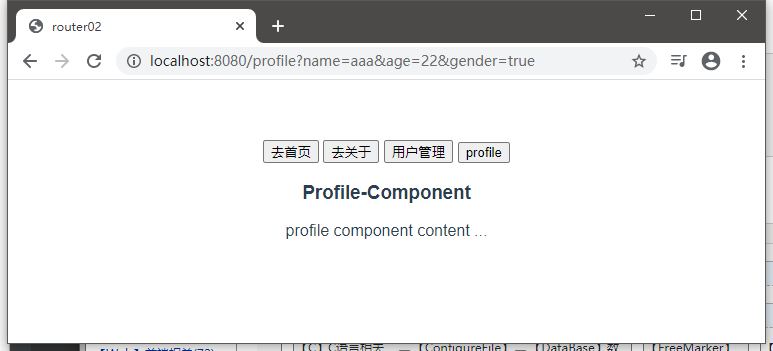
如果要取出请求参数,则可以这样:
写在方法里面获取,记得先从this对象引用
<template> <div> <h3>Profile-Component</h3> <p> profile component content ... <br> name -> {{$route.query.name}} <br> age -> {{$route.query.age}} <br> gender -> {{$route.query.gender}} </p> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "Profile" } </script> <style scoped> </style>
路由的代码写法:
<template> <div id="app"> <router-link to="/home" tag="button" >去首页</router-link> <router-link to="/about" tag="button" >去关于</router-link> <router-link :to="/user/+username" tag="button" >用户管理</router-link> <!-- <router-link :to="ppp" tag="button" >profile</router-link>--> <button @click="toProfile" >profile</button> <!-- <button @click="toHome">首页</button>--> <!-- <button @click="toAbout">关于</button>--> <router-view></router-view> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'App', data() { return { username : 'aaa', ppp : { path : '/profile', query : { name : 'aaa', age : 22, gender : true } } } }, methods : { toHome () { this.$router.push('/home'); }, toAbout () { this.$router.push('/about'); }, toProfile() { this.$router.push(this.ppp); } } } </script> <style> #app { font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; -webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; -moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; text-align: center; color: #2c3e50; margin-top: 60px; } </style>
三、$route & $router的区别?
router是全局路由控制器对象
route是当前活跃的路由对象,是routes属性数组中的一个元素,也可以是router对象内部的一个属性对象
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV15741177Eh?p=113
四、导航守卫方法
1、回顾Vue实例的生命周期
created() { // todo ... Vue创建时调用此函数, }, mounted() { // todo ... Vue实例开始挂载虚拟DOM时调用此函数 }, updated() { // todo ... ... 组件数据发生更新时调用 },
点击不同的子组件,更换标签文本的需求:
每一次访问不同的组件都会调用created函数
所以可以:
created() { // todo ... Vue创建时调用此函数, document.title = '关于-About'; },
但是这样N个组件就要写N次了,都是路由跳转的方式进行的
那么只要在监听路由跳转,在那个时刻把title组件的某一个数据就行了
import Vue from 'vue'; import Router from 'vue-router'; Vue.use(Router); /* 方式一 */ const Home = resolve => { require.ensure( ['../components/Home.vue'], () => resolve(require('../components/Home.vue')) ) } /* 方式二 */ const About = resolve => { require(['../components/About.vue'],resolve); } /* 方式三 */ const User = () => import('../components/User.vue'); const News = () => import('../components/home/News'); const Messages = () => import('../components/home/Messages'); const routerList = [ /* 重定向首页路由配置 */ { path : '', /* 缺省值默认指向 '/' */ redirect : '/home', }, { path : '/home', /* 为什么这里是path不是url? 因为完整的url还包括 项目根url(协议头 + 域名(或者IP地址) + 端口号 + 项目根名称路径(可选)) */ name : 'home', /* 名字可以不加 */ component : Home, /* 使用懒加载后component这里高亮显示 */ children : [ /* 设置子路由 */ { path : '', /* 这个缺省默认/home */ redirect : 'news', }, { path : 'news', /* 等同于 /home + /news = /home/news 这里不需要再加斜杠了 */ component : News, meta : { title : '新闻列表 - News' } }, { path : 'messages', component : Messages, meta : { title : '消息列表 - Messages' } } ], meta : { title : '首页 - Home' } }, { path : '/about', name : 'about', component : About, meta : { title : '关于 - About' } }, { path : '/user/:username', /* 动态路径:冒号+字符 */ name : 'user', component : User, meta : { title : '用户 - User' } }, { path : '/profile', component : () => import('../components/Profile'), meta : { title : '档案 - Profile' } } ] const router = new Router({ routes : routerList, mode : 'history', }); /* 在创建实例后调用 */ router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => { // 调用这个方法以为着重写,一定要调用 next方法, 否则路由无法跳转 // from 来自于哪个路由对象 // to 跳转到哪个路由对象 // 按照案例的需求,就可以这样设置了 route就是一个个routes的元素对象 // 可以设置一个meta属性对象,放入title属性和对应的值即可 document.title = to.meta.title; // 但是子路由没有命名的话会早曾undefined显示,因为meta属性为空 // 解决方案 document.title = to.matched[0].meta.title; // 跳转要放在最后,不然是跳完了再执行标签的文本更换 next(); }); export default router;
afterEach守卫方法:
router.afterEach((to, from) => { // 因为是跳转之后调用,自然而然的不需要next函数了 // TODO ... ... });
上述的两个都是全局守卫方法,在路由配置中重写并调用
五、局部路由守卫
详细资料:
https://router.vuejs.org/guide/advanced/navigation-guards.html
You can define beforeEnter guards directly on a route's configuration object:
const router = new VueRouter({ routes: [ { path: '/foo', component: Foo, beforeEnter: (to, from, next) => { // ... } } ] })
In-Component Guards
Finally, you can directly define route navigation guards inside route components (the ones passed to the router configuration) with the following options:
beforeRouteEnterbeforeRouteUpdatebeforeRouteLeave
const Foo = { template: `...`, beforeRouteEnter (to, from, next) { // called before the route that renders this component is confirmed. // does NOT have access to `this` component instance, // because it has not been created yet when this guard is called! }, beforeRouteUpdate (to, from, next) { // called when the route that renders this component has changed. // This component being reused (by using an explicit `key`) in the new route or not doesn't change anything. // For example, for a route with dynamic params `/foo/:id`, when we // navigate between `/foo/1` and `/foo/2`, the same `Foo` component instance // will be reused (unless you provided a `key` to `<router-view>`), and this hook will be called when that happens. // has access to `this` component instance. }, beforeRouteLeave (to, from, next) { // called when the route that renders this component is about to // be navigated away from. // has access to `this` component instance. } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号