s11 day Linux 和nginx 部署
https://www.cnblogs.com/pyyu/p/9481344.html
1,开机初始化的配置 iptables -F 清空防火墙 /etc/init.d/iptables stop #关闭iptables setenforce 0 #暂停selinux #编译安装python3 环境准备 yum install gcc patch libffi-devel python-devel zlib-devel bzip2-devel openssl-devel ncurses-devel sqlite-devel readline-devel tk-devel gdbm-devel db4-devel libpcap-devel xz-devel -y #下载python3的源码包 wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.4.7/Python-3.4.7.tar.xz #解压缩源码包 xz -d Python-3.4.7.tar.xz tar -xf Python-3.4.7.tar
#切换python3目录
cd Python-3.4.7
#释放脚本文件
./configure --prefix=/opt/python347
#编译,编译安装
make && make install
#建立软连接
ln -s /opt/python347/bin/python3 /usr/local/bin/python3
#将编译的python3的环境变量添加到pATH
vim /etc/profile
#写入到配置文件,永久生效 在最底行写入
export PATH=$PATH:/opt/python347/bin/ 然后 source /etc/profile
使得配置文件生效
#python解释器的自动补全功能 yum install -y readline-devel -y pip install readline import readline,rlcompleter readline.parse_and_bind('tab:complete')
#python虚拟环境 virtualenv --no-site-packages venv
#创建venv虚拟环境 #激活虚拟环境 source venv/bin/activate
#虚拟环境主要是对环境变量进行更改 echo $PATH
#退出虚拟环境 deactivate #ipython pip3 install ipython
#交互式的解释器 #notebook pip3 install notebook
安装python
1,开机初始化的配置 iptables -F 清空防火墙 /etc/init.d/iptables stop #关闭iptables setenforce 0 #暂停selinux #编译安装python3 环境准备 yum install gcc patch libffi-devel python-devel zlib-devel bzip2-devel openssl-devel ncurses-devel sqlite-devel readline-devel tk-devel gdbm-devel db4-devel libpcap-devel xz-devel -y #下载python3的源码包 wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.4.7/Python-3.4.7.tar.xz #解压缩源码包 xz -d Python-3.4.7.tar.xz tar -xf Python-3.4.7.tar #切换python3目录 cd Python-3.4.7 #释放脚本文件 ./configure --prefix=/opt/python347 #编译,编译安装 make && make install #建立软连接 ln -s /opt/python347/bin/python3 /usr/local/bin/python3
下载 readline
yum install -y readline -devel
查看环境变量:
[root@tencentcloud ~]# echo $PATH
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin
虚拟环境的安装
#python虚拟环境 virtualenv --no-site-packages venv #创建venv虚拟环境 #激活虚拟环境 source venv/bin/activate #虚拟环境主要是对环境变量进行更改 echo $PATH #退出虚拟环境 deactivate
1. 下载NGINX
wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.14.0.tar.gz
2.解压
tar xf nginx-1.14.0.tar.gz
3. 编译安装三部曲
进入 nginx 目录下 ,注意目录里有个configure 文件 ./configure --prefix=/opt/nginx-1.14.0 make && make install
4.开启服务
4.启动nginx,进入sbin目录,找到nginx启动命令 cd sbin ./nginx #启动 ./nginx -s stop #关闭 ./nginx -s reload #重新加载
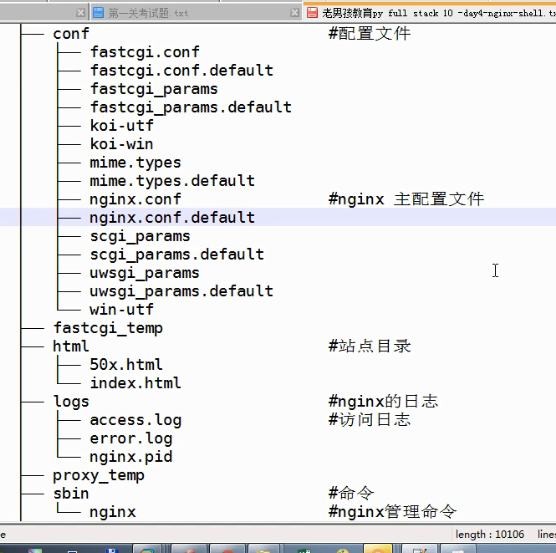
5.查看conf文件
cat conf/nginx.conf

[root@tencentcloud nginx-1.12.2]# cat conf/nginx.conf #user nobody; worker_processes 1; #error_log logs/error.log; #error_log logs/error.log notice; #error_log logs/error.log info; #pid logs/nginx.pid; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; #log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' # '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' # '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; #access_log logs/access.log main; sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 65; #gzip on; server { listen 80; server_name localhost; #charset koi8-r; #access_log logs/host.access.log main; location / { root html; index index.html index.htm; } #error_page 404 /404.html; # redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html # error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } # proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80 # #location ~ \.php$ { # proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1; #} # pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000 # #location ~ \.php$ { # root html; # fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; # fastcgi_index index.php; # fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name; # include fastcgi_params; #} # deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root # concurs with nginx's one # #location ~ /\.ht { # deny all; #} } # another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration # #server { # listen 8000; # listen somename:8080; # server_name somename alias another.alias; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #} # HTTPS server # #server { # listen 443 ssl; # server_name localhost; # ssl_certificate cert.pem; # ssl_certificate_key cert.key; # ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; # ssl_session_timeout 5m; # ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5; # ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #} }

6.创建软连接
[root@tencentcloud nginx-1.12.2]# ln -s /sbin/nginx /sbin/


5.关闭防护墙
chkconfig iptables off
永久关闭。
chkconfig|grep ipt
vim /etc/selinux/config

6. 去掉文件里的# 和空行
egrep -v "^$|#" nginx.conf.default egrep -v "^$|#" nginx.conf.default >nginx.conf
4. 测试
curl 10.10.0.1
今日内容: saltstack(python编写的自动化工具) 原本公司的组织架构是; apahce+oralce数据库+redis+saltstack+java+perl(收费) 走向一个开源,免费的技术架构(省钱) nginx + mysql + redis +stal +java +python(glances一个开源的服务器监控工具) ansible + 一号车面试的时候,ansible+python+django 开发的cmdb平台 saltstack + python +django 运维平台 #salt环境准备,需要再两台机器一起执行 准备好2台服务器 master 192.168.12.44 slave 192.168.12.45 #设置好本地/etc/hosts解析 vim /etc/hosts#写入以下解析记录 192.168.12.44 master 192.168.12.45 slave #关闭服务器安全策略 /etc/init.d/iptables stop iptables -F #关闭服务器selinux getenforce #检测selinux是否开启 setenforce 0 #临时关闭selinux #使用sed永久关闭selinux(此步骤需要重启linux) sed -i 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/' /etc/selinux/config #epel源配置,默认的yum源提供的软件包有限,epel源提供额外的软件包下载(新的仓库) #下载epel源 wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-6.repo #清空yum源缓存,然后更新新的yum缓存(非必须的操作) yum clean all yum makecache #yum install xxx #安装salt-master ############################# yum install salt-master -y #安装好后修改配置文件/etc/salt/master #写入如下配置即可 [root@master ~]# grep -v '^#' /etc/salt/master |grep -v '^$' interface: 0.0.0.0 publish_port: 4505 user: root worker_threads: 5 ret_port: 4506 pidfile: /var/run/salt-master.pid log_file: /var/log/salt/master #启动salt-master /etc/init.d/salt-master start #启动 /etc/init.d/salt-master status #查看状态 /etc/init.d/salt-master stop #停止 #修改minion的配置 ###################### yum install salt-minion -y #vim /etc/salt/minion [root@slave ~]# grep -v '^#' /etc/salt/minion |grep -v '^$' master: master master_port: 4506 user: root id: slave output: nested backup_mode: minion acceptance_wait_time: 10 random_reauth_delay: 60 log_file: /var/log/salt/minion #修改完配置之后,启动salt-minion /etc/init.d/salt-minion start ###################### #salt-master和salt-minion都启动之后 #在salt-master端执行 [root@master ~]# salt-key -L Accepted Keys: Denied Keys: Unaccepted Keys: slave #此时已经出现slave Rejected Keys: #然后salt-master 通过命令接收slave节点的key [root@master ~]# salt-key -a slave The following keys are going to be accepted: Unaccepted Keys: slave Proceed? [n/Y] y Key for minion slave accepted. #确认接收秘钥后,检验minion秘钥是否被接收 [root@master ~]# salt-key -L Accepted Keys: slave Denied Keys: Unaccepted Keys: Rejected Keys: ######################## #此时salt-master已经和salt-minion通信了 #测试用master 控制minion,创建一个文本 [root@master ~]# salt 'slave' cmd.run 'echo '我是master,我在slave上创建了一个文本' > /tmp/master.txt' ############# #在minion节点查看效果即可 [root@slave ~]# cat /tmp/master.txt 我是master,我在slave上创建了一个文本 # 在主节点上,可以分发命令,一条命令即可获取所有被管控机器的ip,hostname等信息 Unaccepted Keys: slave: 15:f2:0c:ea:be:b3:72:b1:c9:78:61:79:9b:3c:2e:47 local: 15:f2:0c:ea:be:b3:72:b1:c9:78:61:79:9b:3c:2e:47 ############################################################################################################# #uWSGI 安装配置 #更详细的查看博客 https://www.cnblogs.com/pyyu/p/9481344.html #基础环境配置 yum groupinstall "Development tools" yum install zlib-devel bzip2-devel pcre-devel openssl-devel ncurses-devel sqlite-devel readline-devel tk-devel #提前安装好python3环境 https://www.cnblogs.com/pyyu/p/7402145.html #virtualenv #请确保你的虚拟环境正常工作 https://www.cnblogs.com/pyyu/p/9015317.html #安装django1.11 pip3 install django==1.11 #创建django项目mysite django-admin startproject mysite #创建app01 python3 manage.py startapp app01 #mysite/settings.py #settings.py设置 ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['*'] install app01 #mysite/urls.py from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls), url(r'^hello_django/', views.hello), ] #app01/views.py from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse # Create your views here. def hello(request): print('request is :',request) return HttpResponse('django is ok ') #pip3安装uwsgi #进入虚拟环境venv,安装uwsgi (venv) [root@slave 192.168.11.64 /opt]$pip3 install uwsgi #检查uwsgi版本 (venv) [root@slave 192.168.11.64 /opt]$uwsgi --version 2.0.17.1 #检查uwsgi python版本 uwsgi --python-version ############################################ #启动一个python web服务 uwsgi --http :8000 --wsgi-file test.py http :8000: 使用http协议,端口8000 wsgi-file test.py: 加载指定的文件,test.py #test.py def application(env, start_response): start_response('200 OK', [('Content-Type','text/html')]) return [b"Hello World"] # python3 #uWsgi热加载python程序 #在启动命令后面加上参数 uwsgi --http :8088 --module mysite.wsgi --py-autoreload=1 #此时修改django代码,uWSGI会自动加载django程序,页面生效 运行django程序 #mysite/wsgi.py 确保找到这个文件 uwsgi --http :8000 --module mysite.wsgi module mysite.wsgi: 加载指定的wsgi模块 #二、nginx+uWSGI+django+virtualenv+supervisor(进程管理工具)发布我们的django项目 1.配置nginx,通过反向代理结合uWSGI location / { root html; include /opt/nginx112/conf/uwsgi_params; uwsgi_pass 0.0.0.0:8000; index index.html index.htm; } 2.安装好supervisor #在python2环境下安装 yum install python-setuptools easy_install supervisor #通过命令生成supervisor的配支文件 echo_supervisord_conf > /etc/supervisord.conf #然后再/etc/supervisord.conf末尾添加上如下代码!!!!!! [program:s10_django] command= /home/venv1/bin/uwsgi --uwsgi 0.0.0.0:8000 --chdir /home/mysite --home=/home/venv1 --module mysite.wsgi directory=/home/mysite startsecs=0 stopwaitsecs=0 autostart=true autorestart=true 3.启动好nginx /opt/nginx112/sbin/nginx 4.启动supervisor supervisord -c /etc/supervisord.conf -管理supervisor的命令 supervisorctl start s10_django supervisorctl stop s10_django supervisorctl restart s10_django 5.此时访问192.168.12.44 访问nginx的80端口,已经反向代理找到后端的django应用 ####补充: PS1命令提示符的更改 export PS1='[\u@\h \w \t]\$' #使得永久生效 vim /etc/profile #写入 export PS1='[\u@\h \w \t]\$' #三、docker容器基本使用 大家可能接触到的服务器环境(代码运行的环境) 物理机+centos vmware esxi + centos 阿里云/腾讯云/亚马逊云 docker容器 (项目跑在容器中) #环境准备 #查看linux发行版 cat /etc/redhat-release #内核版本查看 uname -r #安装docker,配置yum的epel源 yum install docker #启停docker systemctl status docker #检查docker状态 systemctl start docker #启动docker systemctl stop docker #关闭docker #配置docker镜像源加速 curl -sSL https://get.daocloud.io/daotools/set_mirror.sh | sh -s http://95822026.m.daocloud.io #查看镜像源加速 [root@oldboy_python ~ 14:33:39]#cat /etc/docker/daemon.json { "registry-mirrors": ["http://95822026.m.daocloud.io"], "insecure-registries": [] } #下载hello-world镜像 docker pull hello-world #查看docker镜像 docker images #运行docker hello-world镜像 docker run 镜像名/镜像id/镜像id的前3位 #搜索docker镜像(image) docker search centos docker search django(#搜索django镜像) #运行一个交互式的centos容器 docker run -it centos /bin/bash #在后台运行一个容器,执行shell,每秒打印一个hellodocker,(此命令会返回一个容器id) docker run -d centos /bin/sh -c "while true;do echo hello centos; sleep 1;done" #查看容器进程 docker ps #用于查看正在运行的容器 docker ps -a #用于查看所有运行过的容器 #查看容器运行的日志 docker logs 容器id #删除容器 -先停止正在运行的容器 docker stop 容器id docker rm 容器id -强制删除正在运行的容器 docker rm -f 容器id #删除已有的docker镜像(image) docker rmi 镜像id #https://www.cnblogs.com/pyyu/p/9485268.html docker部署博客 ###########重要性 1.uwsgi发布django程序 2.docker容器的使用 3.mysql主从复制 4.把笔记所有linux命令敲一遍


