C++:指针和函数
C++:指针和函数
当指针作为函数形参使用,可以修改形参的值。
函数值传递
普通值传递交换参数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap01(int a, int b) {
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
cout << "swap01 a = " << a << endl;
cout << "swap01 b = " << b << endl;
}
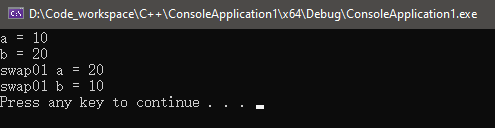
int main() {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
swap01(a, b);
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
函数地址传递
通过交换地址让指针指向相反的值
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap02(int * a, int * b) { //得到地址
int temp = *a;//交换地址
*a =* b;
*b = temp;
}
int main() {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
swap02(&a,&b);//取地址
cout << "swap01 a = " << *a << endl;
cout << "swap01 b = " << *b << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
函数的默认参数(小技巧)
C++中,函数的形参列表中的形参是可以有默认值的。C语言没有。
返回值类型 函数名 (参数 = 默认值){}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int func(int a, int b, int c);
int func(int a, int b=2, int c=3) {
return a + b + c;
}
int main(){
cout << func(1) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
函数占位参数
返回值类型 函数名 (数据类型){}
不管用不用,先占一个。🎃
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//返回值类型 函数名 (数据类型){}
void func(int a,int) {
cout << "this is func" << endl;
}
int main(){
func(10,10);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
函数的重载与Java一样
参考java重载
调用函数时与数据类型匹配。
C++对象模型和this指针
C++中,类内的成员变量和成员函数分开存储。
下列示例中空类占1个字节,int类型占4个字节。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Person {
//空为一个字节
int m_A;//4字节
static int m_B;
void func() {}
static void func1;
};
void test() {
Person p;
//空对象占用内存空间为:
//C++编译器会给每个空对象也分配一个字节空间,
//是为了区分空对象占内存的位置
//每个空对象也应该有一个独一无二的内存地址
cout << "size of p = " <<sizeof(p) << endl;
}
int main(){
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
C++提供特殊的对象指针,this指针指向被调用的成员函数所属的对象。
- this指针是
隐含每一个非静态成员函数的一种指针。 - this指针
不需要定义,直接使用即可。
this指针的用途:
- 当形参和成员变量
重名时,可用this指针来区分。 - 在类的
非静态成员函数中返回对象本身,可使用return * this
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
//解决名称冲突
//返回对象本身 * this
class Person {
public:
Person(int age) {
this->age = age;//解决名称冲突
}
int age;
void PersonAddAge(Person &p) {
this->age += p.age;
}
};
void test() {
Person p1(18);
cout << p1.age << endl;
}
void test1() {
Person p1(19);
Person p2(10);
p2.PersonAddAge(p1);
cout << p2.age << endl;
}
int main(){
test();
test1();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
空指针访问成员函数
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
//空指针调用成员函数
class Person {
public:
void showClassName() {
cout << "this is Person class" << endl;
}
void showPersonAge() {
if (this == NULL) {
return;
}
cout << "age = " << this->m_Age << endl;
}
int m_Age;
};
void test1() {
Person* p = NULL;
p->showClassName();
p->showPersonAge();
}
int main(){
test1();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
posted on 2022-04-16 09:48 Michael_chemic 阅读(62) 评论(0) 收藏 举报



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号