二叉树的遍历-递归-非递归
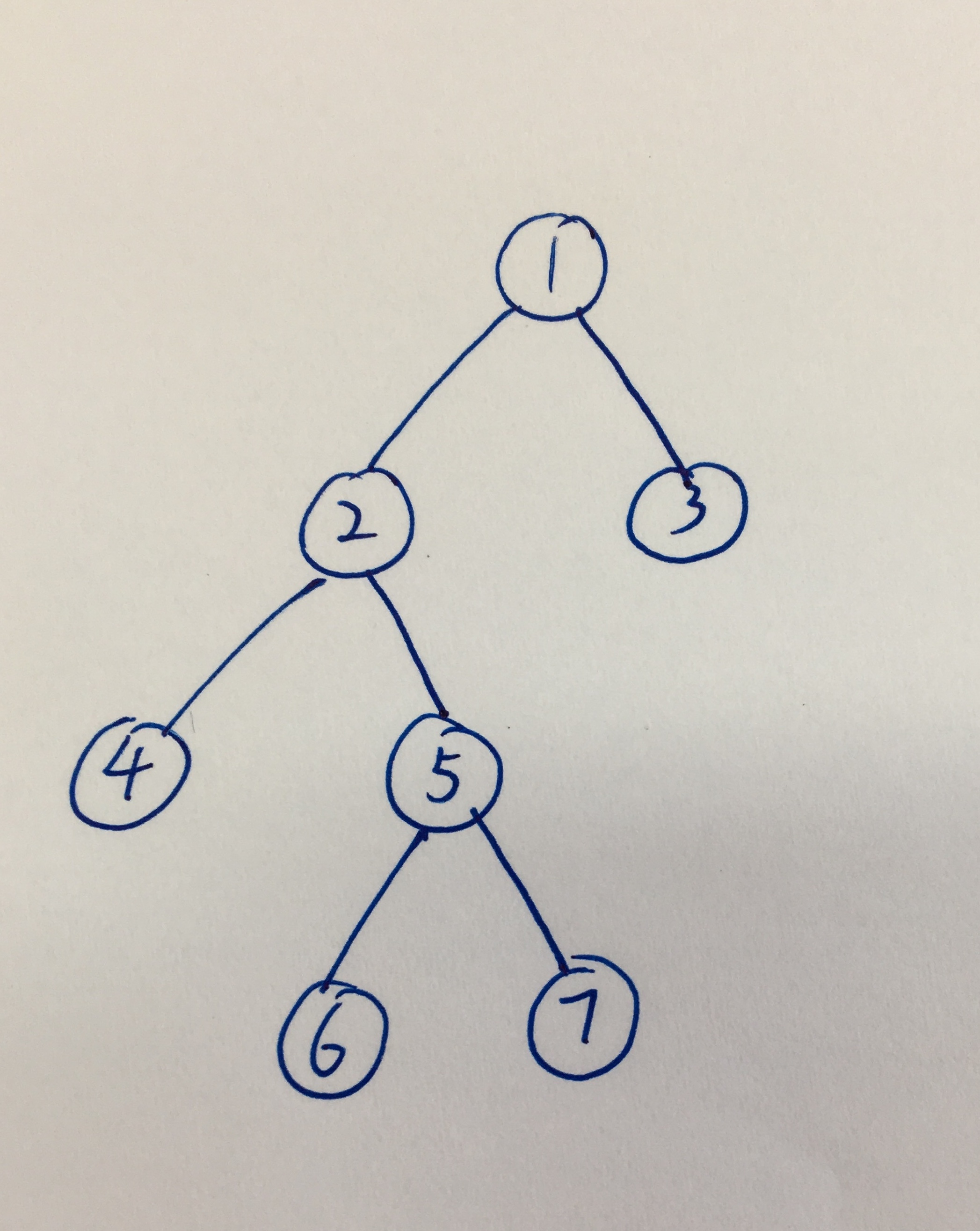
二叉树如上图所示。
一、递归遍历
#include <iostream> #include <stack> using namespace std; struct TreeNode { int val; TreeNode* left; TreeNode* right; TreeNode(int x): val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} }; // 先序遍历,递归 // [1] [2] [4] [5] [6] [7] [3] void preorder1(TreeNode* root) { if(!root) return; cout << '[' << root->val << "] "; preorder1(root->left); preorder1(root->right); } // 中序遍历,递归 // [4] [2] [6] [5] [7] [1] [3] void inorder1(TreeNode* root) { if(!root) return; inorder1(root->left); cout << '[' << root->val << "] "; inorder1(root->right); } // 后序遍历,递归 // [4] [6] [7] [5] [2] [3] [1] void postorder1(TreeNode* root) { if(!root) return; postorder1(root->left); postorder1(root->right); cout << '[' << root->val << "] "; }
二、非递归遍历
要借助栈或队列
// 先序遍历,非递归 void preorder2(TreeNode* root) { if(!root) return; stack<TreeNode*> s; s.push(root); while(!s.empty()) { TreeNode* node = s.top(); cout << '[' << node->val << "] "; s.pop(); if(node->right) s.push(node->right); if(node->left) s.push(node->left); } }
初始化把根节点压栈,访问根节点并弹出,然后依次将右节点、左节点入栈,直到栈为空。
// 先序遍历,非递归 void preorder3(TreeNode* root) { stack<TreeNode*> s; while(root != NULL || !s.empty()) { if(root != NULL) { s.push(root); cout << '[' << root->val << "] "; root = root->left; } else { root = s.top(); s.pop(); root = root->right; } } }
思路:回溯。访问根节点的左孩子,访问左孩子的左孩子,直到左孩子为空,这个过程中把所有访问过的节点压栈,当左孩子为空,pop该节点,访问该节点的右孩子。空间复杂度O(logN) 和树的深度有关。时间复杂度O(N),所有节点都访问了一遍。
// 中序遍历,非递归 void inorder2(TreeNode* root) { stack<TreeNode*> s; while(root != NULL || !s.empty()) { if(root != NULL) { s.push(root); root = root->left; } else { root = s.top(); cout << '[' << root->val << "] "; s.pop(); root = root->right; } } }
和上面回溯的思路相同,只是访问根节点的时机不一样。
// 后序遍历,非递归 void postorder2(TreeNode* root) { if(root == NULL) return; stack<TreeNode*> s1; stack<TreeNode*> s2; s1.push(root); while(!s1.empty()) { root = s1.top(); s2.push(root); s1.pop(); if(root->left) s1.push(root->left); if(root->right) s1.push(root->right); } while(!s2.empty()) { cout << '[' << s2.top()->val << "] "; s2.pop(); } }
用2个栈实现后序遍历。后序遍历,可以看作这样一个过程的逆过程:访问某个节点,访问其右节点,访问其左节点。这是一个“变形”的先序遍历,可以通过修改先序遍历的程序得到,这里用到第1个栈。把这个过程的输出全部压入第2个栈,再从上到下弹出第2个栈的元素就得到后序遍历的次序了。
参考链接: https://blog.csdn.net/sgbfblog/article/details/7773103



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号