In the<list/>,<set/>, <map/>,and <props/> elements,you set the properties and arguments of the Java Collection types List,Set, Map, and Properties,respectively。
案例分析:
1、创建相应的Java类
1.1创建一个CollectionBean存放Java Collections types List、Set、Map and Properties集合对象。
package www.csdn.spring.collection.set;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
publicclass CollectionBean {
// set集合
public Set<String>sets;
publicvoid setSets(Set<String> sets){
this.sets =sets;
}
// list集合
public List<User>users;
publicvoid setUsers(List<User> users){
this.users =users;
}
// map集合
public Map<Integer, User>map;
publicvoid setMap(Map<Integer, User>map) {
this.map =map;
}
// props集合
public Propertiesprops;
publicvoid setProps(Properties props) {
this.props =props;
}
}
1.2 在上类中使用到User类,User的代码如下:
package www.csdn.spring.collection.set;
publicclass User {
private Stringname;
private Integerage;
public String getName() {
returnname;
}
publicvoid setName(String name) {
this.name =name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
returnage;
}
publicvoid setAge(Integer age) {
this.age =age;
}
}
2、在spring-collection.xml文件中配置bean
<?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beansxmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<beanid="collectionBean"class="www.csdn.spring.collection.set.CollectionBean"
scope="singleton"lazy-init="default">
<!-- set集合 -->
<propertyname="sets">
<set>
<value>常瑞鹏</value>
<value>chrp99</value>
</set>
</property>
<!-- list集合 -->
<propertyname="users">
<!-- 采用array配置 -->
<array>
<refbean="li1"/>
<refbean="li2"/>
</array>
<!-- 或者采用list配置-->
<!--
<list>
<refbean="li1"/>
<ref bean="li2"/>
</list>
-->
</property>
<!-- map集合 -->
<propertyname="map">
<map>
<entry key="1"value-ref="li1"/>
<entry key="2">
<ref bean="li2"/>
</entry>
>
</map>
</property>
<!-- props集合 -->
<propertyname="props">
<props>
<prop key="1">jdbc:oracle</prop>
<prop key="2">jdbc:mysql</prop>
<prop key="3">jdbc:access</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- User实体Bean的配置 -->
<beanid="li1"class="www.csdn.spring.collection.set.User">
<propertyname="name"value="常瑞鹏"/>
<propertyname="age"value="23"/>
</bean>
</bean>
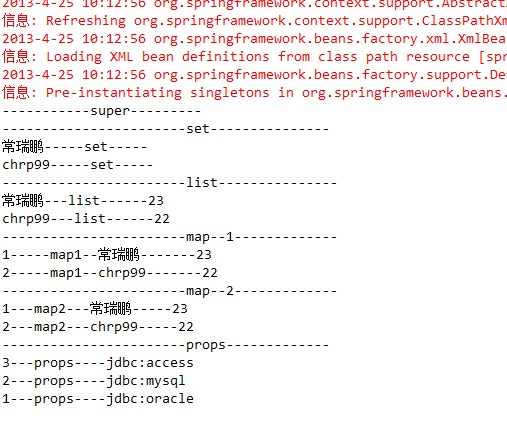
3、创建测试类 测试代码如下:
@Test
publicvoid testSets() {
//创建应用上下文对象
ApplicationContextcontext = newClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring-collection.xml");
//根据上下文对象的getBean方法获取指定的Bean对象
CollectionBeanbean = context.getBean("collectionBean", CollectionBean.class);
System.out.println("-----------------------set------------------------------");
// 获取set集合
Set<String>sets = bean.sets;
// 得到迭代器
Iterator<String>it = sets.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
System.out.println("-----------------------list------------------------------");
List<User>users = bean.users;
for (User u : users) {
System.out.println(u.getName() +"-------------" + u.getAge());
}
//map第一种遍历方式
System.out.println("-----------------------map1------------------------------");
Map<Integer,User> map = bean.map;
// 得到map集合的key键值的set集合
Set<Integer>setkeys = map.keySet();
// 得到key键值set集合的迭代器
Iterator<Integer>itkeys = setkeys.iterator();
// 迭代键值
while (itkeys.hasNext()) {
// 得到一个具体的键值
Integerkey = itkeys.next();
// 通过map集合的get(key)方法 获取key键值对应的value值
Useruser = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key +"===========" + user.getName()+"======" + user.getAge());
}
// map第二种遍历方式
System.out.println("----------------------------map2-----------------------------------");
// 获取实体对象的set集合
Set<Entry<Integer,User>> setentry = map.entrySet();
// 获取实体对象的迭代器
Iterator<Entry<Integer,User>> itentry = setentry.iterator();
// 迭代
while (itentry.hasNext()) {
// 得到具体的Entry对象
Entry<Integer,User> entry = itentry.next();
// 通过entry对象的getKey() 和getValue分别得到key与value值
System.out.println(entry.getKey() +"======="+entry.getValue().getName() +"====="+ entry.getValue().getAge());
}
System.out.println("--------------------------props---------------------------");
Propertiesprops = bean.props;
//得到这个集合键值的key的set集合
Set<String>setprops = props.stringPropertyNames();
//key集合迭代器
Iterator<String>keystr = setprops.iterator();
while(keystr.hasNext()){
//具体键值
Stringkey = keystr.next();
//getProperty(key)获取key对应的value值
System.out.println(key+"-------------"+props.getProperty(key));
}
}
4、执行结果