redux学习
redux学习:
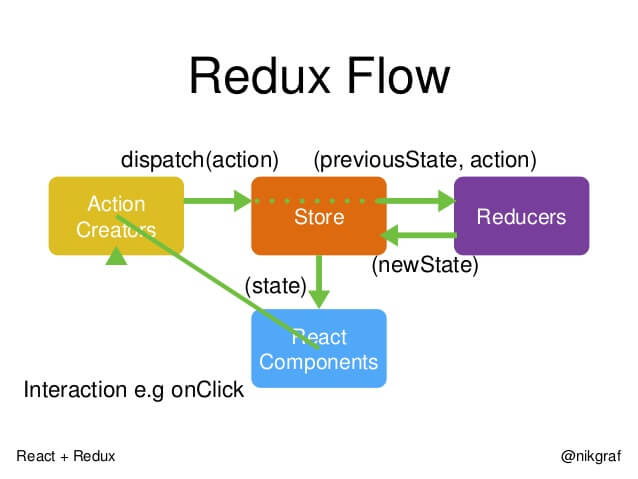
1.应用只有一个store,用于保存整个应用的所有的状态数据信息,即state,一个state对应一个页面的所需信息
注意:他只负责保存state,接收action, 从store.dispatch(aciton)获得一个action, 然后要通过reducer整理,旧state和新action,计算出新的state
1.1 创建:
store = Redux.createStore( reducer, initState)
1.2 方法:
store.getState() //获取当前额state
store.dispatch() //view 执行了某个操作,使用这个函数告诉store,不然store是不知道的
store.subscribe() //用于component 监听state变化,注册监听事件,返回取消监听的函数
2.Action 一次操作,类型为对象
2.1
{
type:‘add_count’, //type属性为必须存在 payload:‘something’ //该操作要改变或增加的数据 }
2.2 Action Creater: View 要发送多少种消息,就会有多少种 Action。如果都手写,会很麻烦。可以定义一个函数来生成 Action,这个函数就叫 Action Creator。
const ADD_TODO = '添加 TODO';
function addTodo(text) { return { type: ADD_TODO, text } } const action = addTodo('Learn Redux');
3.store.dispatch() //view 执行了某个action操作,使用这个函数告诉store,不然store是不知道的
import { createStore } from 'redux';
const store = createStore(fn);
//既然是告诉store执行了action,参数当然就是action了
store.dispatch({
type: 'ADD_TODO',
payload: 'Learn Redux'
});
4.Reducer : 函数,接收( state,action)作为参数,为store计算出新的state
const defaultState = 0; //初始state, 通过es6,传递默认值 const reducer = (state = defaultState, action) => { switch (action.type) { case 'ADD': return state + action.payload; default: return state; } }; const state = reducer(1, { type: 'ADD', payload: 2 });
4.1 reducer自动执行:
在react中,不需要每次执行了有action之后手动执行 reducer,每一次store从store.dispatch(action),中获得一个action后,都会自动执行reducer,所有我们只需要告诉store,reducer函数是怎样的就可以了
const store = createStore(reducer, initState); //其中initState是store的初始值,若有第二个参数,则忽略reducer中设置的默认值
4.2 纯函数
Reducer 函数最重要的特征是,它是一个纯函数。也就是说,只要是同样的输入,必定得到同样的输出。
纯函数是函数式编程的概念,必须遵守以下一些约束。
不得改写参数 不能调用系统 I/O 的API 不能调用Date.now()或者Math.random()等不纯的方法,因为每次会得到不一样的结果
4.3 由于 Reducer 是纯函数,就可以保证同样的State,必定得到同样的 View。但也正因为这一点,Reducer 函数里面不能改变 State,必须返回一个全新的对象,请参考下面的写法
// State 是一个对象 function reducer(state, action) { return Object.assign({}, state, { thingToChange }); // 或者 return { ...state, ...newState }; } // State 是一个数组 function reducer(state, action) { return [...state, newItem]; }
5. store.subscribe()
5.1 Store 允许使用store.subscribe方法设置监听函数,一旦 State 发生变化,就自动执行这个函数。
这api接收一个函数 listener 作为参数,放在在react component中,每当state变化,就执行对应的该component应该的显示改变
5.2 该api返回一个终止 该 listener的函数,执行可以终止监听
let unsubscribe = store.subscribe(() =>
console.log(store.getState())
);
unsubscribe();
6.对store的解读,createStore的简单实现
const createStore = (reducer) => { let state; let listeners = []; const getState = () => state; const dispatch = (action) => { state = reducer(state, action); listeners.forEach(listener => listener()); }; const subscribe = (listener) => { listeners.push(listener); return () => { listeners = listeners.filter(l => l !== listener); } }; dispatch({}); return { getState, dispatch, subscribe }; };
7.reducer的拆分
7.1 Reducer 函数负责生成 State。由于整个应用只有一个 State 对象,包含所有数据,对于大型应用来说,这个 State 必然十分庞大,导致 Reducer 函数也十分庞大。
请看下面的例子。
const chatReducer = (state = defaultState, action = {}) => { const { type, payload } = action; switch (type) { case ADD_CHAT: return Object.assign({}, state, { chatLog: state.chatLog.concat(payload) }); case CHANGE_STATUS: return Object.assign({}, state, { statusMessage: payload }); case CHANGE_USERNAME: return Object.assign({}, state, { userName: payload }); default: return state; } };
7.2 如何拆分,各管个的,每一个子reducer的state,其实只是整个应用的state.subState
//管理视图的reducer const visibilityFilter = (state = 'SHOW_ALL', action) => { switch (action.type) { case 'SET_VISIBILITY_FILTER': return action.filter default: return state } } export default visibilityFilter
//管理todo任务的reducer const todo = (state, action) => { switch (action.type) { case 'ADD_TODO': return { id: action.id, text: action.text, completed: false } case 'TOGGLE_TODO': if (state.id !== action.id) { return state } return { ...state, completed: !state.completed } default: return state } } const todos = (state = [], action) => { switch (action.type) { case 'ADD_TODO': return [ ...state, todo(undefined, action) ] case 'TOGGLE_TODO': return state.map(t => todo(t, action) ) default: return state } } export default todos
//合并 const todoApp = combineReducers({ todos, visibilityFilter }) export default todoApp
8.工作流程