elasticsearch使用
一. 安装java环境与elasticsearch、kibana
首先要求jdk为1.8及以上,这里elasticsearch(kibana同理,尽量保证elasticsearch版本一致,安装和启动方式也是一样的)版本采用6.5.4。
elasticsearch简介:https://baike.baidu.com/item/elasticsearch/3411206?fr=aladdin
elasticsearch官网:https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/

点击下载,之后下拉选择历史版本past releases

最后点击download即可

java环境配置看该博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/Neeo/articles/10368280.html
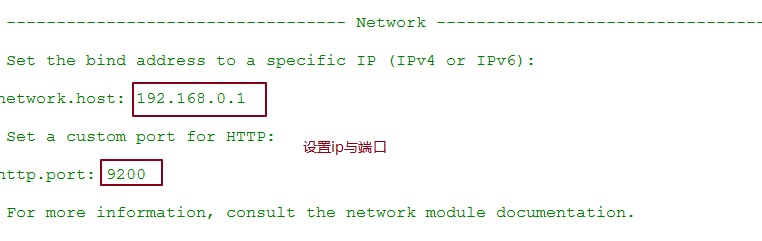
安装完毕后如果没有出现错误,解压elasticsearch,然后进入其bin目录,双击打开其中的elasticsearch.bat文件即可,随后访问127.0.0.1:9200,如果能看到返回的json数据,代表配置成功。(其中9200是节点监听的断开,而9300是集群默认监听的端口)。
未能正常启动原因

二. elasticsearch、kibana的部分文件说明
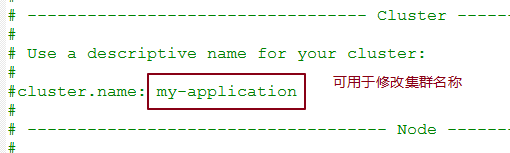
1. 解压后的config中的elasticsearch.yml就是ES的配置文件,这用Notepad打开。


同目录的jvm.options是虚拟机jrel的配置。

同目录的log4j2.properties是日志的配置,可以配置日志的输出、级别等信息,一般不会修改。(log4j是Apache的一个框架,用于控制日志)
- Kibana目录下的config中的kibana.yml存放其配置文件。



三. Kibana的Dev tools中ES的简单命令
数据准备
PUT s18/doc/2
{
"name":"yangtao",
"age": 18,
"tags":"浪",
"b":"19970521",
"sex": "男"
}
PUT s18/doc/1
{
"name":"egon",
"age": 20,
"tags":"认真学习",
"b":"19970781",
"sex": "男"
}
PUT s18/doc/3
{
"name":"sybil",
"age": 3,
"tags":"认真学习",
"b":"19971216",
"sex": "女"
}
以 '索引/类型/文档' 的格式
#增 PUT 如果PUT对的数据已存在,那么会进行更新的操作,但是PUT时传的参数是什么,更新之后的数据就是什么,所以需要填写所有的字段
PUT s18/doc/1 #新增索引s18/doc/1 s18是_index,1是该数据的文档,doc是Type
{
"name":"sybil",
"skill":"fly",
"hobby":"sleep",
"tags":"beautiful"
}
#删 DELETE
DELETE s18 #删除索引(数据库)
DELETE s18/doc/1 #删除索引s18下type是doc,文档是1的数据
DELETE s18/doc/_search?q=tags:beautiful #这是错误的删除方式,要使用search的方式删除需要使用POST
#查 GET
GET s18/doc/1 #查文档为1的数据
GET s18/doc/_search #查所有
GET s18/doc/_search?q=name:sybil #查名字叫sybil的
#更新指定字段POST,或配合search删除
POST s18/doc/1/_update
{
"doc":{ # 需要指定type,相当于指定表名
"tags":"美丽冻人"
}
}
POST s18/doc/_delete_by_query?q=age:18 #删除年龄为18的数据,不过不推荐使用该方式
#查询的两种方式
1.查询字符串 query string
GET s18/doc/_search?q=age:18
2. DSL 结构化查询
GET s18/doc/_search
{
"query":{
"match":{
"age":18
}
}
}
GET s18/doc/_search
{
"query":{
"match_all":{} #因为是查所有,不需要参数
}
}
- GET s18/_mapping
-
GET s18/_settings

-
GET s18
四. ES的复杂查询
1.排序sort、分页、布尔查询bool
#排序 sort 不是所有的字段都能排序,比如名字
GET s18/doc/_search
{
"query":{
"match_all":{}
},
"sort": [ #排序
{
"age":{
"order": "asc" #升序,desc降序
}
}
]
}
#分页 内部会先排好序,保证翻页后不会出现已经返回过的数据
GET s18/doc/_search
{
"query":{
"match_all":{}
},
"from": 0, #从0条开始
"size": 2 #返回2条数据
}
#布尔查询bool: should(or) must(and) must_not(not),must_not
GET s18/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [ #名字是sybil或者年龄18岁
{
"match": {
"name": "sybil"
}
},
{
"match": {
"age": "18"
}
}
]
}
}
}
'查询性别是男的,年龄18'
GET s18/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"bool":{
"must": [
{
"match": {
"age": "18"
}
},
{
"match": {
"sex": "男"
}
}
]
}
}
}
#查询年龄大于19岁的男的 filter尽量用must配合,避免脏数据
GET s18/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{"match": {
"sex": "男"
}}
],
"filter": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 19,
"lte": 20
}
}
}
}
}
}
2.高亮查询highlight
#查询name是sybil的文档
#高亮查询,查询name是sybil的文档,查询的结果需要在前端才能体现高亮,因为是标签的效果
GET s18/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "sybil"
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"name": {} #查询的结果用<em>标签包裹
}
}
}
GET s18/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "sybil" #会将我们这里定义的字段高亮显示
}
},
"highlight": { #可以使用pre_tags与post_tags自定义标签
"pre_tags": "<b style='color:red;font-size:20px'>",
"post_tags": "<\b>",
"fields": {
"name": {} #这里指定字段后空着即可
}
}
}3.结果过滤_source
#过滤出查询结果中想要的字段
GET s18/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "sybil"
}
},
"_source": "name" #单个字段
}
GET s18/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "sybil"
}
},
"_source": ["name", "age"] #多个字段
}
4.聚合查询
#sum,查询所有男生的年龄
GET s18/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"sex": "男"
}
},
"aggs": {
"my_sum": { #这是查询结果的键,可以自定义
"sum": { #这是聚合的方法
"field": "age" #指定聚合的依据
}
}
}
}
#查询最大年龄的男生
GET s18/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"sex": "男"
}
},
"aggs": {
"my_max": {
"max": {
"field": "age"
}
}
}
}
#查询最小年龄的男生
GET s18/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"sex": "男"
}
},
"aggs": {
"my_min": {
"min": {
"field": "age"
}
}
}
}
#查询男生的平均年龄
GET s18/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"sex": "男"
}
},
"aggs": {
"my_avg": {
"avg": {
"field": "age"
}
}
}
}
#分组,根据年龄,0-10,,0-20
GET s18/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"sex": "男"
}
},
"aggs": {
"my_group": { #分组名称
"range": {
"field": "age",
"ranges": [
{
"from": 0, #[0, 10)
"to": 10
},
{
"from": 10,
"to": 20
},
{
"from": 20,
"to": 30
}
]
}
}
}
}
#分组,根据年龄,0-10,,0-20, 对每组年龄求和
GET s18/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"sex": "男"
}
},
"aggs": {
"my_group": {
"range": {
"field": "age",
"ranges": [
{
"from": 0,
"to": 10
},
{
"from": 10,
"to": 20
},
{
"from": 20,
"to": 30
}
]
},
"aggs": {
"my_sum": {
"sum": {
"field": "age"
}
}
}
}
}
}5. ES的mapping映射
#自定义索引的映射
PUT s2
{
"mappings": {
"doc":{ #类型
"properties":{ #文档的属性
"name":{
"type":"text"
},
"age":{
"type":"long"
},
"desc":{
"type":"text"
}
}
}
}
}
#如果给该索引加文档时,额外增加了字段,那么mappings会自动增加该字段,使其能够成为查询条件
GET s2/_mapping
PUT s2/doc/2
{
"name":"catmao",
"age":30,
"desc":"beautiful",
"skill":"sleep"
}
GET s2/_mapping #再次执行会发现字段多了skill
#这是由mappings的dynamic的三种状态,三种状态时,均可以缺省字段
dynamic为true时特征如上。
dynamic为false时,PUT添加的数据有额外字段时,Mapping不会自动添加,该字段也无法成为查询的条件。
dynamic为strict时,添加的数据不能有额外的字段,会直接报错
PUT s6
{
"mappings": {
"doc":{
"dynamic":"strict",
"properties":{
"name":{
"type":"text"
}
}
}
}
}
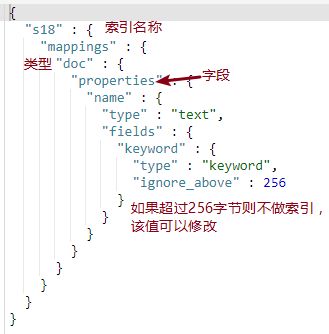
#mapping的ignore_above,不会为超过该设定字符长度的字符串设定索引与存储,即无法成为有效的查询条件,仅对type为keyword的字段有效。
https://www.cnblogs.com/Neeo/articles/10789701.html
PUT s7
{
"mappings": {
"doc":{
"properties":{
"title":{
"type":"keyword",
"ignore_above":10
}
}
}
}
}
PUT s7/doc/2
{
"title":"从手机、平板电脑、路由器"
}
PUT s7/doc/1
{
"title":"1234567"
}
GET s7/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "1234567"
}
}
}
#mappings参数之index,设置为false后,ES不会为该字段建立索引,其实是不会做分词
#mappings的index参数
PUT s8
{
"mappings": {
"doc":{
"properties":{
"t1":{
"type":"text",
"index":"true"
},
"t2":{
"type":"text",
"index":"false"
}
}
}
}
}
PUT s8/doc/1
{
"t1":"论母猪的厂前保养",
"t2":"论母猪的厂后保养"
}
GET s8/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"t2": "母猪"
}
}
}
#mappings的copy_to,把一个字段的值复制给另一个,可以减少一次查询的次数
PUT s9
{
"mappings": {
"doc":{
"properties":{
"t1":{
"type":"text",
"copy_to":"full_name" #复制给多个字段 ["f1", "f2"]
},
"t2":{
"type":"text",
"copy_to":"full_name"
},
"full_name":{
"type":"text"
}
}
}
}
}
PUT s9/doc/1
{
"t1":"xxx",
"t2":"ooo"
}
GET s9/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"full_name": "xxx"
}
}
}6.嵌套属性
#嵌套类型
PUT w1
{
"mappings": {
"doc":{
"properties":{
"name":{
"type":"text"
},
"age":{
"type":"long"
},
"info":{ #info字段嵌套两个字段
"properties":{
"addr":{
"type":"text"
},
"tel":{
"type":"long"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
PUT w1/doc/1 #插入一条数据
{
"name":"tom",
"age":18,
"info":{
"addr":"北京",
"tel":"10010"
}
}
GET w1/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"info.tel": "10010" #以嵌套字段的属性为查询条件时,直接点语法即可
}
}
}7.settings设置主从分片
#主分片一旦设置无法更改,复制分片可以
PUT w2
{
"mappings": {
"doc":{
"properties":{
"title":{
"type":"text"
}
}
}
},
"settings": { #通过settings设置
"number_of_shards": 3, #主分片数量,默认为5
"number_of_replicas": 3 #复制分片数量,默认为1
}
}
GET w28.match系列

博客地址https://www.cnblogs.com/Neeo/articles/10578482.html
#数据准备
PUT t1/doc/1
{
"title":"中国是世界上人口最多的国家"
}
PUT t1/doc/2
{
"title":"美国是世界上军事实力强大多的国家"
}
PUT t1/doc/3
{
"title":"北京是中国 的首都"
} 使用match查询“中国”
#会发现美国也包含在其中,这是因为match内部会散列分词,内部是采用标准的分析器,中国会分为中和国
GET t1/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "中国"
}
}
} 我们想把中国当成一个短语,需要采用match_phrase
#这样就不好分词,把中国当成一个短语去查询
GET t1/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"title": "中国"
"slop": 1 #该参数可以指定分词的间隔
}
}
} 最左前缀查询match_phrase_prefix
PUT t2/doc/1
{
"title":"beautiful girl"
}
PUT t2/doc/2
{
"title":"beautiful so"
}
GET t2/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase_prefix": {
"title": "bea" #只要有单词以bea开头
}
}
} multi_match多字段查询,可以完成match_phrase和match_phrase_prefix的工作,使用很灵活。
PUT t3/doc/1
{
"t1":"beautiful girl",
"t2":"beautiful so"
}
#查找字段t1和t2都包含beautiful的文档
GET t3/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "beautiful",
"fields": ["t1", "t2"]
}
}
}五. elasticsearch分析数据的过程漫谈
详见博客https://www.cnblogs.com/Neeo/p/10304892.html,附带安装ik分词
5.1 ik安装的问题

5.2 ik分词的测试
#ik分词的测试
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text":"上海自来水来自海上"
}
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_smart",
"text":"上海自来水来自海上"
}
#粒度更细,一般存储时建议使用粒度粗的(意义更大),ik_max_word会将文档做最细粒度的拆分
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"text":"上海自来水来自海上"
}
六. python操作Elasticsearch
6.1 python连接 ES
doc_type默认是doc,所以可以不写,不过建议都写上,以防万一
'1. 安装elasticsearch模块'
pip install elasticsearch
# 豆瓣源
pip install -i https://pypi.doubanio.com/simple/ elasticsearch
'2. 连接的方式'
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
# es = Elasticsearch() # 默认连接本地elasticsearch
# es = Elasticsearch(['127.0.0.1:9200']) # 连接本地9200端口
es = Elasticsearch(
["192.168.1.10", "192.168.1.11", "192.168.1.12"], # 连接集群,以列表的形式存放各节点的IP地址
sniff_on_start=True, # 连接前测试
sniff_on_connection_fail=True, # 节点无响应时刷新节点
sniff_timeout=60 # 设置超时时间
)
'3. 配置忽略响应状态码'
es = Elasticsearch(['127.0.0.1:9200'],ignore=400) # 忽略返回的400状态码
es = Elasticsearch(['127.0.0.1:9200'],ignore=[400, 405, 502]) # 以列表的形式忽略多个状态码
'4. 简单的示例'
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
es = Elasticsearch() # 默认连接本地elasticsearch
# print(es.ping()) #可以用该方法查看是否连接成功,如果群集已启动,则返回True,否则返回False
print(es.index(index='p1', doc_type='doc', id=1, body={'name': "sybil", "age": 18})) #index方法,如果索引存在则更新,否则增加新记录
print(es.get(index='p1', doc_type='doc', id=1))6.2 python操作ES
# search方法使用的较多,因为可以跟复杂查询
'对返回的信息的几种过滤方法(过滤出想要显示的信息)'
body = {
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "lou22"
}
}
}
# 返回的是一个大字典
print(es.search(index='p1', body=body))
# 可以使用filter_path过滤出其中想要的信息
print(es.search(index='p1', body=body, filter_path=['hits.hits']))
# 查询出来的信息主要保存在_source中 {'hits': {'hits': [{'_source': {'name': 'lou22'}}]}}
print(es.search(index='p1', body=body, filter_path=['hits.hits._source']))
# 也可以指定多个要显示的信息 {'hits': {'total': 1, 'hits': [{'_source': {'name': 'lou22'}}]}}
print(es.search(index='p1', body=body, filter_path=['hits.hits._source', 'hits.total']))
# 可以用*指定返回hits下所有的内容 *是语法,表示所有
print(es.search(index='p1', body=body, filter_path=['hits.*']))
# 可以用*指定返回hits下的hits中所有的内容
print(es.search(index='p1', body=body, filter_path=['hits.hits._*']))
'过滤出结果中想要的字段,_source'
print(es.search(index='py3', doc_type='doc', body={"query": {"match":{"age": 20}}})) # 一般查询
print(es.search(index='py3', doc_type='doc', body={"query": {"match":{"age": 19}}},_source=['name', 'age'])) # 结果字段过滤
print(es.search(index='py3', doc_type='doc', body={"query": {"match":{"age": 19}}},_source_exclude =[ 'age'])) #除了age字段之外的所有字段都要
print(es.search(index='py3', doc_type='doc', body={"query": {"match":{"age": 19}}},_source_include =[ 'age'])) #只要age字段,同_source差不多get_source直接返回数据字典
# 直接返回数据字典 {'name': 'lou22'}
print(es.get_source(index='p1', doc_type='doc', id=1))count统计查询结果的个数
# 新建几条数据
for i in range(2, 11):
print(es.index(index='p1', doc_type='doc', body={"name": "lou%s" % i}))
# 指定用于查询的方式
body = {
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "lou2"
}
}
}
#查询回来的结果就是字典,可以采用字典的操作方式
print(es.count(index='p1', doc_type='doc', body=body))['count'] # 1
print(es.count(index='w2')) # {'count': 6, '_shards': {'total': 5, 'successful': 5, 'skipped': 0, 'failed': 0}}
print(es.count(index='w2', doc_type='doc')) # {'count': 6, '_shards': {'total': 5, 'successful': 5, 'skipped': 0, 'failed': 0}}es.create创建索引(索引不存在的话)并新增一条数据,索引存在仅新增(只能新增,重复执行会报错
#其实内部调用了es.index,一般不使用create方法
print(es.create(index='py3', doc_type='doc', id='1', body={"name": '王五', "age": 20}))
print(es.get(index='py3', doc_type='doc', id='1'))es.delete与es.delete_by_query
#es.delete,删除指定的文档。比如删除文章id为4的文档,但不能删除索引,如果想要删除索引,还需要es.indices.delete来处理
print(es.delete(index='py3', doc_type='doc', id='4'))
#es.delete_by_query,删除与查询匹配的所有文档
print(es.delete_by_query(index='py3', doc_type='doc', body={"query": {"match":{"age": 20}}}))es.exists与es.info
# es.exists,查询elasticsearch中是否存在指定的文档,返回一个布尔值
print(es.exists(index='py3', doc_type='doc', id='1'))
#es.info,获取当前集群的基本信息,一般使用kibana查看,因为比较直观
print(es.info())6.3 es.indices对索引的操作
es.indices.create在Elasticsearch中创建索引,用的最多
body = {
"mappings": {
"doc": {
"dynamic": "strict", #设置严格模式
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"url": {
"type": "text"
},
"action_type": {
"type": "text"
},
"content": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
}
es.indices.create('py4', body=body) es.indices.analyze,返回分词结果
es.indices.analyze(body={'analyzer': "ik_max_word", "text": "皮特和茱丽当选“年度模范情侣”Brad Pitt and Angelina Jolie"}) es.indices.delete,在Elasticsearch中删除索引
print(es.indices.delete(index='py4'))
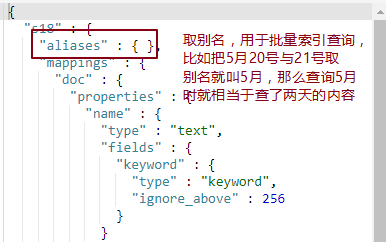
print(es.indices.delete(index='w3')) # {'acknowledged': True} es.indices.put_alias,为一个或多个索引创建别名,查询多个索引的时候,可以使用这个别名
print(es.indices.put_alias(index='py4', name='py4_alias')) # 为单个索引创建别名
print(es.indices.put_alias(index=['py3', 'py2'], name='py23_alias')) # 为多个索引创建同一个别名,联查用 es.indices.delete_alias,删除一个或多个别名
print(es.indices.delete_alias(index='alias1'))
print(es.indices.delete_alias(index=['alias1, alias2'])) es.indices.get_mapping,检索索引或索引/类型的映射定义
print(es.indices.get_mapping(index='py4')) es.indices.get_settings,检索一个或多个(或所有)索引的设置
print(es.indices.get_settings(index='py4')) es.indices.get,允许检索有关一个或多个索引的信息
print(es.indices.get(index='py2')) # 查询指定索引是否存在
print(es.indices.get(index=['py2', 'py3'])) es.indices.get_alias,检索一个或多个别名
print(es.indices.get_alias(index='py2'))
print(es.indices.get_alias(index=['py2', 'py3'])) es.indices.get_field_mapping,检索特定字段的映射信息
print(es.indices.get_field_mapping(fields='url', index='py4', doc_type='doc'))
print(es.indices.get_field_mapping(fields=['url', 'title'], index='py4', doc_type='doc')) 其他
# es.indices.delete_alias,删除特定别名。
# es.indices.exists,返回一个布尔值,指示给定的索引是否存在。
# es.indices.exists_type,检查索引/索引中是否存在类型/类型。
# es.indices.flus,明确的刷新一个或多个索引。
# es.indices.get_field_mapping,检索特定字段的映射。
# es.indices.get_template,按名称检索索引模板。
# es.indices.open,打开一个封闭的索引以使其可用于搜索。
# es.indices.close,关闭索引以从群集中删除它的开销。封闭索引被阻 止进行读/写操作。
# es.indices.clear_cache,清除与一个或多个索引关联的所有缓存或特定缓存。
# es.indices.put_alias,为特定索引/索引创建别名。
# es.indices.get_uprade,监控一个或多个索引的升级程度。
# es.indices.put_mapping,注册特定类型的特定映射定义。
# es.indices.put_settings,实时更改特定索引级别设置。
# es.indices.put_template,创建一个索引模板,该模板将自动应用于创建的新索引。
# es.indices.rollove,当现有索引被认为太大或太旧时,翻转索引API将别名转移到新索引。API接受单个别名和条件列表。别名必须仅指向单个索引。如果索引满足指定条件,则创建新索引并切换别名以指向新别名。
# es.indices.segments,提供构建Lucene索引(分片级别)的低级别段信息6.4 Cluster 集群相关
es.cluster.get_settigns,获取集群设置
print(es.cluster.get_settings()) es.cluster.health,获取有关群集运行状况的非常简单的状态
print(es.cluster.health()) es.cluster.state,获取整个集群的综合状态信息
print(es.cluster.state()) es.cluster.stats,返回群集的当前节点的信息
print(es.cluster.stats())6.5 Node 节点相关
es.nodes.info,返回集群中节点的信息
print(es.nodes.info()) # 返回所节点
print(es.nodes.info(node_id='node1')) # 指定一个节点
print(es.nodes.info(node_id=['node1', 'node2'])) # 指定多个节点列表 es.nodes.stats,获取集群中节点统计信息
print(es.nodes.stats())
print(es.nodes.stats(node_id='node1'))
print(es.nodes.stats(node_id=['node1', 'node2'])) es.nodes.hot_threads,获取指定节点的线程信息
print(es.nodes.hot_threads(node_id='node1'))
print(es.nodes.hot_threads(node_id=['node1', 'node2'])) es.nodes.usage,获取集群中节点的功能使用信息
print(es.nodes.usage())
print(es.nodes.usage(node_id='node1'))
print(es.nodes.usage(node_id=['node1', 'node2']))6.6 Cat 一种查询方式
es.cat.aliases,返回别名信息
#name要返回的以逗号分隔的别名列表。
#formatAccept标头的简短版本,例如json,yaml
print(es.cat.aliases(name='py23_alias'))
print(es.cat.aliases(name='py23_alias', format='json')) es.cat.allocation,返回分片使用情况
print(es.cat.allocation())
print(es.cat.allocation(node_id=['node1']))
print(es.cat.allocation(node_id=['node1', 'node2'], format='json')) es.cat.count,Count提供对整个群集或单个索引的文档计数的快速访问
print(es.cat.count()) # 集群内的文档总数
print(es.cat.count(index='py3')) # 指定索引文档总数
print(es.cat.count(index=['py3', 'py2'], format='json')) # 返回两个索引文档和 es.cat.fielddata,基于每个节点显示有关当前加载的fielddata的信息。有些数据为了查询效率,会放在内存中,fielddata用来控制哪些数据应该被放在内存中,而这个es.cat.fielddata则查询现在哪些数据在内存中,数据大小等信息
print(es.cat.fielddata())
print(es.cat.fielddata(format='json', bytes='b'))
#bytes显示字节值的单位,有效选项为:'b','k','kb','m','mb','g','gb','t','tb' ,'p','pb'
#formatAccept标头的简短版本,例如json,yaml es.cat.health,从集群中health里面过滤出简洁的集群健康信息
print(es.cat.health())
print(es.cat.health(format='json')) es.cat.help,返回es.cat的帮助信息
print(es.cat.help()) es.cat.indices,返回索引的信息
print(es.cat.indices())
print(es.cat.indices(index='py3'))
print(es.cat.indices(index='py3', format='json')) es.cat.master,返回集群中主节点的IP,绑定IP和节点名称
print(es.cat.master())
print(es.cat.master(format='json')) es.cat.nodeattrs,返回节点的自定义属性
print(es.cat.nodeattrs())
print(es.cat.nodeattrs(format='json')) es.cat.nodes,返回节点的拓扑,这些信息在查看整个集群时通常很有用,特别是大型集群。我有多少符合条件的节点
print(es.cat.nodes())
print(es.cat.nodes(format='json')) es.cat.plugins,返回节点的插件信息
print(es.cat.plugins())
print(es.cat.plugins(format='json')) es.cat.segments,返回每个索引的Lucene有关的信息
print(es.cat.segments())
print(es.cat.segments(index='py3'))
print(es.cat.segments(index='py3', format='json')) es.cat.shards,返回哪个节点包含哪些分片的信息
print(es.cat.shards())
print(es.cat.shards(index='py3'))
print(es.cat.shards(index='py3', format='json')) es.cat.thread_pool,获取有关线程池的信息
print(es.cat.thread_pool())6.7 Snapshot 快照相关
# es.snapshot.create,在存储库中创建快照。
repository 存储库名称。
snapshot快照名称。
body快照定义。
# es.snapshot.delete,从存储库中删除快照。
# es.snapshot.create_repository。注册共享文件系统存储库。
# es.snapshot.delete_repository,删除共享文件系统存储库。
# es.snapshot.get,检索有关快照的信息。
# es.snapshot.get_repository,返回有关已注册存储库的信息。
# es.snapshot.restore,恢复快照。
# es.snapshot.status,返回有关所有当前运行快照的信息。通过指定存储库名称,可以将结果限制为特定存储库。
# es.snapshot.verify_repository,返回成功验证存储库的节点列表,如果验证过程失败,则返回错误消息6.8 Task 任务相关
# es.tasks.get,检索特定任务的信息。
# es.tasks.cancel,取消任务。
# es.tasks.list,任务列表七. python使用ES搜索小例子
7.1 settings.py中指定连接数据库
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql',
'NAME': 'test_es',
'HOST': '127.0.0.1',
'PORT': 3306,
'USER': 'root',
'PASSWORD': 'root'
}
}7.2 models.py中建立模型表,并同步至数据库
from django.db import models
class Car(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=255)
summary = models.CharField(max_length=255)
img_url = models.CharField(max_length=255, null=True)
tags = models.CharField(max_length=255)
a_url = models.CharField(max_length=255)
随后执行数据库迁移命令
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate7.3 新建一个spider.py文件,配置django环境,爬取数据
#!/usr/bin/env python
import os
if __name__ == "__main__":
os.environ.setdefault("DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE", "review_django.settings")
import django
django.setup()
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
from app01 import models
def work(k):
response = requests.get(url='https://www.autohome.com.cn/all/{}/#liststart'.format(k))
response.encoding = 'GBK'
soup_obj = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
div_obj = soup_obj.find(name='div', attrs={"id": "auto-channel-lazyload-article"})
li_list = div_obj.find_all(name='li')
for i in li_list:
no_obj = i.find(name='h3')
if not no_obj: continue
title = i.find(name='h3').text
summary = i.find(name='p').text
a = 'https:' + i.find(name='a').get('href')
img = 'https:' + i.find(name='img').get('src')
tags = a.split('/', 4)[3]
print(response.url, title, tags)
print(summary, img)
models.Car.objects.create(
title=title,
summary=summary,
tags=tags,
img_url=img,
a_url=a
)
def spider():
t = ThreadPoolExecutor(10)
for k in range(1, 60):
t.submit(work, k)
t.shutdown()
spider()
7.4 urls.py中配置路由
from django.conf.urls import url
from app01 import views
urlpatterns = [
# 用于简单显示一个页面,同时展示用户搜索的内容
url(r'index', views.index),
# 将数据库数据写入es
url(r'es', views.es2)
]7.5 views.py中视图函数
from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse
from django.http import JsonResponse
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
from elasticsearch import helpers
from app01 import models
# 实例化一个ES对象
es = Elasticsearch()
# Create your views here.
def filter(search_msg):
body = {
"size": 100, # 返回一百条数据
"query": {
"match": {
"title": search_msg # 从标题中查找输入的关键字
}
},
"highlight": { # 内容高亮显示,使用pre_tags与post_tags定义标签,默认是em标签
"pre_tags": "<b style='color:red;font-size:24px'>",
"post_tags": "</b>",
"fields": {
"title": {} # 将标题高亮显示
}
},
}
# 存储es搜索的结果
res = es.search(index='s18', body=body)
# print(res)
return res
def index(request):
if request.method == "POST":
search_msg = request.POST.get('search_msg')
res = filter(search_msg)
# 将es搜索的结果返回
return JsonResponse(res)
return render(request, 'search.html', locals())
def es2(request):
body = {
"mappings": {
"doc": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text"
},
"summary": {
"type": "text"
},
"a_url": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"img_url": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"tags": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
}
# es.indices.create(index='s18', body=body)
# print(es.indices.get_mapping())
query_list = models.Car.objects.all()
# 定义写入es的数据格式,使用生成器,减轻内存压力
action = ({
"_index": "s18", # 索引,相当于指定数据库,不存在则创建
"_type": "doc", # 类型,相当于指定表,不存在则创建
"_source": { # 指定要写入的内容
"title": i.title,
"summary": i.summary,
"a_url": i.a_url,
"img_url": i.img_url,
"tags": i.tags
}
}
for i in query_list
)
# helpers会使用java虚拟机帮我们进行该任务
helpers.bulk(es, action)
return HttpResponse('ok es')
7.6 templates文件下写的search.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.4.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/twitter-bootstrap/3.4.1/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
<link href="https://cdn.bootcss.com/twitter-bootstrap/3.4.1/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<nav class="navbar navbar-default">
<div class="container-fluid">
<!-- Brand and toggle get grouped for better mobile display -->
<div class="navbar-header">
<button type="button" class="navbar-toggle collapsed" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#bs-example-navbar-collapse-1" aria-expanded="false">
<span class="sr-only">Toggle navigation</span>
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
</button>
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Brand</a>
</div>
<!-- Collect the nav links, forms, and other content for toggling -->
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="bs-example-navbar-collapse-1">
<ul class="nav navbar-nav">
<li class="active"><a href="#">Link <span class="sr-only">(current)</span></a></li>
<li><a href="#">Link</a></li>
<li class="dropdown">
<a href="#" class="dropdown-toggle" data-toggle="dropdown" role="button" aria-haspopup="true" aria-expanded="false">Dropdown <span class="caret"></span></a>
<ul class="dropdown-menu">
<li><a href="#">Action</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Another action</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Something else here</a></li>
<li role="separator" class="divider"></li>
<li><a href="#">Separated link</a></li>
<li role="separator" class="divider"></li>
<li><a href="#">One more separated link</a></li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
{# 搜索框 #}
<form class="navbar-form navbar-left">
<div class="form-group">
<input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="Search" oninput="foo()" id="search">
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-default">Submit</button>
<span id="totalNum"></span>
</form>
<ul class="nav navbar-nav navbar-right">
<li><a href="#">Link</a></li>
<li class="dropdown">
<a href="#" class="dropdown-toggle" data-toggle="dropdown" role="button" aria-haspopup="true" aria-expanded="false">Dropdown <span class="caret"></span></a>
<ul class="dropdown-menu">
<li><a href="#">Action</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Another action</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Something else here</a></li>
<li role="separator" class="divider"></li>
<li><a href="#">Separated link</a></li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</div><!-- /.navbar-collapse -->
</div><!-- /.container-fluid -->
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-8 col-lg-offset-2">
<div id="showData"></div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</nav>
</body>
<script>
//搜索
function foo() {
var searchMsg = $('#search').val();
console.log(searchMsg);
$.ajax({
url:"/app01/index",
type: "post",
data: {'search_msg': searchMsg},
success:function (data) {
console.log(data);
if (data){
//展示结果条数
$("#totalNum").html("结果约<b style='color:red'>" + data.hits.total + "<b>")
//结果展示
var html = '';
$.each(data.hits.hits, function (index, item) {
//console.log(item._source.title)
html += "<a href='+ item.a_url +'>\n" +
" <div class=\"article-pic\"></div>\n" +
" <h3>"+item.highlight.title+"</h3>\n" +
" <div class=\"article-bar\">\n" +
" <span class=\"fn-left\"></span>\n" +
" <span class=\"fn-right\">\n" +
" <em><i class=\"icon12 icon12-eye\"></i></em>\n" +
" <em data-class=\"icon12 icon12-infor\" data-articleid=\"945066\"><i class=\"icon12 icon12-infor\"></i>13</em>\n" +
" </span>\n" +
" </div>\n" +
" <p>"+item._source.summary+"</p>\n" +
" </a>";
$("#showData").html(html)
})
}
}
})
}
</script>
</html>

