IPV6 ----- 9 MP-BGP
MP-BGP
BGP就不用说了,
BGP 可以支持更多的协议,
IPV4-tcp-179
IPV6-tcp-179
BGP通过激活属性,来承载更多的协议 ,
(是否还记得mpls vpn中的一些设置)
BGP这个协议就牛多了,
因为它支持多种协议 ,
不管你是IPV4 /IPV6 ,都 一样,
只要是在协议 里面去激活相应的地址簇就,address-famliy ipv6 unicast
并后再指定邻居激活功能nei x.x.x.x active
MP-BGP中无非三种 情况
1 运行ipv4的BGP之上传递IPV6的地址
2 运行IPV6的BGP之上传递IPV4的地址
3 运行IPV6 FE80的BGP 传递ipv4 以及ipv6
第一种,IPV4之上跑IPV6的路由
一起来回顾一下BGP是如何建立的,
我们使用ibgp的关系来建立 ,并且使用eigrp做为底层协议,使用两端的loopback接口1.1.1.1 和2.2.2.2来做为两侧的更新源、
IPV4_BGP部份配置
R1(config)#inter f0/0
R1(config-if)#ip add 12.0.0.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no shu
R1(config-if)#inter lo 1
R1(config-if)#ip add 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#router eigrp 1
R1(config-router)#no au
R1(config-router)#net 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0
R1(config-router)#net 12.0.0.1 0.0.0.0
R1(config-router)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#bgp router-id 1.1.1.1
R1(config-router)#nei 2.2.2.2 remote 100
R1(config-router)#nei 2.2.2.2 up lo 1
R2做同样的配置
R2(config)#inter f0/0
R2(config-if)#ip add 12.0.0.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shu
R2(config-if)#ip add 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shu
R2(config)#router eigrp 1
R2(config-router)#no au
R2(config-router)#net 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0
R2(config-router)#net 12.0.0.2 0.0.0.0
R2(config-router)#router bgp 100
R2(config-router)#bgp router-id 2.2.2.2
R2(config-router)#nei 1.1.1.1 remote 100
R2(config-router)#nei 1.1.1.1 up lo 1
底层IGP完成,BGP也已经建立起来,
现在要开启考虑如何传递IPV6的路由了,
首先要想传递IPV6 的路由就必须要对IPV6 的协议簇进行激活,并且指定邻居开启这个功能(有一个前提 ,就是要在全局下为路由器开启ipv6 unicast-routing功能)
R1(config)#ipv un
R1(config)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#address-family ipv6 unicast //开启ipv6地址簇
R1(config-router-af)#nei 2.2.2.2 activate //激活指定的邻居,可以发送这样IPV6信息
R2(config)#ipv un
R2(config)#router bgp 100
R2(config-router)#address-family ipv6 unicast
R2(config-router-af)#nei 1.1.1.1 activate
然后建立IPV6 地址
R1(config-router)#inter lo 10
R1(config-if)#ipv add 1111::1/128
R2(config-router)#inter lo 10
R2(config-if)#ipv add 2222::2/128
有了地址,也开启了ipv6的功能,现在开始宣告吧
在哪里宣告又是一个问题,
首先要明白,路由器现在运行的是普通 的BGP,是针对 于IPV4的
如果要宣告IPV6 的,肯定要在IPV6 的地址簇中
R1(config)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#address-family ipv6 unicast
R1(config-router-af)#network 1111::1/128
R2(config)#router bgp 100
R2(config-router)#address-family ipv6 unicast
R2(config-router-af)#network 2222::2/128
宣告完成,来查看一下
Show ipv6 route bgp //可以查看IPV6 的BGP路由表

show bgp ipv6 unicast
可以查看到ipv6 的BGP表,
然后会发现,现在2222::2已经过来了,但是无法显示 为最优,best,
怎么回事儿,?
往后看,next-hop是个啥 ?
Ipv6带着ipv4地址 ,这个地址是系统自己弄成的,也是根本就不可达的
我们之前学习BGP时提到过,关于BGP条止,要么被 BGP的防环机制给干掉,要么就是下一跳不可达,才会被处理为不优条目、
那这个时候怎么办呢《?
首先,确认一下这就是由于下一跳不可达造成的,
那么如何来改呢?
修改它的next-hop 值 ,可以用什么 ???对,没错,route-map
但是又有一个问题
我这个下一跳要写谁?IPV4地址 ,还是IPV6地址呢?
如果是IPV4会发生什么 ?
用IPV4 去解析ipv6的地址 ,挺会玩儿的啊 ~,根本就不可能实现
所以只能是IPV6的地址 了,
下一跳 ,怎么做?
在R1/R2上两端做一个同网段的ipv6 global地址 。
R1(config-router)#inter f0/0
R1(config-if)#ipv add 2012::1/64
R2(config-router-af)#inter f0/0
R2(config-if)#ipv add 2012::2/64
配置 完成后最好测试 一下连通性,即便是直连路由,也要测试一下
然后将route-map 的ipv6 下一跳改成ipv6 global地址
R1(config-if)#route-map aa
R1(config-route-map)#set ipv6 next-hop 2012::1
R2(config-if)#route-map aa
R2(config-route-map)#set ipv6 next-hop 2012::2
然后就是最后一步的调用了,
在哪里调用,也是很关键的,
不用去考虑此时运行的BGP是IPV4 只需要考虑的是传递的什么路由,
如果是IPV4的就在IPV4中去做,
如果是IPV6的就在IPV6中去做,
所以,
我们要到IPV6 的地址 簇中去调 用route-map
R1(config-route-map)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#address-family ipv6 unicast
R1(config-router-af)#nei 2.2.2.2 route-map aa out //但是指定的邻居还得是IPV4的邻居,因为BGP是IPV4 建立起来的
R2(config)#router bgp 100
R2(config-router)#address-family ipv6 un
R2(config-router-af)#nei 1.1.1.1 route-map aa out
然后再查看BGP表
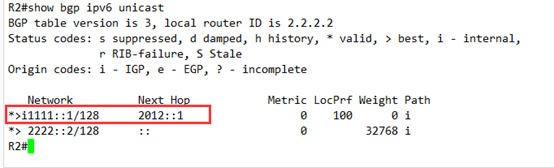
由于next-hop 变得有效,
所在这个条目,也就变成了最优
这样一来在路由表中应该可以看到这个条目了

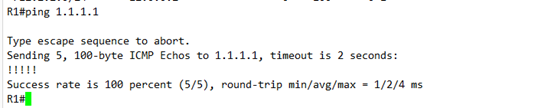
测试一下

OK 没问题
这部份的总结,
1 建立好IPV4 的BGP
2 开启ipv6 的地址簇,并指定neighbor 激活该功能,允许传递IPV6相关数据
3 创建IPV6 global地址
4 使用路由策略route-map,针对于ipv6 地址的下一跳进行改变
5 在ipv6 地址簇下进行调 用
第二种 IPV6BGP上传递IPV4的路由
有了上一个经验,相必这里应该也不难了
一起来看一下
在建立BGP邻居的时候,有一个小点需要注意一下
由于BGP也需要RID,所以必须要有IPV4的地址 在两端 ,可以是loopback接口,
如果没有的话,就需要手动的去指定一个RID了
咱们还是一步一步的来吧
R1(config)#inter f0/0
R1(config-if)#ipv add 2012::1/64
R1(config-if)#no shu
R2(config)#inter f0/0
R2(config-if)#ipv add 2012::2/64
R2(config-if)#no shu
通信 正常,可以建立 BGP邻居
R1(config-if)#inter lo 1
R1(config-if)#ip add 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#inter lo 1
R2(config-if)#ip add 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#bgp rout
R1(config-router)#bgp router-id 1.1.1.1
R1(config-router)#nei 2012::2 remote 100
*Mar 1 00:02:25.399: %BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 2012::2 Up
R2(config-if)#router bgp 100
R2(config-router)#bgp router
R2(config-router)#bgp router-id 2.2.2.2
R2(config-router)#nei 2012::1 remote 100
*Mar 1 00:02:25.399: %BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 2012::1 Up
到这里IPV6 的BGP已经完成,
现考虑在其上传递IPV4路由,
还是一样的道理,想要传递不同协议的路由,就要开启那个协议的协议簇,并激活邻居
R1(config-router)#address-family ipv4 unicast
R1(config-router-af)#nei 2012::2 activate
R1(config-router-af)#network 1.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0 //一并将IPV4的路由宣告
R2(config-router)address-family ipv4 unicast
R2(config-router-af)#nei 2012::1 activate
R2(config-router-af)#network 2.2.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0
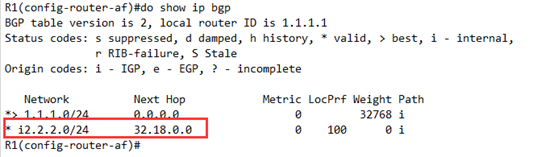
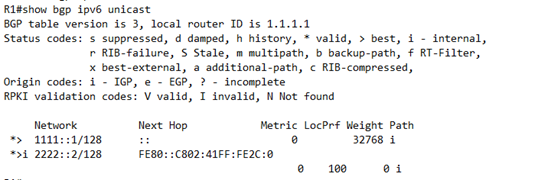
然后在R1上查看bgp 表,
可以看到,路由已经 传递过来了,但是还是存在问题
下一跳 ,又是下一跳 ,
这样的问题基本上都 是因为下一跳 而来的
可以看到32.18.0.0这个地址根本就不存在,是BGP自己生成的,
怎么办?
Route-map
想要传递IPV4的路由,还要在两台设备之间设置 可以互通的IPV4地址
R1(config)#inter f0/0
R1(config-if)#ip add 12.0.0.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no shu
R2(config-router-af)#inter f0/0
R2(config-if)#ip add 12.0.0.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shu
R1(config-if)#route-map aa
R1(config-route-map)#set ip nex
R1(config-route-map)#set ip next-hop 12.0.0.1
% Warning: Next hop address is our address //这里不用怕,只是一个提醒,说下一跳 是自己
R2(config-if)#route-map aa
R2(config-route-map)#set ip nex
R2(config-route-map)#set ip next-hop 12.0.0.2
% Warning: Next hop address is our address
最关键的一步来了,
调用route-map
在哪里?
还记得吗?
让住一句话,你想要最终传递哪种协议 ,就在哪 种协议簇下去调 用即可
错不了的
R1(config-route-map)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#address-family ipv4 unicast
R1(config-router-af)#nei 2012::2 route-map aa out
R2(config-route-map)#router bgp 100
R2(config-router)#address-family ipv4 unicast
R2(config-router-af)#nei 2012::1 route-map aa out
最后再验证其结果
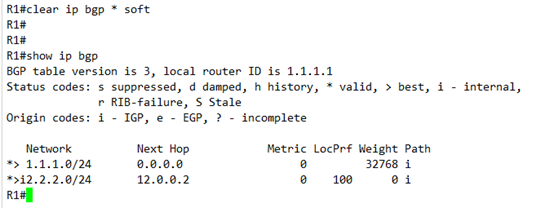
NEXT-HOP 一变,条目立马变成最优的了
测试一下
第三种,使用FE80建立 BGP neighbor,
在其之上运行IPV4 以及IPV6
该实验最难点就是在于FE80地址的使用
其实和第二个差不多的
就是FE80地址看起来有些许的头疼
老规矩一步一步来,
咱们走着瞧
1 配置FE80地址 ,直接开启IPV6功能
R1(config)#inter f0/0
R1(config-if)#ipv en
R1(config-if)#no shu
R2(config)#inter f0/0
R2(config-if)#ipv en
R2(config-if)#no shu

开启完成之后就可以看到IPV6 的linklocal地址了
使用这个地址 建立BGP邻居
R1(config)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#bgp router-id 1.1.1.1
R1(config-router)#address-family ipv6 unicast
R1(config-router)#nei FE80::C802:41FF:FE2C:0%FastEthernet0/0 remote-as 100
邻居+对端FE80地址+%+本地出接口
R2(config)#router bgp 100
R2(config-router)#bgp router-id 2.2.2.2
R2(config-router)#nei FE80::C801:42FF:FE98:0%FastEthernet0/0 remote-as 100
邻居建立可以完成吗?
不行,
因为IPV6 设备默认是不支持传递的
所以还需要激活这个功能,以及指定邻居
R1(config-router-af)#nei FE80::C802:41FF:FE2C:0%FastEthernet0/0 activate
R2(config-router-af)#nei FE80::C801:42FF:FE98:0%FastEthernet0/0 activate
直接使用上面的地址就可以了,
激活了功能,指定了邻居,是不是就可以直接传递IPV6的路由了呢?
是的,没错,因为此时的BGP就是用IPV6来建立的
R1(config-router-af)#inter lo1
R1(config-if)#ipv add 1111::1/128
R2(config-router-af)#inter lo 1
R2(config-if)#ipv add 2222::2/128
创建IPV6地址
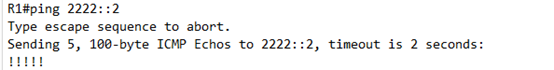
然后进行宣告,
还是要在IPV6的地址 簇中进行
R1(config-if)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#address-family ipv6 unicast
R1(config-router-af)#network 1111::1/128
R2(config-if)#router bgp 100
R2(config-router)#address-family ipv6 un
R2(config-router-af)#network 2222::2/128
最主要的是考虑如何传递IPV4,相必有了上面的经验,在这里就不难,只不过是地址 发生了变化,
先来分析一下 所需要的步骤
1 物理接口的ipv4地址
2 BGP激活IPV4地址簇,并指定邻居
3 宣告IPV4路由
4 route-map 修改下一跳
5 ipv4地址簇下调用route-map
R1(config-router)#inter f0/0
R1(config-if)#ip add 12.0.0.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no shu
R2(config-router-af)#inter f0/0
R2(config-if)#ip add 12.0.0.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shu
R1(config-if)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#address-family ipv4 unicast
R1(config-router-af)#nei FE80::C802:41FF:FE2C:0%FastEthernet0/0 activate
R1(config-router-af)#network 1.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#router bgp 100
R2(config-router)#address-family ipv4 unicast
R2(config-router-af)#nei FE80::C801:42FF:FE98:0%FastEthernet0/0 activate
R2(config-router-af)#net 2.2.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#route-map aa
R1(config-route-map)#set ip next-hop 12.0.0.1
R2(config-if)#route-map aa
R2(config-route-map)#set ip next-hop 12.0.0.2
R1(config-route-map)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#address-family ipv4 unicast
R1(config-router-af)#$802:41FF:FE2C:0%FastEthernet0/0 route-map aa out
R2(config-route-map)#router bgp 100
R2(config-router)#address-family ipv4 unicast
R2(config-router-af)#$801:42FF:FE98:0%FastEthernet0/0 route-map aa out
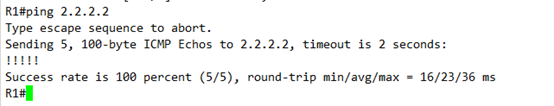
查看IPV4 的bgp表

路由表中同样存在
测试
IPV6最终总结
其实对于IPV6而言,最乱的(难倒是不难,就是来回的绕)就是在路由协议这一块,还有就是当面对着上FE80,以及一些特殊地址时,会有些蒙B的感觉,但是不要慌张。这都不叫事儿,干它就完了,不信学不会。、
-----------------------------------------------------
CCIE成长之 路 --- 梅利



