hive -- 分区,分桶(创建,修改,删除)
分区:
静态创建分区:
1. 数据:
john doe 10000.0
mary smith 8000.0
todd jones 7000.0
boss man 20000.0
freed finance 15000.0
stacy saber 4000.0建表+添加一个数据
create table if not exists employees(
name string,
money float)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t'
stored as textfile;
load data local inpath '/home/data/employees.txt' into table employees;问题:查询工资在8000元到10000元之间的人和工资
select *
from employees
where money between 8000 and 10000;问题:按照工资添加新列,少于5000元的添加low,5000-7000元之间的添加middle,7000-10000元的添加hight,10000元以上添加very hight
select
name,money,
case
when money>=5000 then(
case
when money>=7000 then(
case
when money>=10000 then 'very hight'
else 'hight' end
)
else 'middle' end
)
else 'low' end
from employees;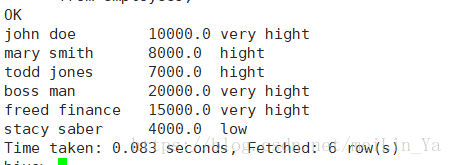
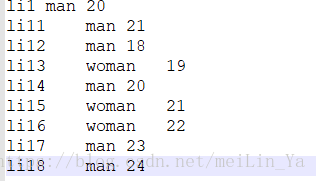
2.数据(分区)
li1 man 20
li11 man 21
li12 man 18
li13 woman 19
li14 man 20
li15 woman 21
li16 woman 22
li17 man 23
li18 man 24建表+添加数据
create table if not exists p0(
name string,
sex string,
age string)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t'
stored as textfile;
load data local inpath '/home/data/p0.txt' into table p0;如何定义分区,准备创建分区 具有了分区的能力的表
分区用途 目的: 查询速度大大增加,所以分区数据分区方式一:静态分区
注:1、静态分区要放在动态分区前面
2、静态分区的字段不要出现在select后面
create table if not exists p0_1(
name string,
age string
)
partitioned by (sex string)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t'
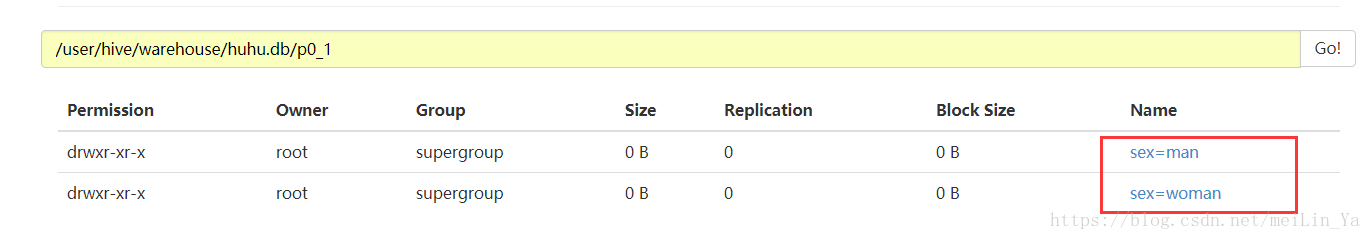
stored as textfile;根据性别分区:
alter table p0_1 add partition (sex='man');
alter table p0_1 add partition(sex='woman');在分区中插入数据
insert into p0_1
partition(sex='man')
select name,age
from p0
where sex='man';
insert into p0_1
partition(sex='woman')
select name,age
from p0
where sex='woman';--显示分区
show partitions p0_1;--显示分区路径
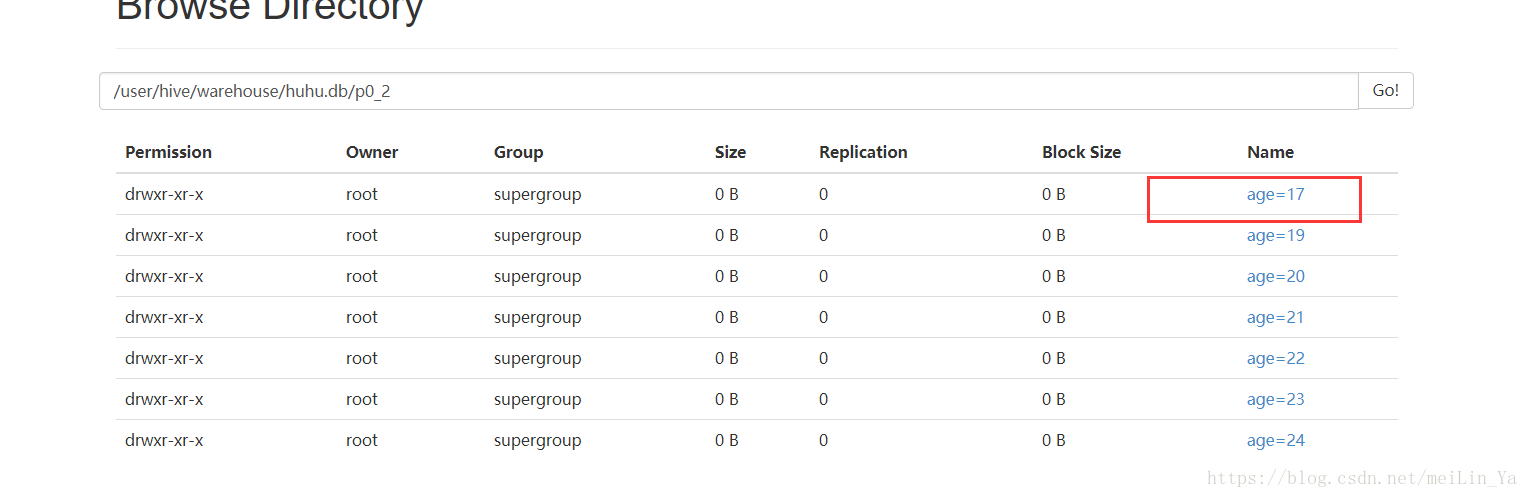
根据年龄分区:
create table if not exists p0_2(
name string,
sex string)
partitioned by (age string)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t'
stored as textfile;
alter table p0_2
add
partition(age='18')
partition(age='19')
partition(age='20')
partition(age='21')
partition(age='22')
partition(age='23')
partition(age='24');
insert into p0_2
partition(age='18')
select name,sex
from p0
where age='18';
insert into p0_2
partition(age='19')
select name,sex
from p0
where age='19';
insert into p0_2
partition(age='20')
select name,sex
from p0
where age='20';
insert into p0_2
partition(age='21')
select name,sex
from p0
where age='21';
insert into p0_2
partition(age='22')
select name,sex
from p0
where age='22';
insert into p0_2
partition(age='23')
select name,sex
from p0
where age='23';
insert into p0_2
partition(age='24')
select name,sex
from p0
where age='24';--修改分区,相当于修改hdfs文件名-->mv {修改时文件名不能重复}
alter table p0_2 partition(age='18') rename to partition(age='17');--删除分区
alter table p0_2 drop partition(age='17');动态创建分区
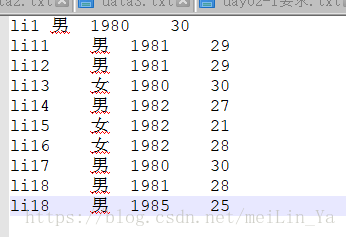
数据一:
建表+填数据
create table if not exists p2(
name string,
sex string,
birth string,
age string)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t'
stored as textfile;
load data local inpath '/home/data/p2.txt' into table p2;--是否开启动态分区功能,默认false关闭
set hive.exec.dynamic.partition=ture;-- 设置动态分区模式
set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode=strict;set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode=nostrict;-- 设置总的动态分区个数
set set hive.exec.dynamic.partitions=1000;-- 设置每个节点上动态分区个数
set set hive.exec.dynamic.partitions.pernode=100;分区:
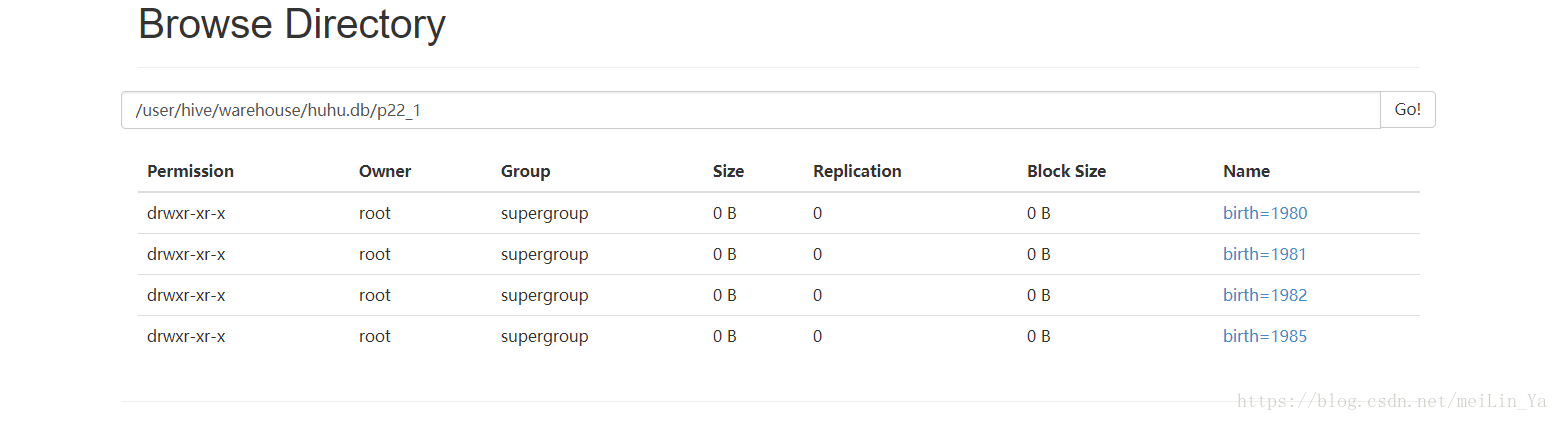
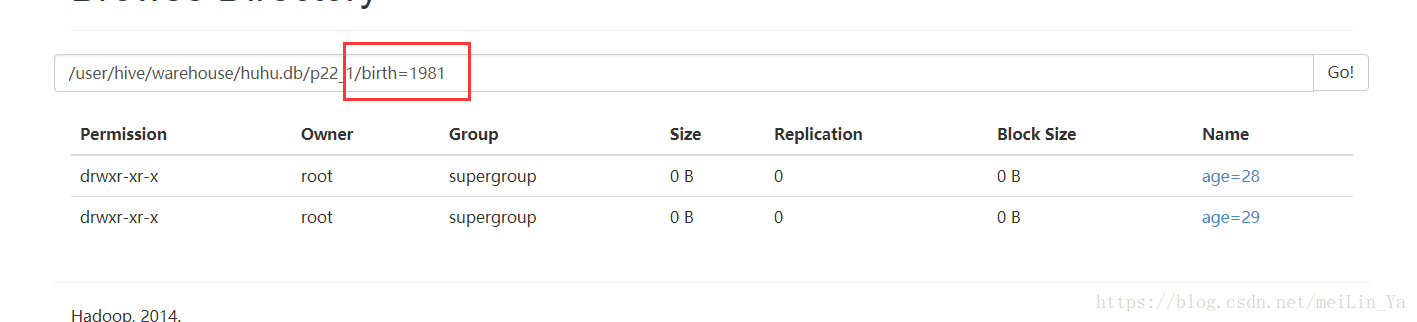
create table if not exists p22_1(
name string,
sex string
)
partitioned by(birth string,age string)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t'
stored as textfile;插入数据:
insert into table p22_1
partition(birth,age)
select name,sex,birth,age
from p22;
分桶:
分桶介绍:
对于每一个表(table)或者分区, Hive可以进一步组织成桶,也就是说桶是更为细粒度的数据范围划分。Hive也是 针对某一列进行桶的组织。Hive采用对列值哈希,然后除以桶的个数求余的方式决定该条记录存放在哪个桶当中。
桶(bucket)是指将表或分区中指定列的值为key进行hash,hash到指定的桶中,这样可以支持高效采样工作。
# ------------------分桶意义---------------------
把表(或者分区)组织成桶(Bucket)有两个理由:
(1)获得更高的查询处理效率。连接两个在相同列上划分了桶的表,可以使用 Map 端连接 (Map-side join)高效的实现。
(2)使取样(sampling)更高效。
数据:
建表+添加数据
create table if not exists bucket_user_tmp(
id int,
name string)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t'
stored as textfile;
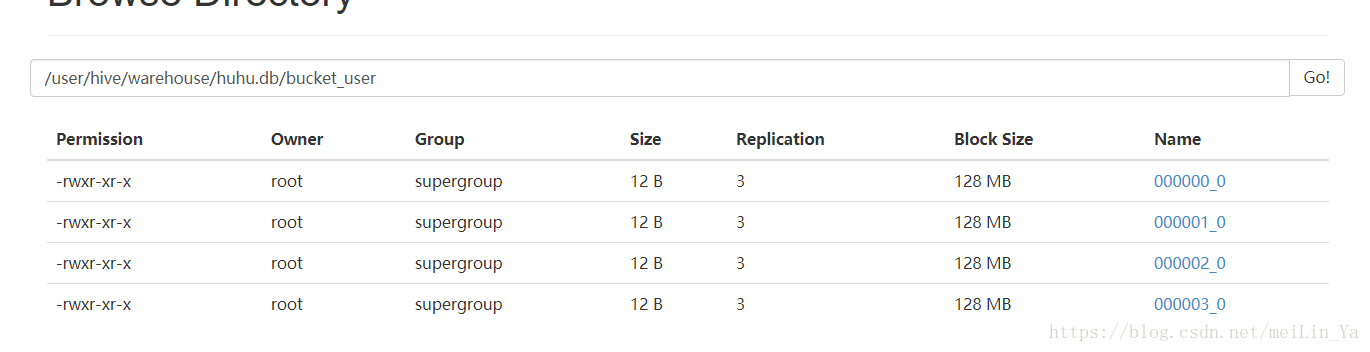
load data local inpath '/home/data/users.txt' into table bucket_user_tmp;创建分桶:按id分
create table bucket_user (id int,name string)
clustered by(id) into 4 buckets;设置分桶:-- 必须设置这个数据,hive才会按照你设置的桶的个数去生成数据
set hive.enforce.bucketing=true;插入数据:
insert into table bucket_user
select id,name
from bucket_user_tmp;
桶中数据:
桶中数据是按照:hive会计算桶列的hash值再以桶的个数取模来计算某条记录属于那个桶,每个桶对应一个reduce
id id%4 0 1 2 3 hashcode
------------------分桶抽样---------------------
建一张分桶的表:
数据:一百万条数据
建表+添加数据:
create table if not exists bucket_tab1_tmp (
id int)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t'
stored as textfile;
load data local inpath '/home/data/data10.txt' into table bucket_tab1_tmp;分桶:
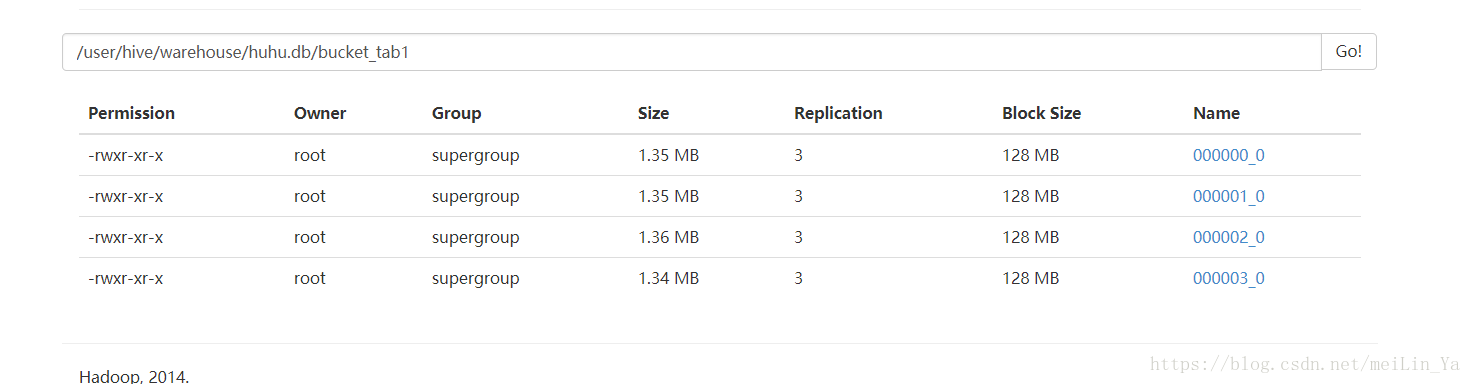
create table bucket_tab1 (id int)
clustered by(id) into 4 buckets;桶内插入数据:
insert into table bucket_tab1
select *
from bucket_tab1_tmp;
1.将会从表lxw1中取样1M的数据:
select *
from bucket_tab1
tablesample(1M);2.-- 带桶表的抽样 1 2 3 4 每个桶 25% 我一共有一百万条数据,25%就是20万条左右,集体还得看每条数据得大小
-- 不带桶表的抽样 不一定哪个桶 25%
select *
from bucket_tab1
tablesample(bucket 1 out of 4 on rand());最后总结下吧
分区+分桶的sql:
create table student(id int,age int,name string)
partitioned by(stat_date string)
clustered by(id) sort by(age) into 2 buckets
row formate delimited fields terminated bu ',';
hive基于hadoop得一个数据仓库,它得数据库建表使用反三范式,一个要求:快!查询快。
所以呢,它又是分区又是分组得,其实就是为了查询快,减少暴力扫描数据量,提高查询效率。
而分桶可以基于原表或分区后得表进行分桶,分桶是细过滤,但是,他们呢都是为了提高效率,那么想想hive会要不要建立索引呢?
我想一般不会,建立索引后原来表所占内存是建立索引后的2-3倍,但是速度也会得到提升,但是所用消耗费用也大,于此分区和分桶就代替了索引,他们跟为方便简介,也达到了同样的效果。












 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号