Astar算法解八数码问题源码
//STATELIST.H
#pragma once
#ifndef _STATE_LIST_H
#define _STATE_LIST_H
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <list>
/* 表示状态的结构体 */
struct State
{
std::string state;
std::string pre_s;
int space_place;
int g;
double h;
State() : state("1234 5678"), space_place(4) {}
State(const std::string& stat, int _g)
{
g = _g;
state = stat;
space_place = state.find(' ');
}
bool operator==(const State& s) const
{
return state == s.state;
}
bool operator<(const State& s) const
{
return g + h < s.g + s.h; //根据估价函数排序
}
};
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream &o, const State& s)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++)
{
if (s.pre_s.empty() || s.state[i] == s.pre_s[i])
o << " " << s.state[i] << " ";
else
o << "[" << s.state[i] << "]";
if (i % 3 == 2)
o << "\n";
}
return o;
}
/* 一系列状态 */
template <typename H>
class StateList
{
public:
struct Compare
{
bool operator()(const State& a, const State& b) const
{
return a.state < b.state;//用于保证唯一性
}
};
private:
std::multiset<State> open; //open表,按f排序
std::set<State, Compare> open_uni;//唯一性open表
std::set<State, Compare> closed; //唯一性closed表
State current; //当前状态
State target; //目标状态
H h_func; //h(n)函数
void generate_sub_state()
{
State next_state(current);
next_state.g += 1; //更新g
next_state.pre_s = current.state; //更新父状态
std::string &s = next_state.state;
int delta[] = { -3, 3, -1, 1 }; //上下左右
int old_place = next_state.space_place;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int new_place = old_place + delta[i];
if (check(old_place, new_place))
{
std::swap(s[old_place], s[new_place]); //更新状态
next_state.h = h_func(next_state, target); //更新h
next_state.space_place = new_place; //更新空位位置
add_to_list(next_state);
std::swap(s[old_place], s[new_place]);
}
}
}
void add_to_list(const State& state)
{
auto iter = open_uni.end();
//如果状态已在open表中
if ((iter = open_uni.find(state)) != open_uni.end() && iter->g > state.g)
{
//且g更小
if (iter->g > state.g)
{
update_state(*iter, state);
open_uni.erase(iter);
open_uni.insert(state);
}
return;
}
//如果状态已在closed表中
if ((iter = closed.find(state)) != closed.end())
{
//且g更小
if (iter->g > state.g)
{
closed.erase(state); //从closed表移动到open表
open.insert(state);
open_uni.insert(state);
}
return;
}
open.insert(state);
open_uni.insert(state);
}
bool check(int old_place, int new_place)
{
bool chk = (0 <= new_place && new_place < 9) && //新的空位在范围内
(abs(new_place % 3 - old_place % 3) != 2); //针对左右位移导致行数变化的检查
return chk;
}
void update_state(const State& old, const State& news)
{
auto i = open.find(old);
while (!(i->state == news.state))
++i;
open.erase(i);
open.insert(news);
}
public:
StateList(const State& from, const State& _target)
{
open.insert(from);
open_uni.insert(from);
current = from;
target = _target;
}
bool is_arrive_target()
{
return current == target;
}
bool is_failed()
{
return !(open.size());
}
/* 进行下一步搜索 */
State next()
{
if (!is_arrive_target() && open.size() != 0)
{
current = *(open.begin()); //取出n
open.erase(open.begin());
open_uni.erase(current);
closed.insert(current);
generate_sub_state(); //生成子状态
}
return current;
}
/* 利用closed表进行回溯 */
std::list<State> get_path()
{
std::list<State> path;
path.push_back(current);
State pre(current);
if (!is_arrive_target())
{
return path;
}
while (!pre.pre_s.empty())
{
pre.state = pre.pre_s; //生成父状态
pre = *(closed.find(pre));//在closed表中找到父状态
path.push_front(pre); //添加到path
}
return path;
}
int open_list_size()
{
return open.size();
}
int closed_list_size()
{
return closed.size();
}
};
/* 不同数据的数量 */
struct HFunc1
{
double operator()(const State& cur, const State& tar)
{
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++)
{
cnt += (cur.state[i] != tar.state[i]);
}
return cnt;
}
};
/* 曼哈顿距离 */
struct HFunc2
{
double operator()(const State& cur, const State& tar)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++)
{
int p1 = cur.state.find(tar.state[i]);
//dis = abs(y1 - y2) + abs(x1 - x2)
int dis = abs(i / 3 - p1 / 3) + abs(i % 3 - p1 % 3);
sum += dis;
}
return sum;
}
};
/* 宽度优先搜索 */
struct HFunc3
{
double operator()(const State& cur, const State& tar)
{
return 0;
}
};
#endif
//main.cpp
#include "StateList.h"
using std::cout;
using std::string;
int main()
{
typedef HFunc2 HFunc;//估价函数,可选HFunc[1/2/3]
//1:按不同数字的数量;2:曼哈顿距离;3:0
State begin("7245 3816", 0); //起点,第二个参数为g
State target("1234 5678", 0); //终点,第二个参数无意义
//初始化状态表
begin.h = HFunc()(begin, target);
cout << "from:\n" << begin << "\n";
cout << "to:\n" << target << "\n";
StateList<HFunc> slist(begin, target);
//开始搜索
while (!slist.is_arrive_target())
{
if (slist.is_failed())
{
cout << "Failed" << "\n";
return 0;
}
slist.next();
}
//打印结果
auto path = slist.get_path();
for (auto &s : path)
{
cout << s;
printf("(g, f)=(%d, %g)\n\n", s.g, s.g + s.h);
}
printf("final open list size: %d\n", slist.open_list_size());
printf("final closed list size: %d\n", slist.closed_list_size());
return 0;
}
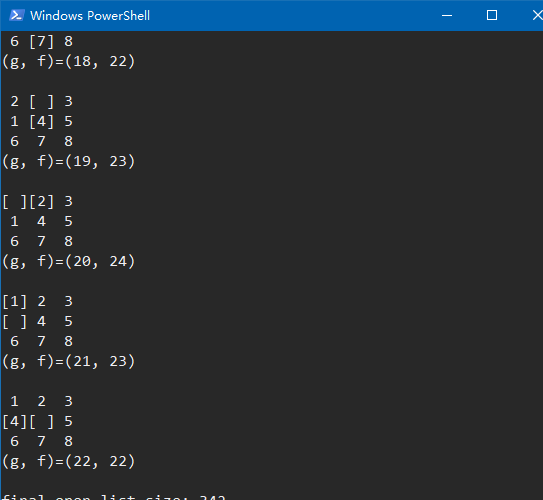
效果图如下,代码会打印出搜索路径


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号