python 之字符串的使用
在python中,字符串是最常用的数据类型,通常由单引号(' ')、双引号(" ")、三重引号(''' ''',""" """)引起来。
# 字符串的创建 str1 = "hello world" str2 = 'sunlight' str3 = '''On a new day, the sun rises in the East ''' str4 = """On a new day, the sun rises in the East""" str5 = "What's this?"
使用单引号、双引号、三重引号创建的字符串是无区别的,验证如下
str1 = 'sunlight' str2 = "sunlight" str3 = """sunlight""" str4 = '''sunlight''' print(str1 == str2 == str3 == str4) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py True Process finished with exit code 0
三重引号的使用场景一般用于类、函数等注释,或者定义含有多行的字符串
字符串是一个由独立字符组成的序列,意味着可以
1.获取字符串长度
# 获取字符串长度 str1 = 'sunlight' print(len(str1)) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py 8 Process finished with exit code 0
2、通过下标读取其中的某个字符
# 通过下标读取字符 str1 = 'sunlight' print(str1[1]) print(str1[0]) print(str1[-1]) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py u s t Process finished with exit code 0
3、通过切片方式读取字符串片段
# 切片方式读取片段 str1 = 'sunlight' print(str1[2:4]) print(str1[-4:-1]) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py nl igh
4.字符串拼接
# 字符串拼接 str1 = 'sunlight' str2 = 'hello ' print(str2 + str1) print(str1[2:4] + str2[1:3]) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py hello sunlight nlel
5.遍历字符串
# 遍历字符串 str1 = 'sunlight' for i in str1: print(i) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py s u n l i g h t Process finished with exit code 0
python中的转义字符:就是用反斜杠开头的字符串,表示特定的意义,常见的转义字符如表中所示
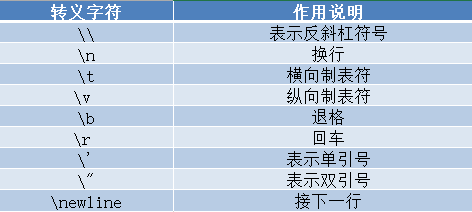
# 转义示例 str4 = """On a new day,the sun rises in the East""" str5 = 'what\t do\b you \v do' str6 = 'What\'s this?' str7 = "It's \"cat\"" print(str4, "\n", str5, "\n", str6, "\n", str7) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py On a new day,the sun rises in the East what d you do What's this? It's "cat" Process finished with exit code 0
python中字符串常用的运算符
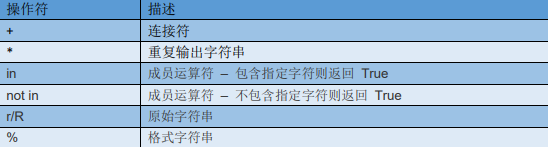
# 运算符示例 str1 = 'sun' + 'light ' s = "r" in str1 t = "r" not in str1 w = r'\n' + R'\t' z = 3.14159 print(str1, str1*3 + "\n", s, t, "\n" + w) print("Π的值是%s:" % z) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py sunlight sunlight sunlight sunlight False True \n\t Π的值是3.14159: Process finished with exit code 0
改变字符串:
在数组中可以通过下标直接更改值,但是字符串中同样的操作会提示“'str' object does not support item assignment”
# 变更字符串 str1 = 'sunlight' str1[0] = "D" print(str) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py Traceback (most recent call last): File "D:/demo/str_1.py", line 52, in <module> str1[0] = "D" TypeError: 'str' object does not support item assignment Process finished with exit code 1
通过创建新的字符串间接更改
# 创建新的字符串间接更改 str1 = 'sunlight' s = "S" + str1[1:] t = str1.replace("s", "S") str1 = s print(str1, t) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py Sunlight Sunlight Process finished with exit code 0
通过符号 += 更改
# 通过 += 符号 更改 str1 = 'sun' str1 += 'light' print(str1) info = "start " for s in str1: info += s print(info) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py sunlight start sunlight Process finished with exit code 0
python中的字符串格式化
字符串格式化可以理解为将实际值插入模板中
# 使用%实现字符串格式化 student = {"张三": 19, "李四": 20, "王五": 20} for info in student: print("学生 %s的年龄为 %s" % (info, student[info])) # 使用string.format()方法实现字符串格式化 prices = {"apple": 8.99, "banana": 6.99, "orange": 7.99} for price in prices: print("水果 {}的单价为 {}".format(price, prices[price])) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py 学生 张三的年龄为 19 学生 李四的年龄为 20 学生 王五的年龄为 20 水果 apple的单价为 8.99 水果 banana的单价为 6.99 水果 orange的单价为 7.99 Process finished with exit code 0
常用字符串内建函数
string.split(sep, maxsplit):maxsplit给定值max,sep在字符串中出现的次数为num, 且给定的值0<= max <=num,以sep作为分隔符进行切片字符串,则分割max+1个字符串,若max不传(不传时默认为-1)或者传入的值大于num,则默认分割num+1个字符串,并返回由字符串组成的数组
str1 = 'sunlight' r = str1.split("l") # maxsplit不传时,默认为-1,返回1+1个字符 s = str1.split("l", 0) # maxsplit传入0则返回0+1个字符 t = str1.split("l", 3) # maxsplit传入值大于分隔符出现的次数,返回1+1个字符 w = str1.split() # sep 不传时,默认为空白字符 print(r, "\n", s, "\n", t, "\n", w) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py ['sun', 'ight'] ['sunlight'] ['sun', 'ight'] ['sunlight'] Process finished with exit code 0
string.strip(chars): 从起始至末尾去掉指定的chars,若不指定默认去除字符串左边空格和末尾空格(相当于执行了string.lstrip()和string.rstrip()),并返回去除后的字符串
# 常用内建函数 str1 = ' sunlight ' t = str1.strip() w = str1.strip("t ") print(t) print(str1) print(w) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py sunlight sunlight sunligh Process finished with exit code 0
string.rstrip(chars): 右起去掉指定的chars,若不指定默认去除字符串末尾空格,并返回去除后的字符串
# 常用内建函数 str1 = ' sunlight ' x = str1.rstrip() y = str1.rstrip("t ") print(str1) print(x) print(y) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py sunlight sunlight sunligh Process finished with exit code 0
string.lstrip(chars): 左起删除指定的chars,若不指定默认去除字符串左边空格,并返回去除后的字符串
# 常用内建函数 str1 = ' sunlight ' z = str1.lstrip() t = str1.lstrip(' su') print(z) print(t) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py sunlight nlight Process finished with exit code 0
string.find(sub, start, end):检测字符串中是否包含指定字符串sub,如果包含则返回首次出现的位置索引值,否则返回-1,start、end非必填,若指定start、end则在指定范围内查找
# 常用内建函数 str1 = 'sunlightn' a = str1.find("n") # 字符串中含有n,返回首次出现的位置索引值2 b = str1.find("n", 3) # 从索引为3开始检测,返回首次出现的位置索引值8 c = str1.find("n", 0, 2) # 从索引[0, 2)开始检测,检测不到返回-1 print(a, b, c) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py 2 8 -1 Process finished with exit code 0
string.rfind(sub, start, end):用法与find类似,区别在返回指定sub最后出现的位置索引值,否则返回-1
# 常用内建函数 str1 = 'sunlightn' e = str1.rfind("n") # 字符串中含有n,返回最后出现的位置索引值8 f = str1.rfind("n", 0, 3) # 从索引[0, 3)开始检测 print(e, f) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py 8 2 Process finished with exit code 0
string.count(sub, start, end):返回指定sub在字符串中出现的次数,若指定start、end则在指定范围内统计
# 常用内建函数 str1 = ' sunlight ' j = str1.count(" ") k = str1.count(" ", 2, 9) print(j, k) "D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/str_1.py 5 2 Process finished with exit code 0





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 从HTTP原因短语缺失研究HTTP/2和HTTP/3的设计差异
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~