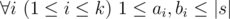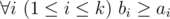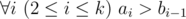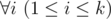【codeforces #282(div 1)】AB题解
Malek has recently found a treasure map. While he was looking for a treasure he found a locked door. There was a string s written on the door consisting of characters '(', ')' and '#'. Below there was a manual on how to open the door. After spending a long time Malek managed to decode the manual and found out that the goal is to replace each '#' with one or more ')' characters so that the final string becomes beautiful.
Below there was also written that a string is called beautiful if for each i (1 ≤ i ≤ |s|) there are no more ')' characters than '(' characters among the first i characters of s and also the total number of '(' characters is equal to the total number of ')' characters.
Help Malek open the door by telling him for each '#' character how many ')' characters he must replace it with.
The first line of the input contains a string s (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 105). Each character of this string is one of the characters '(', ')' or '#'. It is guaranteed that s contains at least one '#' character.
If there is no way of replacing '#' characters which leads to a beautiful string print - 1. Otherwise for each character '#' print a separate line containing a positive integer, the number of ')' characters this character must be replaced with.
If there are several possible answers, you may output any of them.
(((#)((#)
1 2
()((#((#(#()
2 2 1
#
-1
(#)
-1
贪心。
(表示1,)表示-1。
满足条件则前缀和时刻都要>=0。
那么遇到#我们仅仅让他表示一个)。前缀和仅仅-1。遇到最后一个#再把前面的债还清。
一開始WA了,由于我遇到最后一个#就无论前缀和了。
。
因此(#(这种数据就过不了。
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#define M 100000+5
using namespace std;
char s[M];
int ans[M];
int main()
{
scanf("%s",s);
int l=strlen(s);
int la,now=0,tot=0;
for (int i=0;i<l;i++)
{
if (s[i]=='#')
{
ans[++tot]=1;
now--;
la=i;
}
if (s[i]=='(') now++;
if (s[i]==')') now--;
if (now<0)
{
puts("-1");
return 0;
}
}
int x=0;
for (int i=l-1;i>la;i--)
{
if (s[i]=='(')
x--;
else x++;
if (x<0)
{
puts("-1");
return 0;
}
}
ans[tot]+=now;
for (int i=1;i<=tot;i++)
printf("%d\n",ans[i]);
return 0;
}
kmp+dp。
首先用kmp高速求出每一位的ok[i],也就是从i到ok[i]包括t,且ok[i]最小。
然后进行dp:
f[i]表示a[1]=i的方案数。这显然要倒着做。
f[i]=sigma(sigma(f[ok[i]+1...n-1)+sigma(f[ok[i]+2...n-1]...+f[n-1]))
维护后缀和sum[i]表示i到n-1的f值得后缀和。
再维护后缀和的后缀和ss[i]表示i到n-1的sum[i]的后缀和。
于是f[i]=ss[ok[i]+1],转移变成O(1)了!
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdlib>
#define mod 1000000007
#define M 100000+5
using namespace std;
int ss[M],ne[M],n,m,ok[M],sum[M],f[M];
char s[M],t[M];
void Getfail()
{
ne[0]=0;
ne[1]=0;
for (int i=1;i<m;i++)
{
int j=ne[i];
while (j&&t[i]!=t[j])
j=ne[j];
ne[i+1]=t[i]==t[j]?j+1:0;
}
}
void Find()
{
Getfail();
int j=0;
int now=0;
for (int i=0;i<n;i++)
ok[i]=n;
for (int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
while (j&&t[j]!=s[i])
j=ne[j];
if (t[j]==s[i])
j++;
if (j==m)
{
for (int k=now;k<=i-m+1;k++)
ok[k]=min(i,ok[k]);
now=i-m+2;
j=ne[j];
}
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%s",s);
scanf("%s",t);
n=strlen(s),m=strlen(t);
Find();
for (int i=n-1;i>=0;i--)
{
f[i]=n-1-(ok[i]-1);
f[i]=(f[i]+ss[ok[i]+1])%mod;
sum[i]=(sum[i+1]+f[i])%mod;
ss[i]=(ss[i+1]+sum[i])%mod;
}
cout<<sum[0]%mod<<endl;
return 0;
}