.NET List常见操作之交集并集差集(转)
一、简单类型List的交集并集差集
1、先定义两个简单类型的List
List<int> listA = new List<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };
List<int> listB = new List<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4, 9 };
2、取两个List的并集
var resultUnionList= listA.Union(listB).ToList();
执行结果如下:

3、取两个List的交集
var resultIntersectList = listA.Intersect(listB);
执行结果如下:
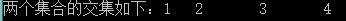
4、取两个List的差集,差集是指取在该集合中而不在另一集合中的所有的项
var resultExceptList = listA.Except(listB);
执行结果如下:
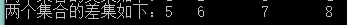
二、对象List集合的交集并集差集
1、先定义一个类
2、定义两个List
//LISTA
List<Student> stuListA = new List<Student>();
stuListA.Add(new Student
{
Name = "A1",
Age = 10,
Sex = "男"
});
stuListA.Add(new Student
{
Name = "A2",
Age = 11,
Sex = "男"
});
//LISTB
List<Student> stuListB = new List<Student>();
stuListB.Add(new Student
{
Name = "B1",
Age = 10,
Sex = "女"
});
stuListB.Add(new Student
{
Name = "B2",
Age = 11,
Sex = "男"
});
3、取上述两个list集合的并集
var result = stuListA.Union(stuListB).ToList();
4、取上述两个list集合的交集,应为是对象集合,可以根据一定规则 Func<TSource, bool> predicate限定那些属于交集
(1)取两个对象集合中对象名称一样的交集
var result = stuListA.Where(x => stuListB.Any(e => e.Name == x.Name)).ToList();
(2)取两个对象集合中对象名称、对象年龄、对象性别都一样的交集
var result = stuListA.Where(x => stuListB.Any(e => e.Name == x.Name && e.Age == x.Age && e.Sex == x.Sex)).ToList();
5、取上述两个list集合的差集,可以根据一定规则 Func<TSource, bool> predicate限定那些属于差集
(1)取差集,根据两个对象集合中对象名称一样的规则取差集
var result = stuListA.Where(x =>! stuListB.Any(e => e.Name == x.Name)).ToList();
(2)取差集,根据两个对象集合中对象名称、对象年龄、对象性别都一样的规则取差集
var result = stuListA.Where(x => !stuListB.Any(e => e.Name == x.Name && e.Age == x.Age && e.Sex == x.Sex)).ToList();
三、List<string>和List<int>互相转换
List<string> 转 List<int>
var list = (new[]{"1","2","3"}).ToList();
var newlist = list.Select<string,int>(x =>Convert.ToInt32(x));List<int> 转List<string>
List<int> list = new List<int>(new int[] { 1,2,3 } );
List<string> newList = list.ConvertAll<string>(x => x.ToString());
四、List排重
1、使用linq提供的Distinct方法
public class Test
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
public class TestMain
{
public static void TestMothod()
{
List<Test> testList = new List<Test>();
testList.Add(new Test { ID = 1, Name = "小名" });
testList.Add(new Test { ID = 1, Name = "小红" });
testList.Add(new Test { ID = 2, Name = "小名" });
//通过使用默认的相等比较器对值进行比较返回序列中的非重复元素。
List<Test> tempList = testList.Distinct<Test>().ToList();
}
}
2、根据某个字段排除重复项
添加一个扩展排重扩展方法:
public static class DistinctExtension
{
public static IEnumerable<TSource> DistinctBy<TSource, TKey>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source, System.Func<TSource, TKey> keySelector)
{
HashSet<TKey> seenKeys = new HashSet<TKey>();
foreach (TSource element in source)
{
if (seenKeys.Add(keySelector(element)))
{
yield return element;
}
}
}
}
使用上述扩展方法:
public class TestMain
{
public static void TestMothod()
{
List<Test> testList = new List<Test>();
testList.Add(new Test { ID = 1, Name = "小名" });
testList.Add(new Test { ID = 1, Name = "小红" });
testList.Add(new Test { ID = 2, Name = "小名" });
//根据某个字段排除重复项。
List<Test> tempList = testList.DistinctBy(p => p.ID).ToList();
}
}





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?