JWT校验流程源码
一. jwt token校验源码简析
1.1 前言
之前使用jwt签发了token,里面的头部包含了加密的方式、是否有签名等,而载荷中包含用户名、用户主键、过期时间等信息,最后的签名还使用了摘要算法进行不可逆的加密。
同时检验签名时还需进行签名的碰撞检测,判断该token是否合法。jwt提供了一个校验token的认证方法,使用时只需要CBV中进行局部身份验证配置即可。使用如下:
from rest_framework_jwt.authentication import JSONWebTokenAuthentication class 类名(JSONWebTokenAuthentication): authentication_classes = [JSONWebTokenAuthentication]
不过自身的校验还存在一些缺陷,不能完全满足的需求,这时候我们可以继承该类后重写其中校验token的方法,具体是什么方法,我们接着往下看。
1.2 jwt的authenticate方法
以前走过APIView的源码,从源码得知身份校验走的是类中的authenticate的方法。定位至JSONWebTokenAuthentication,依据属性的查找顺序找到authenticate方法:
可以看出主要的方法是以上三个,接下来一一点进去瞅瞅(遵循属性查找顺序),首先是get_jwt_value(request)方法:

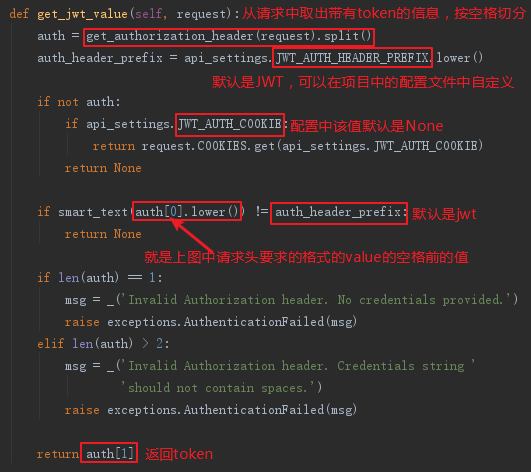
看看get_jwt_value中的get_authorization_header方法:

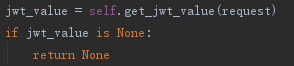
回到authenticate方法,此时jwt_value的值要么是None,要么是token:
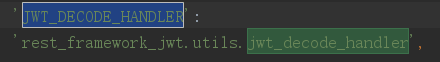
再看看重点的校验token的方法jwt_decode_handler(jwt_value):

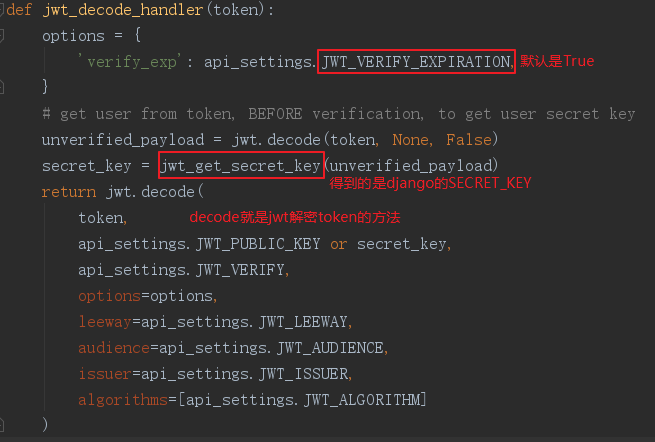
上述jwt.decode返回的载荷,有兴趣可以点进去看看源码,这里直接略过。
往下看看authenticate_credentials(payload)方法:
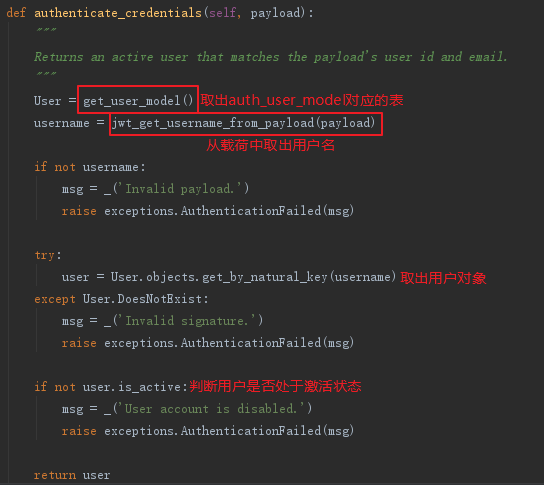
该函数返回一个user对象,最终由authenticate方法返回该user对象及token。不过试验时发现get_jwt_value方法返回的是None而不是token时,authenticate方法return None,这时也能通过校验,所以我们可以重写authenticate方法,对get_jwt_value中用于取头部token信息的get_authorization_header返回的值进行判断,增加健壮性。
import jwt from rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailed from rest_framework_jwt.authentication import jwt_decode_handler from rest_framework_jwt.authentication import get_authorization_header from rest_framework_jwt.authentication import BaseJSONWebTokenAuthentication class JSONWebTokenAuthentication(BaseJSONWebTokenAuthentication): def authenticate(self, request): # 采用drf获取token的手段 - HTTP_AUTHORIZATION - Authorization token = get_authorization_header(request) if not token: raise AuthenticationFailed('Authorization 字段是必须的') # 可以添加反扒措施:原功能是token有前缀 # drf-jwt认证校验算法 try: payload = jwt_decode_handler(token) except jwt.ExpiredSignature: raise AuthenticationFailed('签名过期') except jwt.InvalidTokenError: raise AuthenticationFailed('非法用户') user = self.authenticate_credentials(payload) # 将认证结果丢该drf return user, token
AUTHENTICATION_BACKENDS = ['user.utils.JWTModelBackend']
二. jwt的RefreshJSONWebToken
jwt生成token后,因为token有个过期时间,而这个时间默认是五分钟,之后客户端携带token重新访问时,会调用jwt的RefreshJSONWebToken中的RefreshJSONWebTokenSerializer类中的validate方法,来刷新客户端的token,而刷新的时间也是有上限的,默认是七天,可以在项目下的配置中自定义。
# 配置的默认过期时间 'JWT_EXPIRATION_DELTA': datetime.timedelta(seconds=300) # token刷新的最大时间间隔,默认七天 'JWT_REFRESH_EXPIRATION_DELTA': datetime.timedelta(days=7)
如自定义过期时间:
import datetime JWT_AUTH = { # 过期时间 'JWT_EXPIRATION_DELTA': datetime.timedelta(days=1), }
接下来看看RefreshJSONWebTokenSerializer的源码。
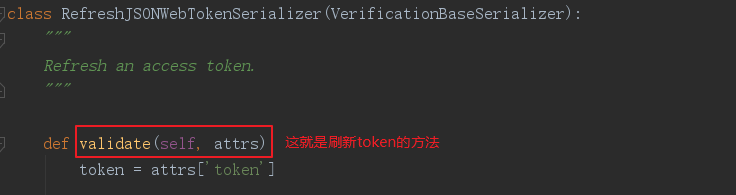
让我们看看validate方法:
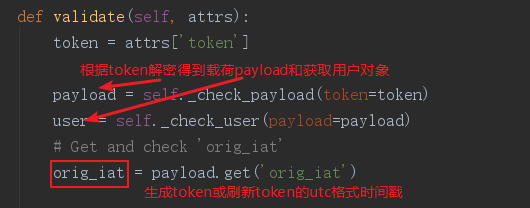
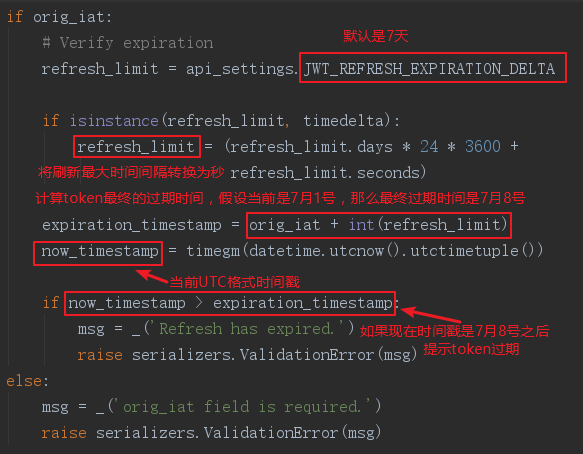
validate方法源码如下:
def validate(self, attrs): token = attrs['token'] payload = self._check_payload(token=token) user = self._check_user(payload=payload) # Get and check 'orig_iat' orig_iat = payload.get('orig_iat') if orig_iat: # Verify expiration refresh_limit = api_settings.JWT_REFRESH_EXPIRATION_DELTA if isinstance(refresh_limit, timedelta): refresh_limit = (refresh_limit.days * 24 * 3600 + refresh_limit.seconds) expiration_timestamp = orig_iat + int(refresh_limit) now_timestamp = timegm(datetime.utcnow().utctimetuple()) if now_timestamp > expiration_timestamp: msg = _('Refresh has expired.') raise serializers.ValidationError(msg) else: msg = _('orig_iat field is required.') raise serializers.ValidationError(msg) new_payload = jwt_payload_handler(user) new_payload['orig_iat'] = orig_iat return { 'token': jwt_encode_handler(new_payload), 'user': user }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号