3.NetDh框架之缓存操作类和二次开发模式简单设计(附源码和示例代码)
前言
NetDh框架适用于C/S、B/S的服务端框架,可用于项目开发和学习。目前包含以下四个模块
1.数据库操作层封装Dapper,支持多种数据库类型、多库实例,简单强大;
此部分具体说明可参考博客: https://www.cnblogs.com/michaeldonghan/p/9317078.html
2.提供简单高效的日志操作类使用,支持日志写入Db和txt、支持任何数据库类型写入(包括传统sql数据库和nosql数据库等)、支持同步写入日志和后台独立线程异步处理日志队列;
此部分具体说明可参考博客: https://www.cnblogs.com/michaeldonghan/p/9321691.html
3.提供简单缓存设计和使用;
此部分具体说明可参考博客: 本文以下章节内容。
4.业务逻辑层服务简单设计,可方便支持二次开发模式。
此部分具体说明可参考博客: 本文以下章节内容。
1.缓存操作类
项目中应当都要考虑缓存的设计,不管是小项目的内存缓存还是大项目中的Redis/Memcache等。缓存的介质比较有可能切换,比如由于数据量的提高,会从内存缓存切换到memcache。这时候就要设计缓存接口,用接口操作缓存动作,如下图的ICacheHandle接口。之前文章有讲到数据库操作是设计为抽象基类DbHandleBase,抽象类注重代码的重用,接口定义类的行为,类可以实现多个接口,但只能继承一个抽象类。
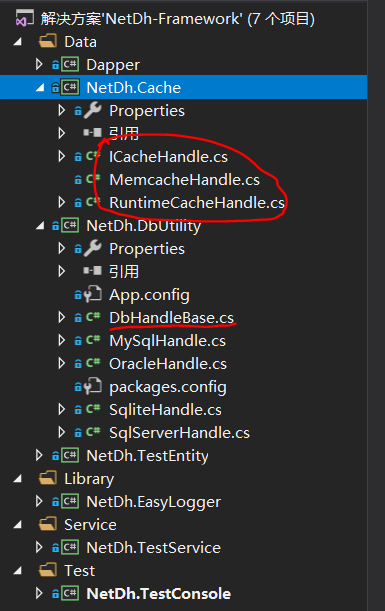
缓存操作类比较简单,上图的内存缓存操作类RuntimeCacheHandle直接使用现成的System.Web.HttpRuntime.Cache实现,B/S、C/S都可以使用。上代码(取缓存使用泛型操作,使用起来方便很多):
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Web; using System.Web.Caching; namespace NetDh.Cache { /* * 如果你的缓存介质会有切换的可能,则建议用接口操作, * 此内存缓存操作类RuntimeCacheHandle是使用现成的System.Web.HttpRuntime实现,B/S、C/S都可以使用。 */ /// <summary> /// 内存缓存操作类。 /// </summary> public class RuntimeCacheHandle : ICacheHandle { /// <summary> /// 取缓存。 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T">T可以是引用类型,也可以是值类型</typeparam> /// <param name="key"></param> /// <returns>当缓存不存在时,引用类型返回null;而值类型返回的默认值,并不代表缓存存在。</returns> public T Get<T>(string key) { object value = HttpRuntime.Cache.Get(key); if (value != null) { return (T)value; } return default(T);//注意:值类型返回的默认值 ,并不代表缓存存在。 } /// <summary> /// 存入缓存。存入的是源value数据的备份,源数据修改不影响缓存。 /// (一般直接写Set("key1",obj),而不用Set<object>("key1",obj),因为.net会自动根据obj判断T的类型) /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T">T可以是引用类型,也可以是值类型</typeparam> /// <param name="key"></param> /// <param name="value"></param> /// <param name="timeOut">缓存的过期时间(秒),-1代表不过期。</param> /// <returns></returns> public bool Set<T>(string key, T value, int timeOut = -1) { if (timeOut == -1) { HttpRuntime.Cache.Insert(key, value); } else { var timeSpan = new TimeSpan(0, 0, timeOut); HttpRuntime.Cache.Insert(key, value, null, System.Web.Caching.Cache.NoAbsoluteExpiration, timeSpan); } return true; } /// <summary> /// 如果不存在key缓存,则添加,返回true。如果已经存在key缓存,则不作操作,返回false。 /// (存入的是源value数据的备份,源数据修改不影响缓存。) /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T">T可以是引用类型,也可以是值类型</typeparam> /// <param name="key"></param> /// <param name="value"></param> /// <param name="timeOut">缓存的过期时间(秒),-1代表不过期。</param> /// <returns></returns> public bool AddIfNotExist<T>(string key, T value, int timeOut = -1) { var timeSpan = timeOut > 0 ? new TimeSpan(0, 0, timeOut) : System.Web.Caching.Cache.NoSlidingExpiration; var oldCache = HttpRuntime.Cache.Add(key, value, null, System.Web.Caching.Cache.NoAbsoluteExpiration, timeSpan, CacheItemPriority.Normal, null); return oldCache == null; } /// <summary> /// 删除缓存 /// </summary> /// <param name="key"></param> public void Remove(string key) { HttpRuntime.Cache.Remove(key); } public List<T> GetList<T>(List<string> keys) { //内存缓存不实现此接口函数,直接多次使用Get函数。 //memcache/redis一般会实现此接口函数,是为了一次连接可取回多个值。 throw new NotImplementedException(); } } }
memcache的操作类,网上代码很多,这边不再介绍。
2.二次开发模式简单设计
需求场景:多个客户需要同一个项目产品,但是客户之间对该产品的需求点又有些不一样。如果为多个客户都建立一个.net项目,那通用功能的代码就要维护多份,如果只建立一个.net项目,然后在同一个项目里加if判断,那改一个客户的需求,可能会影响到其它客户的功能。
解决方案:设计一种“二次开发模式”,即写一套通用功能的.net通用项目(实际环境中,如果一开始只有一个客户,那就以第一个客户的需求为通用项目,具体问题具体分析),不同客户都建立一个.net项目,但只处理客户定制的功能,这就涉及到override通用项目功能。
上示例代码来说明:
#region 正常调用服务和调用二次开发服务 //可以用服务工厂调用相应方法 ServiceFactory.Get<UserService>().TestFunc(); //也可以直接调用服务静态方法 UserService.TestStaticFunc(); //二次开发模式 //1.调用的是UserService中的TestVirtualFunc方法 ServiceFactory.Get<UserService>().TestVirtualFunc(); //2.场景:后续不改原系统代码,只是在原来基础上做二次开发 //注册二次开发Service //ServiceFactory.AddSecondaryAssembly(typeof(UserServiceX).Assembly);//其中UserServiceX继承自UserService //3.假如执行了ServiceFactory.AddSecondaryAssembly,则下行代码会调用到UserServiceX中的TestVirtualFunc方法 ServiceFactory.Get<UserService>().TestVirtualFunc(); #endregion
当注册了二次开发的程序集Assembly,就可以不改变通用项目的代码,而运行到二次开发程序集中的代码。
上ServiceFactory源码:
using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Concurrent; using System.Reflection; using System.Text; namespace NetDh.TestService { /// <summary> /// 获取Service对象帮助类 /// </summary> public class ServiceFactory { private static readonly ConcurrentDictionary<Type, BaseService> _services = new ConcurrentDictionary<Type, BaseService>(); static ServiceFactory() { //默认添加本程序集Service var types = Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetTypes(); var baseType = typeof(BaseService); foreach (var type in types) { if (type.IsSubclassOf(baseType)) { //不会实例化服务对象。只有用到时才会实例化 _services.TryAdd(type, null); } } } /// <summary> /// 获取服务,T一定是继承自BaseService /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T">BaseService子类</typeparam> /// <returns></returns> public static T Get<T>() where T : BaseService { Type type = typeof(T); BaseService service; if (!_services.TryGetValue(type, out service)) { throw new Exception("This service cannot be found"); } if (service == null) { service = Activator.CreateInstance(type) as BaseService; _services[type] = service; } return (T)service; } /// <summary> /// 添加二次开发Service程序集 /// </summary> /// <param name="assembly"></param> public static void AddSecondaryAssembly(Assembly secondaryAssembly) { if (secondaryAssembly == null) return; var secTypes = secondaryAssembly.GetTypes(); var baseType = typeof(BaseService); foreach (var secType in secTypes) { if (secType.IsSubclassOf(baseType)) { Type parentType = null; foreach (var type in _services.Keys) { if (secType.IsSubclassOf(type)) { parentType = type; break; } } if (parentType != null) {//如果二次开发重写了原Service类 //优先使用二次开发的Service对象。需要在初始化时就实例化。 _services[parentType] = Activator.CreateInstance(secType) as BaseService; } else {//如果二次开发的Service类是新增的,则直接添加,使用时再实例化 _services.TryAdd(secType, null); } } } } } }
3.NetDh框架完整源码
国外有github,国内有码云,在国内使用码云速度非常快。NetDh框架源码放在码云上:
https://gitee.com/donghan/NetDh-Framework



