Java Web(5)-Servlet详解(上)
一、Servlet
1. 什么是Servlet
- Servlet 是 JavaEE 规范之一,规范就是接口
- Servlet 就 JavaWeb 三大组件之一,三大组件分别是:Servlet 程序、Filter 过滤器、Listener 监听器
- Servlet 是运行在服务器上的一个 java 小程序,它可以接收客户端发送过来的请求,并响应数据给客户端
2. 手动实现Servlet程序
首先还是在IDEA中创建一个对应的模块,具体看上一个,结果如下

- 编写一个类去实现 Servlet 接口
- 实现 service 方法,处理请求,并响应数据
- 到 web.xml 中去配置 servlet 程序的访问地址
1. 首先在src下建立一个java文件,实现Servlet接口,重写方法
现在先看Servlet(),其他的省略
package com.md.servlet;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author MD
* @create 2020-07-24 14:44
*/
public class HelloServlet implements Servlet {
/**
* service方法专门用来处理请求和响应的
* @param servletRequest
* @param servletResponse
* @throws ServletException
* @throws IOException
*/
@Override
public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("Service方法");
}
}
2. web.xml中进行配置,具体参数如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<!--servlet标签给Tomcat配置Servlet程序-->
<servlet>
<!--给servlet程序起一个别名,通常是类名-->
<servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name>
<!--servlet程序全类名-->
<servlet-class>com.md.servlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<!--servlet-mapping标签给servlet程序配置访问地址-->
<servlet-mapping>
<!--servlet-name 作用是告诉服务器,当前配置的地址给那个Servlet程序使用-->
<servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name>
<!-- 配置访问的地址 http://ip:port/hello , 可以自定义-->
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
当访问地址http://localhost:8080/hello时,可以看到输出语句了
3. url地址到Servlet程序
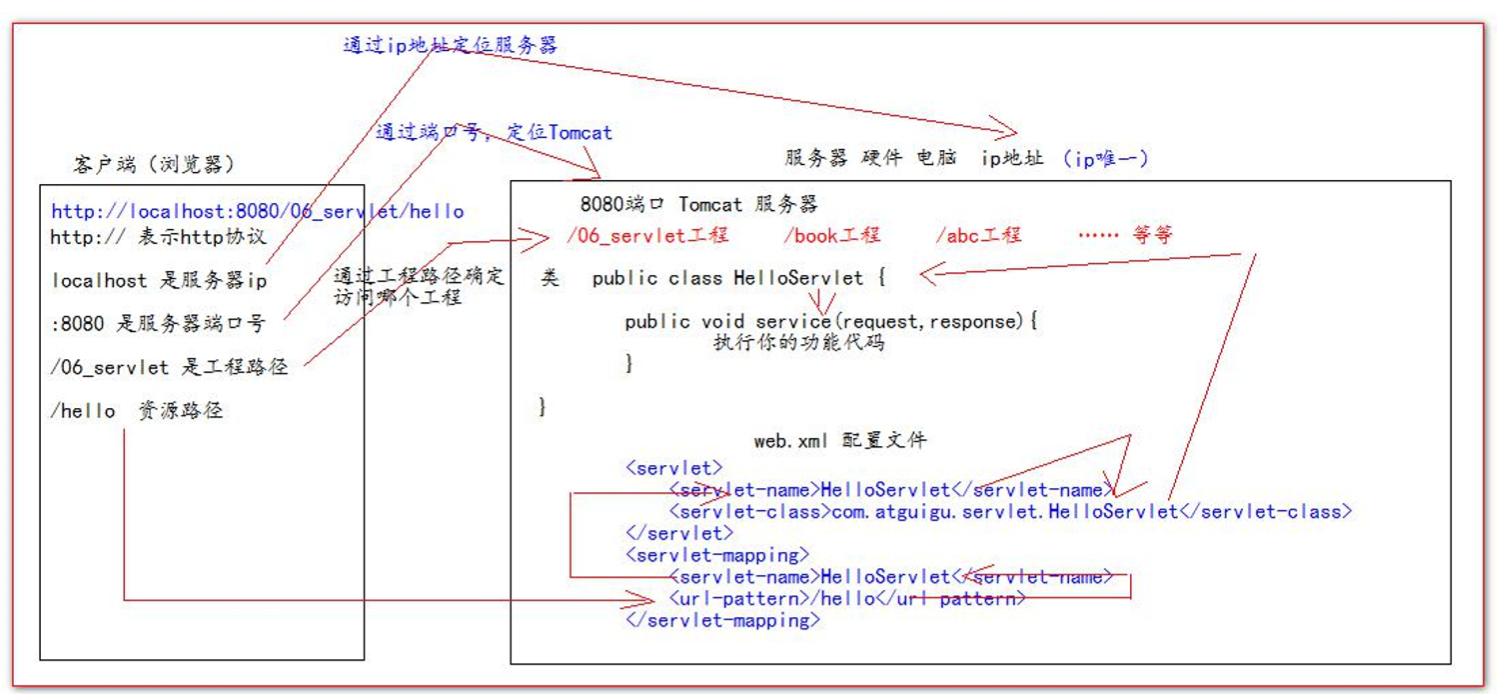
4. Servlet的声明周期
- 执行 Servlet 构造器方法
- 执行 init 初始化方法
第一、二步,是在第一次访问的时候创建 Servlet 程序会调用
- 执行 service 方法 每次访问都会调用
- 执行 destroy 销毁方法 在 web 工程停止的时候调用
package com.md.servlet;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author MD
* @create 2020-07-24 14:44
*/
public class HelloServlet implements Servlet {
public HelloServlet() {
System.out.println("1 构造器方法");
}
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig servletConfig) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("2 init初始化方法");
}
@Override
public ServletConfig getServletConfig() {
return null;
}
/**
* service方法专门用来处理请求和响应的
* @param servletRequest
* @param servletResponse
* @throws ServletException
* @throws IOException
*/
@Override
public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("3. service方法");
}
@Override
public String getServletInfo() {
return null;
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("4 destroy销毁方法");
}
}
// 结果如下:
//1 构造器方法
//2 init初始化方法 只有第一次访问执行
//3. service方法
//3. service方法 每次刷新都会执行这个方法
//4 destroy销毁方法 关闭Tomcat会执行这个方法
4. GET 和 POST 请求的分发处理
此时请求的话无论执行get或者是post请求都会执行service()方法,这样不方便,所以做了如下的改进,
其他方法省略,主要看service()
public class HelloServlet implements Servlet {
@Override
public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("3. service方法");
// 1. 类型转换
HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = (HttpServletRequest)servletRequest;
// 2. 获取请求的方式
String method = httpServletRequest.getMethod();
// 3. 处理不同的请求
if ("GET".equals(method)){
doGet();
}else if ("POST".equals(method)){
doPost();
}
}
/**
* 做get请求的操作
*/
public void doGet(){
System.out.println("get请求正在操作");
}
/**
* 做post请求的操作
*/
public void doPost(){
System.out.println("post请求正在操作");
}
}
5. 通过继承 HttpServlet 实现 Servlet 程序
一般在实际项目开发中,都是使用继承 HttpServlet 类的方式去实现 Servlet 程序
- 编写一个类去继承 HttpServlet 类
- 根据业务需要重写 doGet 或 doPost 方法
- 到 web.xml 中的配置 Servlet 程序的访问地址
Servle类中的代码
package com.md.servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author MD
* @create 2020-07-24 15:25
*/
public class HelloServlet2 extends HttpServlet {
/**
* get请求时调用
* @param req
* @param resp
* @throws ServletException
* @throws IOException
*/
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("HelloServlet2 --- get");
}
/**
* post请求时调用
* @param req
* @param resp
* @throws ServletException
* @throws IOException
*/
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("HelloServlet2 --- post");
}
}
在web.xml中的配置
<servlet>
<servlet-name>HelloServlet2</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.md.servlet.HelloServlet2</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>HelloServlet2</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello2</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
6. 使用IDEA创建Servlet程序
方便,快捷
配置Servlet信息
最后在web.xml中添加信息就可以了
<servlet>
<servlet-name>HelloServlet3</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.md.servlet.HelloServlet3</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>HelloServlet3</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello3</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
7. Servlet类的继承体系
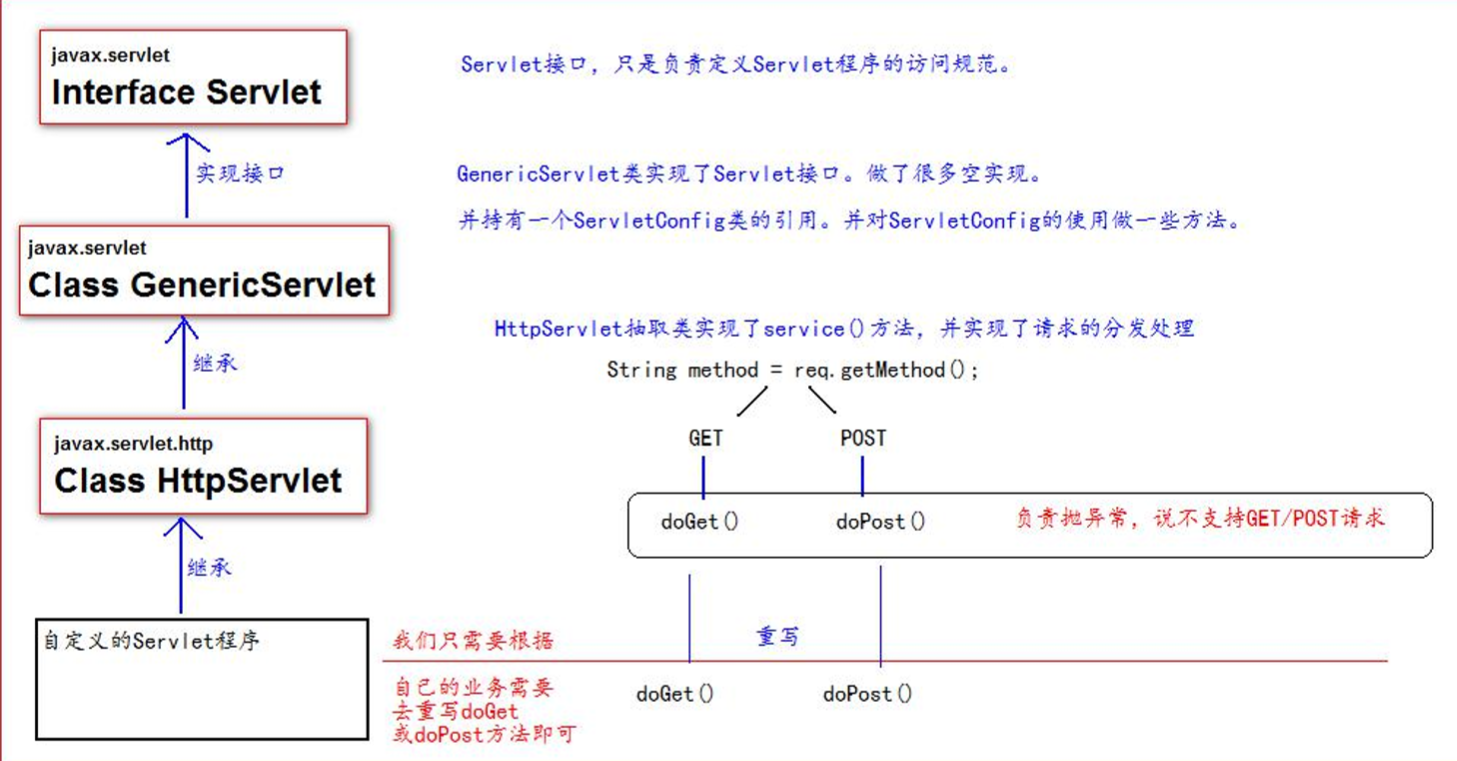
二、ServletConfig类
ServletConfig 是 Servlet 程序的配置信息类
Servlet 程序和 ServletConfig 对象都是由 Tomcat 负责创建,我们负责使用
Servlet 程序默认是第一次访问的时候创建,ServletConfig 是每个 Servlet 程序创建时,就创建一个对应的 ServletConfig 对象
1. ServletConfig 类的三大作用
- 可以获取 Servlet 程序的别名 servlet-name 的值
- 获取初始化参数 init-param
- 获取 ServletContext 对象
首先还是在web.xml中进行配置
<!--servlet标签给Tomcat配置Servlet程序-->
<servlet>
<!--给servlet程序起一个别名,通常是类名-->
<servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name>
<!--servlet程序全类名-->
<servlet-class>com.md.servlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class>
<!--初始化参数-->
<init-param>
<!--参数名-->
<param-name>url</param-name>
<!--参数值-->
<param-value>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--可以配置多个-->
<init-param>
<!--参数名-->
<param-name>username</param-name>
<!--参数值-->
<param-value>root</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<!--servlet-mapping标签给servlet程序配置访问地址-->
<servlet-mapping>
<!--servlet-name 作用是告诉服务器,当前配置的地址给那个Servlet程序使用-->
<servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name>
<!-- 配置访问的地址 http://ip:port/hello , 可以自定义-->
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
Servlet中的代码:
其他方法就省略了,主要看这个就行,启动Tomcat之后在地址栏输入地址http://localhost:8080/hello时,可以看到输出语句了,
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig servletConfig) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("2 init初始化方法");
// 1. 可以获取Servlet程序的别名servlet-name的值
System.out.println("HelloServlet的别名是:"+servletConfig.getServletName());
//HelloServlet的别名是:HelloServlet
// 2. 获取初始化参数init-param
System.out.println("初始化参数url:"+servletConfig.getInitParameter("url"));
//初始化参数url:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
System.out.println("初始化参数username:"+servletConfig.getInitParameter("username"));
//初始化参数username:root
// 3. 获取ServletContext对象
System.out.println(servletConfig.getServletContext());
//org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationContextFacade@521f9e31
}
注意:
重写init方法里面一定要调用父类的init(config)操作
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
super.init(config);
System.out.println("重写的init方法");
}
三、ServletContext 类
1. 什么是 ServletContext?
- ServletContext 是一个接口,它表示 Servlet 上下文对象
- 一个 web 工程,只有一个 ServletContext 对象实例
- ServletContext 对象是一个域对象
- ServletContext 是在 web 工程部署启动的时候创建。在 web 工程停止的时候销毁
什么是域对象?
域对象,是可以像 Map 一样存取数据的对象,叫域对象。
这里的域指的是存取数据的操作范围,整个 web 工程
| 存数据 | 取数据 | 删除数据 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Map | put() | get() | remove() |
| 域对象 | setAttribute() | getAttribute() | removeAttribute() |
2. ServletContext 类的四个作用
- 获取 web.xml 中配置的上下文参数 context-param
- 获取当前的工程路径,格式:/工程路径
- 获取工程部署后在服务器硬盘上的绝对路径
- 像 Map 一样存取数据
在ContextServlet类中,
package com.md.servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author MD
* @create 2020-07-24 16:17
*/
public class ContextServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 1. 获取web.xml中配置的上下文参数
ServletContext context = getServletConfig().getServletContext();
String username = context.getInitParameter("username");
System.out.println("context-param中参数username的值为:"+username);
System.out.println("context-param中参数pwd的值为:"+context.getInitParameter("pwd"));
// 2. 获取当前工程的路径
System.out.println("当前工程的路径:"+context.getContextPath());
// 3. 获取工程部署后在服务器磁盘上的绝对路径,映射到IDEA代码的web目录,
// 相当于直接到了web目录那,如果使用web目录下的其他文件,直接/目录名就可以
System.out.println("工程部署路径:"+context.getRealPath("/"));
// 工程的绝对路径:E:\Java\code\JavaWeb\out\artifacts\03_web_war_exploded\
// 比如web下有css目录和imgs目录
System.out.println(context.getRealPath("/css"));
System.out.println(context.getRealPath("/imgs/1.jpg"));
}
}
对应的配置文件web.xml
这个是直接在<web-app标签下,而不是某个<servlet标签下,
<!--context-param 是上下文参数,属于整个的Web工程-->
<context-param>
<param-name>username</param-name>
<param-value>context</param-value>
</context-param>
<context-param>
<param-name>pwd</param-name>
<param-value>123456</param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>ContextServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.md.servlet.ContextServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ContextServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/context</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
ServletContext 像Map一样存取数据,直接可以这样
在ContextServlet1中,这个对应的web.xml就省略了
package com.md.servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author MD
* @create 2020-07-24 16:40
*/
public class ContextServlet1 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 1. 通过getServletContext()直接获取ServletContext对象
ServletContext context = getServletContext();
System.out.println("保存前:"+context.getAttribute("key1")); // null
// 2. 设置值
context.setAttribute("key1","value1");
// 3. 获取值
System.out.println("保存后:"+context.getAttribute("key1")); //value1
//
}
}
也可以在不同的Service中获取的到,因为是域对象
这个是整个web都可以获取到这个值,通过ContextServlet2也是可以获取到的
public class ContextServlet2 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 由于context是域对象,整个web只有一个,所以这个获取的和ContextServlet1里的是同一个
ServletContext context = getServletContext();
// 只要ContextServlet1运行过,设置过这个值,那么这个就可以获取到值
System.out.println(context.getAttribute("key1")); //value1
}
}
-------------------------------------------
你闻讯而来,我大喜过望,我在这等你,你又在哪呢?喜欢的话加一个“关注”呗!
如果觉得这篇文章对你有小小的帮助的话,记得在右下角点个“推荐”哦,博主在此感谢!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号