CMDB学习之四 ——DEBUG模式
定义一个debug,进行解析调试,到测试文件
配置文件,配置debug模式,定义环境变量,
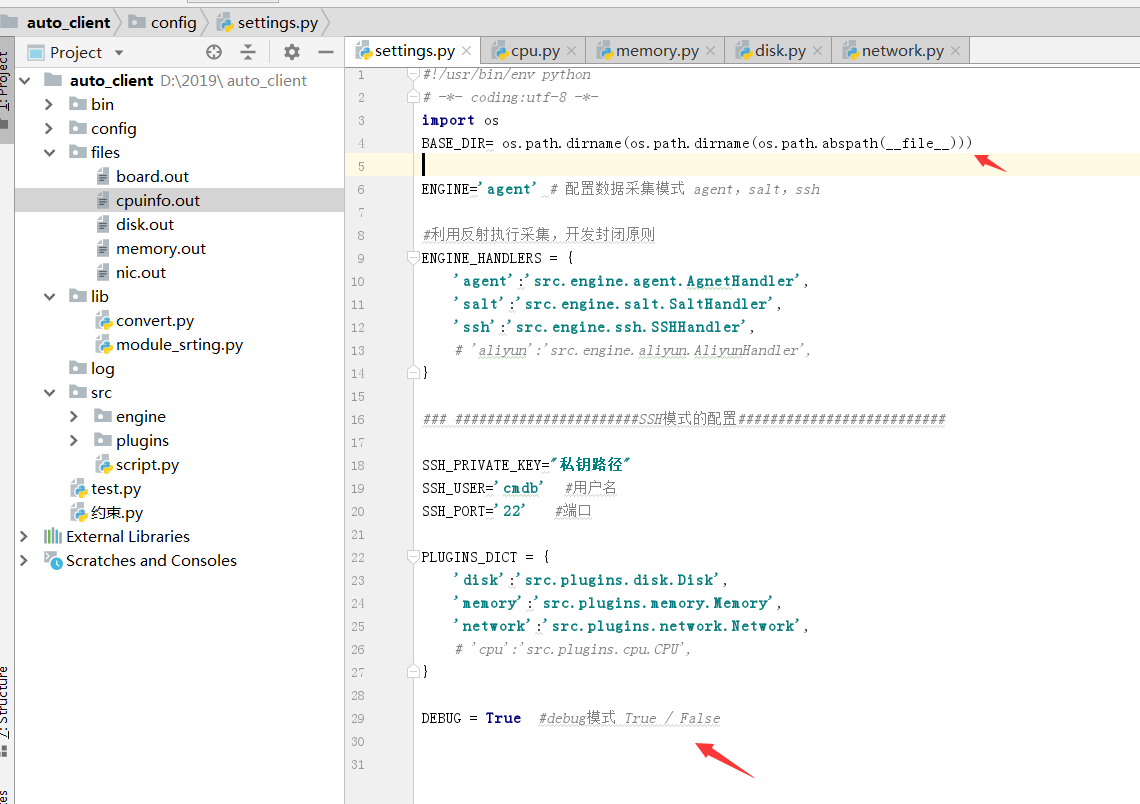
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import os BASE_DIR= os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))) ENGINE='agent' # 配置数据采集模式 agent,salt,ssh #利用反射执行采集,开发封闭原则 ENGINE_HANDLERS = { 'agent':'src.engine.agent.AgnetHandler', 'salt':'src.engine.salt.SaltHandler', 'ssh':'src.engine.ssh.SSHHandler', # 'aliyun':'src.engine.aliyun.AliyunHandler', } ### #######################SSH模式的配置########################## SSH_PRIVATE_KEY="私钥路径" SSH_USER='cmdb' #用户名 SSH_PORT='22' #端口 PLUGINS_DICT = { 'disk':'src.plugins.disk.Disk', 'memory':'src.plugins.memory.Memory', 'network':'src.plugins.network.Network', # 'cpu':'src.plugins.cpu.CPU', } DEBUG = True #debug模式 True / False
内存采集解析,内存采集中使用的 convert,导入文件在lib目录下
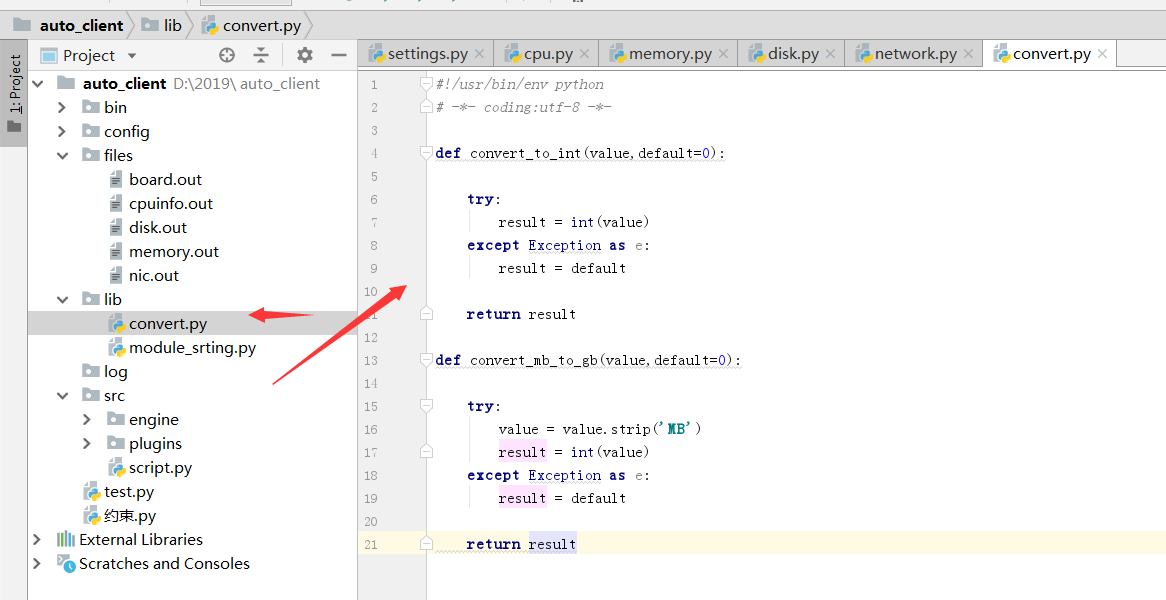
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- def convert_to_int(value,default=0): try: result = int(value) except Exception as e: result = default return result def convert_mb_to_gb(value,default=0): try: value = value.strip('MB') result = int(value) except Exception as e: result = default return result
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import os from .base import BasePlugin from lib import convert class Memory(BasePlugin): def win(self,handler,hostname): ''' 执行命令拿到结果-内存 :return: ''' print("执行win方法") ret = handler.cmd('wmic memphysical list brief',hostname)[0:10] return ret # def linux(self,handler,hostname): # ''' # 执行命令拿到结果-内存 # :return: # ''' # print("执行Linux方法") # ret = handler.cmd('free',hostname)[0:10] # return ret def linux(self, handler, hostname): if self.debug: output = open(os.path.join(self.base_dir, 'files', 'memory.out'), 'r').read() else: shell_command = "sudo dmidecode -q -t 17 2>/dev/null" output = handler.cmd(shell_command, hostname) return self.parse(output) def parse(self, content): """ 解析shell命令返回结果 :param content: shell 命令结果 :return:解析后的结果 """ ram_dict = {} key_map = { 'Size': 'capacity', 'Locator': 'slot', 'Type': 'model', 'Speed': 'speed', 'Manufacturer': 'manufacturer', 'Serial Number': 'sn', } devices = content.split('Memory Device') for item in devices: item = item.strip() if not item: continue if item.startswith('#'): continue segment = {} lines = item.split('\n\t') for line in lines: if len(line.split(':')) > 1: key, value = line.split(':') else: key = line.split(':')[0] value = "" if key in key_map: if key == 'Size': segment[key_map['Size']] = convert.convert_mb_to_gb(value, 0) else: segment[key_map[key.strip()]] = value.strip() ram_dict[segment['slot']] = segment return ram_dict
磁盘采集解析
# !/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- from .base import BasePlugin import os,re class Disk(BasePlugin): def win(self,handler,hostname): ''' 执行命令拿到结果-磁盘 :return: ''' print("执行win方法") ret = handler.cmd('wmic diskdrive',hostname)[0:10] return ret # def linux(self,handler,hostname): # ''' # 执行命令拿到结果-磁盘 # :return: # ''' # print("执行Linux方法") # # ret = handler.cmd('df -h',hostname)[0:10] # return ret def linux(self, handler, hostname): if self.debug: output = open(os.path.join(self.base_dir, 'files', 'disk.out'), 'r').read() else: shell_command = "sudo MegaCli -PDList -aALL" #根据执行的命令 output = handler.cmd(shell_command, hostname) return self.parse(output) def parse(self, content): """ 解析shell命令返回结果 :param content: shell 命令结果 :return:解析后的结果 """ response = {} result = [] for row_line in content.split("\n\n\n\n"): result.append(row_line) for item in result: temp_dict = {} for row in item.split('\n'): if not row.strip(): continue if len(row.split(':')) != 2: continue key, value = row.split(':') name = self.mega_patter_match(key) if name: if key == 'Raw Size': raw_size = re.search('(\d+\.\d+)', value.strip()) if raw_size: temp_dict[name] = raw_size.group() else: raw_size = '0' else: temp_dict[name] = value.strip() if temp_dict: response[temp_dict['slot']] = temp_dict return response @staticmethod def mega_patter_match(needle): grep_pattern = {'Slot': 'slot', 'Raw Size': 'capacity', 'Inquiry': 'model', 'PD Type': 'pd_type'} for key, value in grep_pattern.items(): if needle.startswith(key): return value return False
网络采集解析
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import os,re from .base import BasePlugin class Network(BasePlugin): def win(self,handler,hostname): ''' 执行命令拿到结果-网卡 :return: ''' print("执行win方法") ret = handler.cmd('ipconfig',hostname)[0:10] return ret # def linux(self,handler,hostname): # ''' # 执行命令拿到结果-网卡 # :return: # ''' # print("执行Linux方法") # ret = handler.cmd('ifconfig',hostname)[0:10] # return ret def linux(self, handler, hostname): if self.debug: output = open(os.path.join(self.base_dir, 'files', 'nic.out'), 'r').read() interfaces_info = self._interfaces_ip(output) else: interfaces_info = self.linux_interfaces(handler) self.standard(interfaces_info) return interfaces_info def linux_interfaces(self, handler): ''' Obtain interface information for *NIX/BSD variants ''' ifaces = dict() ip_path = 'ip' if ip_path: cmd1 = handler.cmd('sudo {0} link show'.format(ip_path)) cmd2 = handler.cmd('sudo {0} addr show'.format(ip_path)) ifaces = self._interfaces_ip(cmd1 + '\n' + cmd2) return ifaces def which(self, exe): def _is_executable_file_or_link(exe): # check for os.X_OK doesn't suffice because directory may executable return (os.access(exe, os.X_OK) and (os.path.isfile(exe) or os.path.islink(exe))) if exe: if _is_executable_file_or_link(exe): # executable in cwd or fullpath return exe # default path based on busybox's default default_path = '/bin:/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/local/bin' search_path = os.environ.get('PATH', default_path) path_ext = os.environ.get('PATHEXT', '.EXE') ext_list = path_ext.split(';') search_path = search_path.split(os.pathsep) if True: # Add any dirs in the default_path which are not in search_path. If # there was no PATH variable found in os.environ, then this will be # a no-op. This ensures that all dirs in the default_path are # searched, which lets salt.utils.which() work well when invoked by # salt-call running from cron (which, depending on platform, may # have a severely limited PATH). search_path.extend( [ x for x in default_path.split(os.pathsep) if x not in search_path ] ) for path in search_path: full_path = os.path.join(path, exe) if _is_executable_file_or_link(full_path): return full_path return None def _number_of_set_bits_to_ipv4_netmask(self, set_bits): # pylint: disable=C0103 ''' Returns an IPv4 netmask from the integer representation of that mask. Ex. 0xffffff00 -> '255.255.255.0' ''' return self.cidr_to_ipv4_netmask(self._number_of_set_bits(set_bits)) def cidr_to_ipv4_netmask(self, cidr_bits): ''' Returns an IPv4 netmask ''' try: cidr_bits = int(cidr_bits) if not 1 <= cidr_bits <= 32: return '' except ValueError: return '' netmask = '' for idx in range(4): if idx: netmask += '.' if cidr_bits >= 8: netmask += '255' cidr_bits -= 8 else: netmask += '{0:d}'.format(256 - (2 ** (8 - cidr_bits))) cidr_bits = 0 return netmask def _number_of_set_bits(self, x): ''' Returns the number of bits that are set in a 32bit int ''' # Taken from http://stackoverflow.com/a/4912729. Many thanks! x -= (x >> 1) & 0x55555555 x = ((x >> 2) & 0x33333333) + (x & 0x33333333) x = ((x >> 4) + x) & 0x0f0f0f0f x += x >> 8 x += x >> 16 return x & 0x0000003f def _interfaces_ip(self, out): ''' Uses ip to return a dictionary of interfaces with various information about each (up/down state, ip address, netmask, and hwaddr) ''' ret = dict() right_keys = ['name', 'hwaddr', 'up', 'netmask', 'ipaddrs'] def parse_network(value, cols): ''' Return a tuple of ip, netmask, broadcast based on the current set of cols ''' brd = None if '/' in value: # we have a CIDR in this address ip, cidr = value.split('/') # pylint: disable=C0103 else: ip = value # pylint: disable=C0103 cidr = 32 if type_ == 'inet': mask = self.cidr_to_ipv4_netmask(int(cidr)) if 'brd' in cols: brd = cols[cols.index('brd') + 1] return (ip, mask, brd) groups = re.compile('\r?\n\\d').split(out) for group in groups: iface = None data = dict() for line in group.splitlines(): if ' ' not in line: continue match = re.match(r'^\d*:\s+([\w.\-]+)(?:@)?([\w.\-]+)?:\s+<(.+)>', line) if match: iface, parent, attrs = match.groups() if 'UP' in attrs.split(','): data['up'] = True else: data['up'] = False if parent and parent in right_keys: data[parent] = parent continue cols = line.split() if len(cols) >= 2: type_, value = tuple(cols[0:2]) iflabel = cols[-1:][0] if type_ in ('inet',): if 'secondary' not in cols: ipaddr, netmask, broadcast = parse_network(value, cols) if type_ == 'inet': if 'inet' not in data: data['inet'] = list() addr_obj = dict() addr_obj['address'] = ipaddr addr_obj['netmask'] = netmask addr_obj['broadcast'] = broadcast data['inet'].append(addr_obj) else: if 'secondary' not in data: data['secondary'] = list() ip_, mask, brd = parse_network(value, cols) data['secondary'].append({ 'type': type_, 'address': ip_, 'netmask': mask, 'broadcast': brd, }) del ip_, mask, brd elif type_.startswith('link'): data['hwaddr'] = value if iface: if iface.startswith('pan') or iface.startswith('lo') or iface.startswith('v'): del iface, data else: ret[iface] = data del iface, data return ret def standard(self, interfaces_info): for key, value in interfaces_info.items(): ipaddrs = set() netmask = set() if not 'inet' in value: value['ipaddrs'] = '' value['netmask'] = '' else: for item in value['inet']: ipaddrs.add(item['address']) netmask.add(item['netmask']) value['ipaddrs'] = '/'.join(ipaddrs) value['netmask'] = '/'.join(netmask) del value['inet']



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号