交点问题
交点问题
一、写前预测和实际花费和项目信息
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 60 | 90 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 10 | 10 |
| Development | 开发 | 60 | 90 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 30 | 60 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 10 | 20 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 0 | 0 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 10 | 10 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 60 | 60 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 120 | 240 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 30 | 20 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 180 | 180 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 30 | 30 |
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 30 | 30 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 20 | 20 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 20 | 20 |
| 合计 | 670 | 880 |
项目信息
-
教学班级:005
二、解题思路描述。即刚开始拿到题目后,如何思考,如何找资料的过程。
思路:
①列出数学公式(计算焦点的公式);
②由于要限制程序的执行时间,计算出新的交点时顺序遍历所有交点肯定是最差解,然后最符合我的思考的是hashmap数据结构,但是因为自己过去三年没怎么了解C++,加上找的资料网站不太行,原理没有弄明白,最后还是选择了红黑树原理的map结构;
③因为计算包括线和线、线和圆、圆和线交点,所以要分为三种情况,并且要建立两个数据结构来储存线和圆的信息;
④建立新的数据结构储存点的信息;
④利用map的特性去除重复点;
⑥将点的个数输出到目的文件;
寻找资料:
因为自己之前主要用C和JAVA所以对c++很陌生,这个学期准备好好练一练,主要在菜鸟网站看c++的基础。复杂一些的知识主要靠csdn和博客园的文章。比如关于c++的hashmap、map,以及数据类型转换的知识,都是百度之后找文章仔细看的。
四、设计实现过程。设计包括代码如何组织,比如会有几个类,几个函数,他们之间关系如何,关键函数是否需要画出流程图?单元测试是怎么设计的?
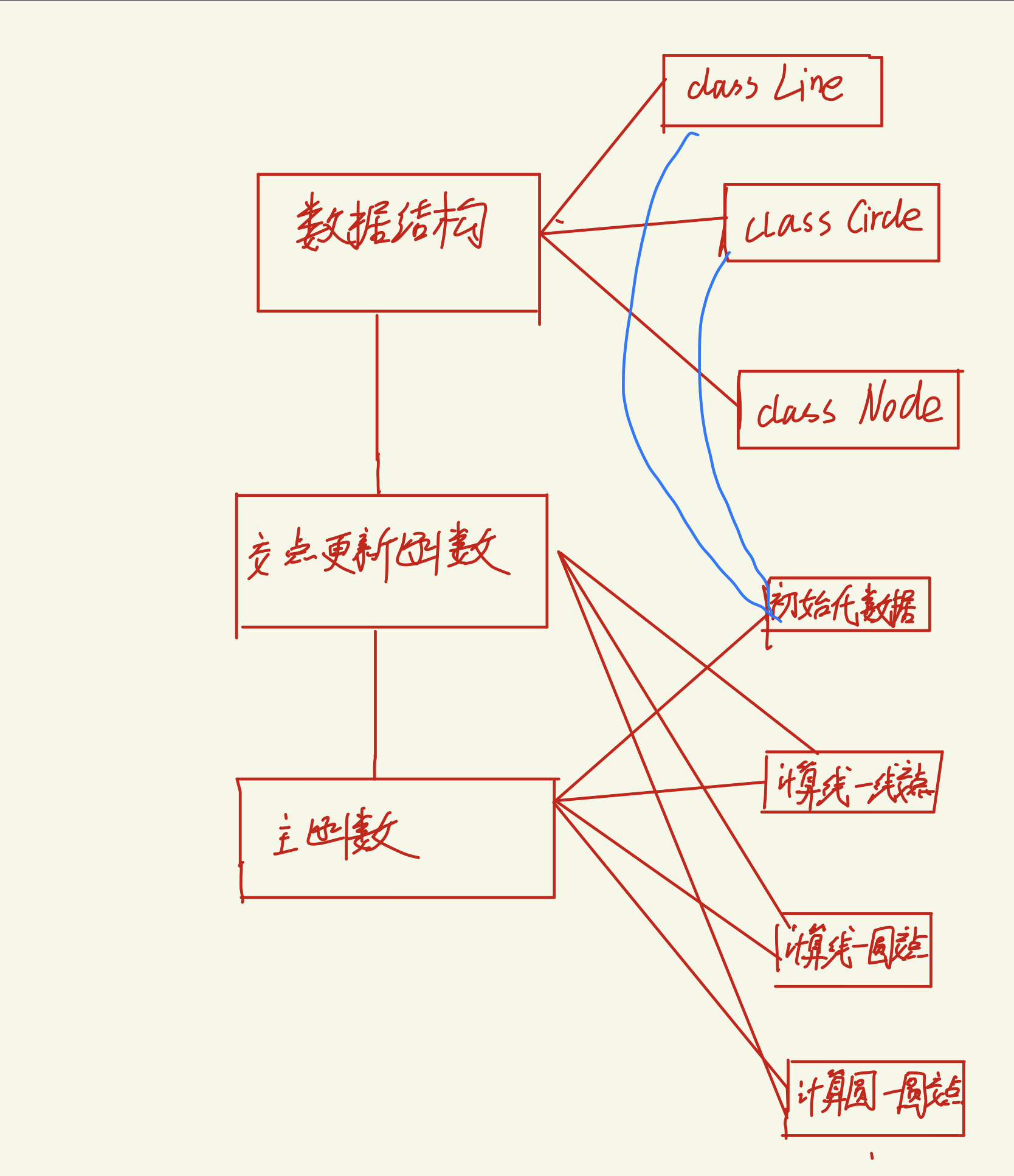
这就是我的程序各个部分之间的关系。
五、记录在改进程序性能上所花费的时间,描述你改进的思路,并展示一张性能分析图(由 VS 2019 的性能分析工具自动生成),并展示你程序中消耗最大的函数。
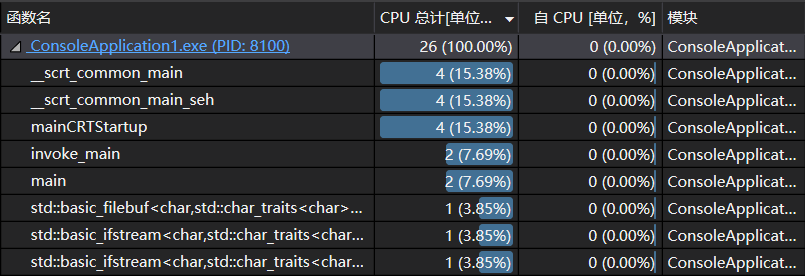
我在改进程序上面花费了一个小时的时间,减少了线和线、线和圆、圆和圆的重复计算。
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
string input;
string output;
string buffer;
char type;
double x1, y1, x2, y2, x, y, r;
int count = 0;
Node node;
list<line> L1;
list <line>::iterator L1_iter;
list<circle> L2;
list<circle>::iterator L2_iter;
map<double, map<double, Node>> Nodemap;
input = argv[2];
output = argv[4];
ifstream infile;
infile.open(input);
ofstream outfile;
outfile.open(output);
if (infile.eof() || outfile.eof()) {
cout << "Open file failed" << endl;
}
getline(infile, buffer);
int n = stoi(buffer);
int i = 0;
while (i < n) {
getline(infile, buffer);
if (buffer[0] == 'C') {
if (sscanf(buffer.c_str(), "%c %lf %lf %lf", &type, &x, &y, &r) == NULL) {
return 0;
}
circle cir(x,y,r);
L2.push_back(cir);
}
else {
if (sscanf(buffer.c_str(), "%c %lf %lf %lf %lf", &type, &x1, &y1, &x2, &y2) == NULL) {
return 0;
}
line li(x1, y1, x2, y2);
L1.push_back(li);
}
i++;
}
for (L1_iter = L1.begin(); L1_iter != L1.end(); L1_iter++) {///line with line
list <line>::iterator temp = L1_iter;
for (++temp; temp != L1.end(); temp++) {
if (temp == L1.end()) {
break;
}
if ((*L1_iter).i == 0 && (*temp).i == 0) {
if ((*L1_iter).a == (*temp).a) {
continue;
}
x = ((*L1_iter).b - (*temp).b) / ((*temp).a - (*L1_iter).a);
y = (*L1_iter).a * x + (*L1_iter).b;
}
else if ((*L1_iter).i == 1 && (*temp).i == 0) {
x = (*L1_iter).a;
y = (*temp).a * x + (*temp).b;
}
else if ((*L1_iter).i == 0 && (*temp).i == 1) {
x = (*temp).a;
y = (*L1_iter).a * x + (*L1_iter).b;
}
else {
continue;
}
node.setx(x);
node.sety(y);
count = update(node, &Nodemap) + count;
}
}
double a, b, c_x, c_y;
for (L1_iter = L1.begin(); L1_iter != L1.end(); L1_iter++) {//////line and circle
a = (*L1_iter).a;
b = (*L1_iter).b;
i = (*L1_iter).i;
for (L2_iter = L2.begin(); L2_iter != L2.end(); L2_iter++) {
c_x = (*L2_iter).x;
c_y = (*L2_iter).y;
r = (*L2_iter).r;
if (i == 1) {
double temp = pow(r, 2) - pow(a - c_x, 2);
if (temp < 0) {
continue;
}
else if (temp == 0) {
x = a;
y = c_y;
}
else {
x = a;
y = sqrt(temp) + c_y;
//////update
node.setx(x);
node.sety(y);
count = update(node, &Nodemap) + count;
y = -sqrt(temp) + c_y;
//////update
node.setx(x);
node.sety(y);
count = update(node, &Nodemap) + count;
}
}
else {
double temp1 = 1 + pow(a,2);
double temp2 = 2 * a * (b - c_y) - 2 * c_x;
double temp3 = pow(b - c_y, 2) + pow(c_x, 2) - pow(r, 2);
double delt = pow(temp2, 2) - 4 * temp1 * temp3;
if (delt < 0) {
continue;
}
else if (delt == 0) {
x = -temp2 / (2 * temp1);
y = a * x + b;
node.setx(x);
node.sety(y);
count = update(node, &Nodemap) + count;
}
else {
x = (-temp2 + sqrt(delt)) / (2 * temp1);
y = a * x + b;
/////update;
node.setx(x);
node.sety(y);
count = update(node, &Nodemap) + count;
x = (-temp2 - sqrt(delt)) / (2 * temp1);
y = a * x + b;
/////update;
node.setx(x);
node.sety(y);
count = update(node, &Nodemap) + count;
}
}
}
}
double r1, r2,c;
for (L2_iter = L2.begin(); L2_iter != L2.end(); L2_iter++) {///circle with circle
x1 = (*L2_iter).x;
y1 = (*L2_iter).y;
r1 = (*L2_iter).r;
list <circle>::iterator temp = L2_iter;
for (++temp; temp != L2.end(); temp++) {
if (temp == L2.end()) {
break;
}
x2 = (*temp).x;
y2 = (*temp).y;
r2 = (*temp).r;
a = 2 * (x1 - x2);
b = 2 * (y1 - y2);
c = pow(x2, 2) - pow(x1, 2) + pow(y2, 2) - pow(y1, 2) + pow(r1, 2) - pow(r2, 2);
if (x1 == x2 && y1 == y2) {//same center
continue;
}
else if ((fabs(a*x1+b*y1+c)/sqrt(pow(a,2)+pow(b,2))) > r1 ||
(fabs(a * x2 + b * y2 + c) / sqrt(pow(a, 2) + pow(b, 2))) > r2){
continue;
}
else {
if (b == 0) {
x = -c / a;
y = y1 + sqrt(pow(r1, 2) - pow(x - x1, 2));
/////update
node.setx(x);
node.sety(y);
count = update(node, &Nodemap) + count;
y = y2 + sqrt(pow(r1, 2) - pow(x - x1, 2));
/////update
node.setx(x);
node.sety(y);
count = update(node, &Nodemap) + count;
}
else {
a = -a / b;
b = -c / b;
double temp1 = 1 + pow(a, 2);
double temp2 = 2 * a * (b - y1) - 2 * x1;
double temp3 = pow(b - y1, 2) + pow(x1, 2) - pow(r1, 2);
double delt = pow(temp2, 2) - 4 * temp1 * temp3;
if (delt < 0) {
continue;
}
else if (delt == 0) {
x = -temp2 / (2 * temp1);
y = a * x + b;
}
else {
x = (-temp2 + sqrt(delt)) / (2 * temp1);
y = a * x + b;
/////update;
node.setx(x);
node.sety(y);
count = update(node, &Nodemap) + count;
x = (-temp2 - sqrt(delt)) / (2 * temp1);
y = a * x + b;
/////update;
node.setx(x);
node.sety(y);
count = update(node, &Nodemap) + count;
}
}
}
}
}
outfile << count;
infile.close();
outfile.close();
}
因为计算交点的三个循环都在main()函数之中,所以cpu占用这段函数最高。
六、 代码说明。展示出项目关键代码,并解释思路与注释说明。
更新交点
int update(Node node, map<double, map<double, Node>> *Nodemap) {
if ((*Nodemap).count(node.getx()) == 0) {
map<double, Node> temp;
temp.insert(pair<double, Node>(node.gety(),node));///mapStudent.insert(pair<int, string>(000, "student_zero"));
(*Nodemap).insert(pair<double, map<double, Node>>(node.getx(), temp));
return 1;
}
else {
map<double, Node> temp = (*Nodemap)[node.getx()];
if (temp.count(node.gety()) == 0) {
temp[node.gety()] = node;
(*Nodemap)[node.getx()] = temp;
return 1;
}
else {
return 0;
}
}
return 0;
}
map<double, map<double, Node>> *Nodemap
我采用了Map的结构,外层map的key为交点x值,第二个Map的key为节点y值,借此来储存交点。
如果Nodemap的key无value,则插入交点,更新,函数返回1,
否则,根据key确定内层的map,将交点的y值作为新的key更新。
七、测试
主要通过写测试样例进行测试,一共测试了线与线相交(四种情况)、线与线平行(三种情况)、线与圆相交(六种情况)、线与圆无交点(三种情况)、圆与圆相交(两种情况)和圆与圆不相交(三种情况)。测试样例大多上传到了GitHub上。
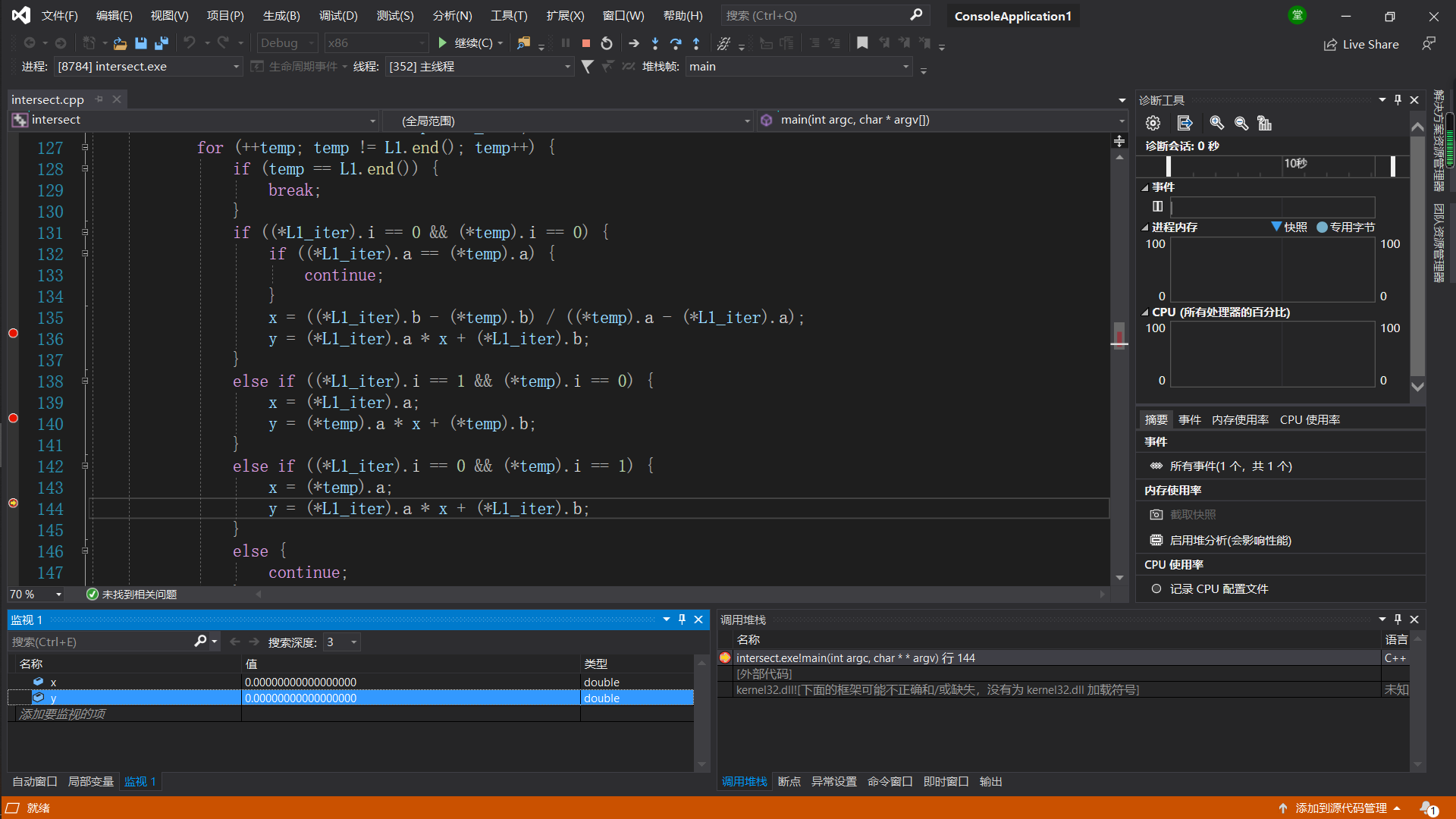
具体操作主要是设置断点来在检测窗口观测计算的点是否和预测一致。测试方法比较原始,但是是我比较熟悉的方式。