python3笔记十二:python数据类型-Dictionary字典
一:学习内容
- 字典概念
- 字典创建
- 字典访问
- 字典添加
- 字典删除
- 字典遍历
- 字典与列表比较
二:字典概念
1.使用键值对(key-value)存储,具有极快的查找速度
2.注意:字典是无序的
3.特性:
- 字典中的key必须唯一
- key必须是不可变的对象
- 字符串、整数、元组等都是不可变的,可以作为key
- list是可变的,不能作为key
三:字典创建
1.创建空字典
dict0={}
2.创建有元素的字典
dict1 = {"tom":60, "tester":88,"lili":100}
四:字典访问
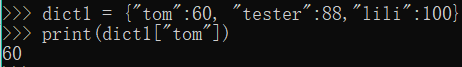
1.获取:字典名[key] 没有这个key就会报错
dict1 = {"tom":60, "tester":88,"lili":100}
print(dict1["tom"])
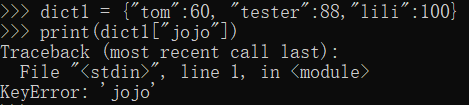
dict1 = {"tom":60, "tester":88,"lili":100}
print(dict1["jojo"]) #没有这个key会报错
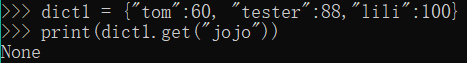
2.获取:dict1.get(key) 没有这个key返回None
dict1 = {"tom":60, "tester":88,"lili":100}
print(dict1.get("jojo")) #没有这个key不会报错,返回None
五:字典添加
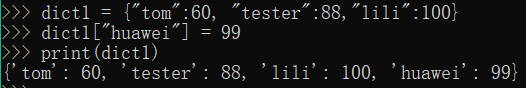
1.字典名[key] = value,如果key存在字典中就为修改
dict1 = {"tom":60, "tester":88,"lili":100}
dict1["huawei"] = 99
print(dict1)
#因为一个key对应一个value,所以多次对一个key赋值其实就是修改这个key的值
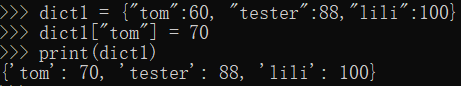
dict1 = {"tom":60, "tester":88,"lili":100}
dict1["tom"] = 70
print(dict1)
六:字典删除
1.字典名.pop(key)
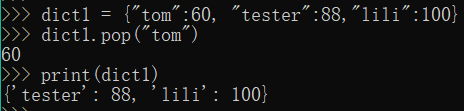
dict1 = {"tom":60, "tester":88,"lili":100}
dict1.pop("tom")
print(dict1)
七:字典遍历
1.遍历key
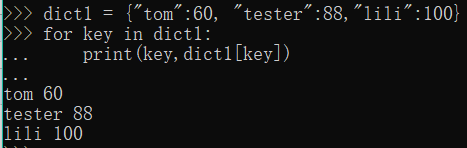
dict1 = {"tom":60, "tester":88,"lili":100}
for key in dict1:
print(key,dict1[key])
2.遍历value
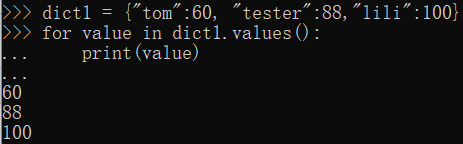
dict1 = {"tom":60, "tester":88,"lili":100}
for value in dict1.values():
print(value)
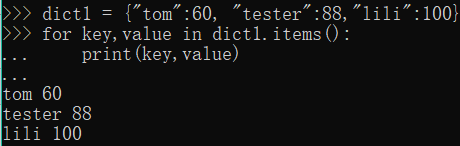
3.遍历key和value
dict1 = {"tom":60, "tester":88,"lili":100}
for key,value in dict1.items():
print(key,value)
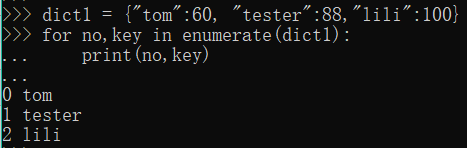
4.枚举遍历key,遍历key和key的序号,这个序号是我们存入字典里key的顺序
dict1 = {"tom":60, "tester":88,"lili":100}
for no,key in enumerate(dict1):
print(no,key)
八:字典与列表的区别
和list比较:
1、字典查找和插入的速度极快,不会随着key-value的增加变慢;列表查找和插入的速度会随着数据量的增加而变慢
2、字典需要占用大量的内存,内存浪费多,(多存了key的部分);列表占用空间少,浪费内存少





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!