【设计模式学习笔记】解释器模式、迭代器模式案例详解(C++实现)
目录
一、解释器模式
1. 什么是解释器模式
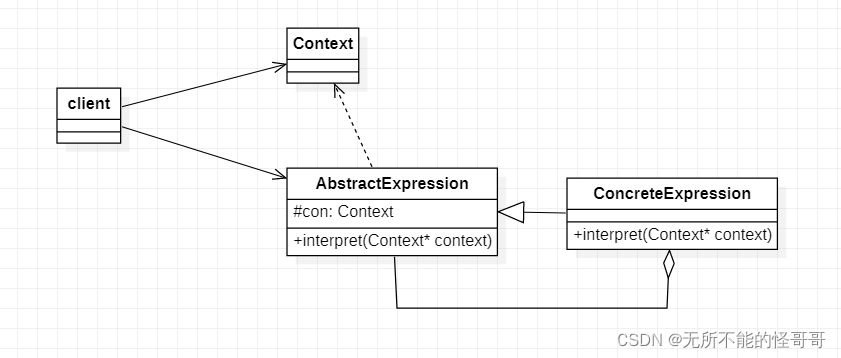
interpreter Pattern,解释器模式,是一种行为型模式。解释器模式提供一种对自定义语句的解释机制,解释器模式包含以下几种角色:
- Context:解释器的上下文环境,包含了不属于解释器的其他信息;
- AbstractExpression:抽象解释器,定义了一个抽象的解释操作接口;
- ConcreteExpression:具体解释器,实现对相关操作的解释;
2. 解释器模式案例
定义上下文环境
class Context
{
private:
int data;
int ret;
public:
void set_data(int data)
{
this->data = data;
}
void set_ret(int ret)
{
this->ret = ret;
}
int get_data()
{
return this->data;
}
int get_ret()
{
return this->ret;
}
};定义抽象解释器类,并实现一个加法解释器,加法解释器的操作是对传入的数据执行+1操作
class Expression
{
protected:
Context* context;
public:
virtual void interpret(Context* context) = 0;
};
class PlusExpression : public Expression
{
virtual void interpret(Context* context)
{
int temp = context->get_data();
temp++;
context->set_ret(temp);
}
};客户端操作,向加法解释器传入一个数据,打印处理结果
int main()
{
Expression* e = NULL;
Context* data = NULL;
e = new PlusExpression;
data = new Context;
data->set_data(1);
cout << "原始数据:" << data->get_data() << endl;
e->interpret(data);
data->get_ret();
cout << "经加法解释器处理后:" << data->get_ret() << endl;
delete data;
delete e;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
二、迭代器模式
1. 什么是迭代器模式
Iterator Pattern,迭代器模式,是行为型模式的一种。迭代器模式提供了一种从外部遍历访问一个容器的方法,并且在不需知道容器内部细节的前提下就可以完成对容器的顺序遍历。所以,创建迭代器的容器应该将自身的引用(this指针)传递给迭代器,迭代器通过持有的这个容器的引用来实现对容器的遍历。
- Iterator:迭代抽象类,用于提供实现迭代的最小方法集,一般包括获取开始对象、获取下一个对象、获取当前对象、判断是否结束这几个方法;
- ConcreteIterator:具体的迭代器,实现抽象迭代器定义的方法;
- Aggregate:聚集抽象类,可以理解为一个容器的接口;
- ConcreteAggregate:具体聚集类,容器的实现类;

2. 迭代器模式案例
定义一个抽象的迭代器类
class Iterator
{
public:
virtual void first() = 0;
virtual void next() = 0;
virtual bool is_done() = 0;
virtual int current_item() = 0;
};定义抽象容器类
class Aggregate
{
public:
virtual Iterator* create_iterator() = 0;
virtual int get_item(int index) = 0;
virtual int get_size() = 0;
};实现一个int类型的迭代器
class IntIterator : public Iterator
{
private:
Aggregate* age;
int index;
public:
IntIterator(Aggregate* age) //迭代器应该持有一个创建迭代器的容器的引用,这样才能通过迭代器访问容器
{ //谁创建迭代器就把谁的引用传递给迭代器
this->age = age;
this->index = 0;
}
virtual void first()
{
index = 0;
}
virtual void next()
{
if (index < age->get_size())
{
index++;
}
}
virtual bool is_done()
{
if (index == age->get_size())
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
virtual int current_item()
{
return age->get_item(index);
}
};定义一个int类型的容器
class IntArray : Aggregate
{
private:
int size;
int* array;
public:
IntArray(int size)
{
this->size = size;
array = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
array[i] = i + 1;
}
}
~IntArray()
{
if (array != NULL)
{
delete array;
array = NULL;
}
this->size = 0;
}
virtual Iterator* create_iterator()
{
return new IntIterator(this); //把自己的引用传给迭代器
}
virtual int get_item(int index)
{
return array[index];
}
virtual int get_size()
{
return this->size;
}
};客户端,通过迭代器来遍历数组
int main()
{
Iterator* it = NULL;
IntArray* array = NULL;
array = new IntArray(10);
it = array->create_iterator();
cout << "遍历数组:";
for (; !(it->is_done()); it->next())
{
cout << it->current_item() << " ";
}
cout << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号