spring Bean类自动装载实现
先贴spring的开发文档,有助于大家学习http://shouce.jb51.net/spring/beans.html#beans-factory-class
一直想研究一下spring bean的控制反转的实现,废话不多说。
1、先建了一个WEB工程,导入相关spring的jar包,装载到tomcat上,成功访问,有不懂的童鞋可以移步http://www.cnblogs.com/mei0619/p/6560332.html。
2.为了方便研究,我将对象的调用直接写在controller里,输出相应的日志,如果可以输出,证明bean是创建成功的,代码如下:
package com.controller; import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.ui.Model; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; import com.entity.User; import com.entity.World; @Controller public class SpringServlet { /** * @Autowired 自动装载world对象 自动按type装载,也就是bean的class属性 * 或者@Resource(name="world") 按name装载,也就是bean的id */ @Resource(name="world") //这里的@Resource(name="world")和@Autowired是一模一样的, public World world; @RequestMapping("/index") public String index(Model model){ world.worldTest(); return "index"; } @RequestMapping("/save") public String Save(@ModelAttribute("form") User user, Model model) { // user:视图层传给控制层的表单对象;model:控制层返回给视图层的对象 System.out.println(model.toString()); model.addAttribute("user", user); return "detail"; } }
3、然后还写了两个类,代码如下:
package com.entity; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.Date; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Repository public class User implements Serializable{ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private Integer id; // id private String name; // name private String pwd; // pwd private Integer age; // age // private Date creatTime; // creatTime public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPwd() { return pwd; } public void setPwd(String pwd) { this.pwd = pwd; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } // public Date getCreatTime() { // return creatTime; // } // // public void setCreatTime(Date creatTime) { // this.creatTime = creatTime; // } public String toString(){ return name+"333"+age; } public void test(){ System.out.println("22222"); } }
package com.entity; import java.io.Serializable; import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; public class World implements Serializable{ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; // @Resource(name="user") //这里的@Resource(name="user")和@Autowired是一模一样的, private User user; private String type; public String getType() { return type; } public void setType(String type) { this.type = type; } public void setUser(User user) { this.user = user; } public void worldTest(){ user.test(); System.out.println("worldTest------" + type+"------"+user.getName()); } }
在上述代码中,SpringServlet里的world是IOC容器通过标签@Resource从配置文件中根据name装载的,而World类里同样有一个User类,这个类没有加标签,他是通过setUser()的方法装载的user bean类,配置文件里配置一下bean类,代码如下:
<bean id="world" class="com.entity.World"> <property name="user" ref="user" /> <property name="type" value="stringWorld"></property> </bean> <bean id="user" class="com.entity.User"/>
这样,SpringServlet里的world就通过控制反转的方式生成对象,然后调用world的worldTest()方法,就可以成功输出,如果world对象没有成功生成,调用他的方法的时候会报 java.lang.NullPointerException,
后台日志打印:
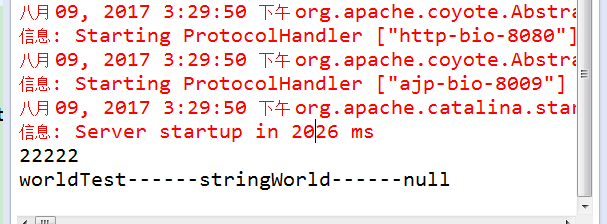
证明对象已经成功创建,如果想给对象添加属性,可以直接在配置文件里添加,如下形式:
<bean id="user" class="com.entity.User"> <property name="id" value="1"></property> <property name="name" value="guan"></property> <property name="pwd" value="111111"></property> <property name="age" value="12"></property> </bean>
最后,我想让代码更精简,不想写那么多配置文件,可以采用注解的形式,为World.java的User属性添加@Autowired或者@Resource(name="user")标签,然后改一下配置文件,只需要写两行,如下:
<bean id="world" class="com.entity.World" /> <bean id="user" class="com.entity.User"/>
是不是代码精简了好多,也装逼了好多,程序可以成功运行,同时日志台输出: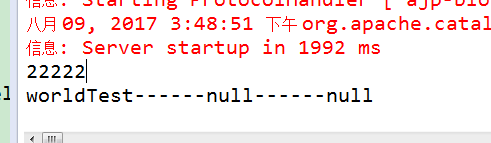
然后就结束了,很多东西还有待学习,,,有很多不明白,最后贴一下配置文件springSerblet-config.xml代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:task="http://www.springframework.org/schema/task" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/task http://www.springframework.org/schema/task/spring-task.xsd "> <!-- 使用默认的注解映射 --> <mvc:annotation-driven /> <!-- <mvc:resources location="/" mapping="/index.html" /> <context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config>--> <!-- world bean类 --> <bean id="world" class="com.entity.World" /> <!-- <property name="user" ref="user" /> <property name="type" value="stringWorld"></property> </bean> --> <bean id="user" class="com.entity.User"/> <!-- user bean类 --> <!-- <bean id="user" class="com.entity.User"> <property name="id" value="1"></property> <property name="name" value="guan"></property> <property name="pwd" value="111111"></property> <property name="age" value="12"></property> </bean> --> <!-- <bean id="world" class="com.entity.World"> <property name="user"> <idref bean="user"/> </property> <property name="type" value="stringWorld"></property> </bean> --> <!-- 自动扫描controller包中的控制器 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.controller" /> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" > <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/" /> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp" /> </bean> <!-- <bean id="urlMapping" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping"> <property name="mappings"> <props> <prop key="/index.do">controllerDoem</prop> </props> </property> </bean> <bean id="controllerDoem" class="com.controller"> <property name="view"> <value>index</value> </property> </bean>--> </beans>
applicationContext.xml和web.xml里的是一些web工程基本配置,不要动它,整体结构是这样的:
最后,欢迎各位大神指导,指出错误和不足。。。。 正在努力学习中。。。


