Linux系统调用二、open()函数与close()函数介绍

❀1. open函数
- 包含头文件
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
- 函数原型
int open(const char *pathname, int flags);
int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);
-
函数功能
打开一个文件,并返回文件描述符。
-
函数参数
- pathname:文件名
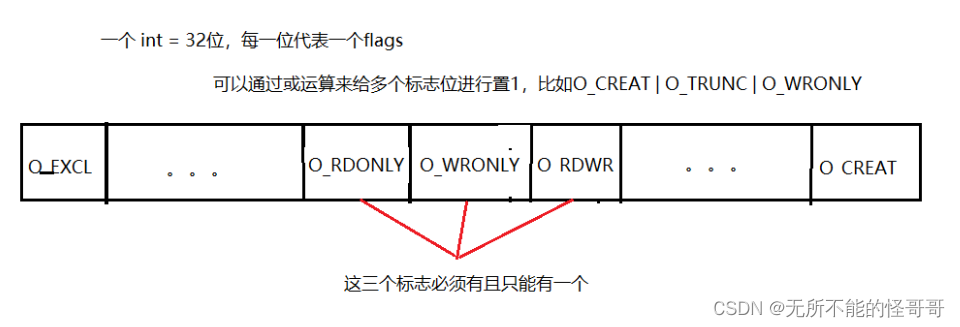
- flags:
- 必选参数(下面三个必须要有一个)
- O_RDONLY :只读
- O_WRONLY :只写
- O_RDWR :可读可写
- 可选参数(仅列出常用参数)
- O_APPEND :追加的方式打开,The file is opened in append mode.
- O_CREAT :如果文件不存在则创建,If the file does not exist it will be created.
- O_EXCL :和O_CREAT一块使用,如果文件存在则报错,if this flag is specified in conjunction with O_CREAT, and pathname already exists, then open() will fail.
- O_NONBLOCK :非阻塞的方式打开文件
![在这里插入图片描述]()
- 必选参数(下面三个必须要有一个)
- mode:权限位 (实际的权限是mode & ~umask的结果)
-
函数返回值
返回最小的空闲的文件描述符,如果失败则返回-1并设置errno,fopen() and creat() return the new file descriptor, or -1 if an error occurred (in which case, errno is set appropriately).
❀2. close函数
- 包含头文件
#include <unistd.h>
- 函数原型
int close(int fd);
-
函数功能
close() closes a file descriptor, so that it no longer refers to any file and may be reused.
-
函数参数
fd :一个文件的文件描述符
-
函数返回值
成功返回0,失败返回-1且设置errno,close() returns zero on success. On error, -1 is returned, and errno is set appropriately.
❀3. 使用open与close实现touch命令
/************************************************************
>File Name : mtouch.c
>Author : QQ
>Company : QQ
>Create Time: 2022年05月12日 星期四 19时48分14秒
************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if(argc < 2)
{
printf("not found file name\n");
return -1;
}
int i = 0;
for(i = 1; i < argc; i++)
{
int fd = open(argv[i], O_RDONLY | O_CREAT, 0666);
close(fd);
}
return 0;
}

实际上main函数也是有参数和返回值的,只不过我们在平时的学习中可能很少用到,main的返回值是int类型的,main函数的参数在Linux下编程用的还是比较多的。我们在运行一个可执行文件的时候可以在命令行传入参数给argv[],也就是说argv[]是用来存放我们在命令行传入的参数的,而参数argc用于统计参数的个数。不管我们传不传参数, argv[0]默认就是程序运行的路径名。也就是说argc最小为1(命令行不传参),argv[0]是程序运行路径。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号