<一>接口测试:requests库的常用方法和鉴权
好用的接口https://api.oioweb.cn/
requests库的常用方法
requests是python的第三方库
pip3 install requests
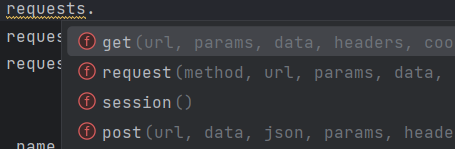
常用的6种方法:
def requests.post(url, data=None, json=None, **kwargs) 增加, 返回的是response
def requests.delete(url, **kwargs) 删除, 返回的是response
def requests.put(url, data=None, **kwarge) 修改, 返回的是response
def requests.get(url, params=None, **kwargs) 查询, 返回的是response
以上四种.(基于Restful API架构)
def requests.request(method,url, **kwargs), 返回的是response
def requests.session() 获得回话对象
res = requests.put()
备注: *args和 **kwargs区别
*args 可变长度的元祖 (a,b,c)
**kwargs 可变长度的字典 {a:1,b:2,c:3}
发送get请求
def requests.get(url, params=None, **kwargs)
def get(url, params=None, **kwargs): r"""Sends a GET request. :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. :param params: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples or bytes to send in the query string for the :class:`Request`. :param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes. :return: :class:`Response <Response>` object :rtype: requests.Response """ return request("get", url, params=params, **kwargs)
发送post请求
def requests.post(url, data=None, json=None, **kwargs)
def post(url, data=None, json=None, **kwargs): r"""Sends a POST request. :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. :param data: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples, bytes, or file-like object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`. :param json: (optional) A JSON serializable Python object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`. :param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes. :return: :class:`Response <Response>` object :rtype: requests.Response """ return request("post", url, data=data, json=json, **kwargs)
发送put请求
def requests.put(url, data=None, **kwarge)
def put(url, data=None, **kwargs): r"""Sends a PUT request. :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. :param data: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples, bytes, or file-like object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`. :param json: (optional) A JSON serializable Python object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`. :param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes. :return: :class:`Response <Response>` object :rtype: requests.Response """ return request("put", url, data=data, **kwargs)
发送delete请求
def requests.delete(url, **kwargs)
def delete(url, **kwargs): r"""Sends a DELETE request. :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. :param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes. :return: :class:`Response <Response>` object :rtype: requests.Response """ return request("delete", url, **kwargs)
---------------------前面四种方法都调用下面request方法-------------------
根据method传参的请求方式发送请求
def requests.request(method,url, **kwargs)
def request(method, url, **kwargs): """Constructs and sends a :class:`Request <Request>`. :param method: method for the new :class:`Request` object: ``GET``, ``OPTIONS``, ``HEAD``, ``POST``, ``PUT``, ``PATCH``, or ``DELETE``. :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object. :param params: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples or bytes to send in the query string for the :class:`Request`. :param data: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples, bytes, or file-like object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`. :param json: (optional) A JSON serializable Python object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`. :param headers: (optional) Dictionary of HTTP Headers to send with the :class:`Request`. :param cookies: (optional) Dict or CookieJar object to send with the :class:`Request`. :param files: (optional) Dictionary of ``'name': file-like-objects`` (or ``{'name': file-tuple}``) for multipart encoding upload. ``file-tuple`` can be a 2-tuple ``('filename', fileobj)``, 3-tuple ``('filename', fileobj, 'content_type')`` or a 4-tuple ``('filename', fileobj, 'content_type', custom_headers)``, where ``'content-type'`` is a string defining the content type of the given file and ``custom_headers`` a dict-like object containing additional headers to add for the file. :param auth: (optional) Auth tuple to enable Basic/Digest/Custom HTTP Auth. :param timeout: (optional) How many seconds to wait for the server to send data before giving up, as a float, or a :ref:`(connect timeout, read timeout) <timeouts>` tuple. :type timeout: float or tuple :param allow_redirects: (optional) Boolean. Enable/disable GET/OPTIONS/POST/PUT/PATCH/DELETE/HEAD redirection. Defaults to ``True``. :type allow_redirects: bool :param proxies: (optional) Dictionary mapping protocol to the URL of the proxy. :param verify: (optional) Either a boolean, in which case it controls whether we verify the server's TLS certificate, or a string, in which case it must be a path to a CA bundle to use. Defaults to ``True``. :param stream: (optional) if ``False``, the response content will be immediately downloaded. :param cert: (optional) if String, path to ssl client cert file (.pem). If Tuple, ('cert', 'key') pair. :return: :class:`Response <Response>` object :rtype: requests.Response Usage:: >>> import requests >>> req = requests.request('GET', 'https://httpbin.org/get') >>> req <Response [200]> """ # By using the 'with' statement we are sure the session is closed, thus we # avoid leaving sockets open which can trigger a ResourceWarning in some # cases, and look like a memory leak in others. with sessions.Session() as session: return session.request(method=method, url=url, **kwargs)
-------------------------上面request调用的是下面session的request()方法---------------------------------
def session.request(self, method, url, **kwargs)
def request( self, method, url, params=None, data=None, headers=None, cookies=None, files=None, auth=None, timeout=None, allow_redirects=True, proxies=None, hooks=None, stream=None, verify=None, cert=None, json=None, ):
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
def session() 获得回话对象
------------------------------------------
各参数意思
method 请求方式
url 请求路径
params get请求传参
data post或put传参
json post请求的第二种方式
(data是表单传参,json是数据传参)
headers 请求头
cookies 请求头里面的coolies信息
file 文件上传
stream 文件下载
response常用方法
对接口响应内容的获取
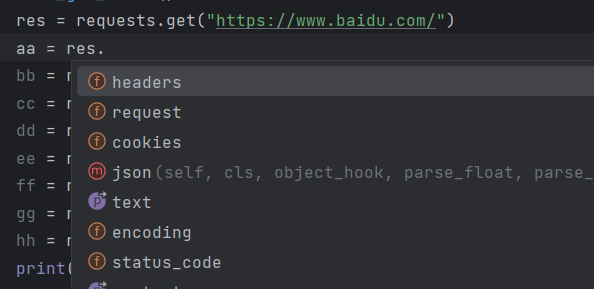
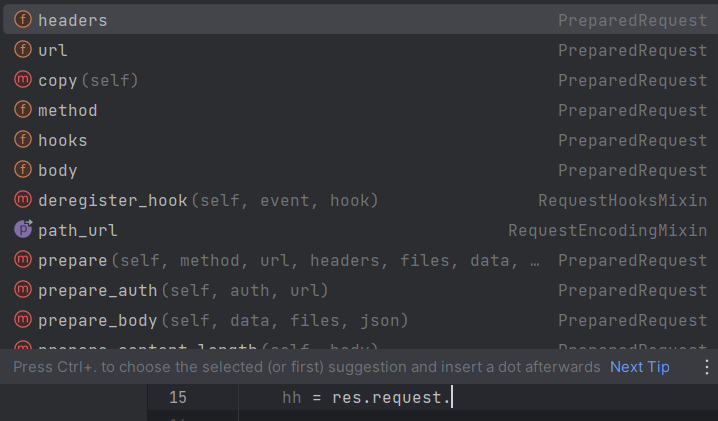
res.text # 返回字符串 res.content # 返回字节数据 res.json() # 返回json数据,python是字典 res.status_code # 返回状态码 res.cookies # 返回响应cookies res.encoding # 返回响应编码 res.headers # 返回响应头 res.request.xxx # 返回请求的一些数据
实战
1.get用例
接口文档https://api.oioweb.cn/doc/qq/info
测试用例:
def test_get_qq(): urls = "https://api.oioweb.cn/api/qq/info" paramas = { "qq": "599928887" } res = requests.get(url=urls, params=paramas) print(res.json())
运行结果:
testcases/test_api.py::test_get_qq {'code': 200, 'result': {'user_id': 599928887, 'nickname': '叾屾', 'sex': 'unknown', 'age': 0, 'area': ''}, 'msg': 'success'}
PASSED
2. post用例(文件上传)
识别图片里的文字,接口文档:https://api.oioweb.cn/doc/ocr

测试用例:
def test_picture_text(): urls = 'https://api.oioweb.cn/api/ocr' datas = { "file": open(f"C://study//aa.jpg", "rb") } res = requests.post(url=urls, files=datas) print(res.json())
运行结果:
testcases/test_api.py::test_picture_text {'code': 200, 'result': [':', '自由', '心自由', '生活就自由', '到哪都有快乐'], 'msg': 'success'}
PASSED
==========================================================================
因为session自带cookie,所以建议使用session进行编写,上面的例子可以写成下面这样:
class TestApi: sess = requests.session() def test_get_qq(self): urls = "https://api.oioweb.cn/api/qq/info" paramas = { "qq": "599928887" } res = TestApi.sess.request(method="get", url=urls, params=paramas) # res = requests.get(url=urls, params=paramas) print(res.json()) def test_picture_text(self): urls = 'https://api.oioweb.cn/api/ocr' datas = { "file": open(f"C://study//aaa.jpg", "rb") } res = TestApi.sess.request(method="post", url=urls, files=datas) # res = requests.post(url=urls, files=datas) print(res.json()) if __name__ == '__main__': pytest.main('-vs')
运行结果:
collected 2 items testcases/test_api.py::TestApi::test_get_qq {'code': 200, 'result': {'user_id': 599928887, 'nickname': '叾屾', 'sex': 'unknown', 'age': 0, 'area': ''}, 'msg': 's uccess'} PASSED testcases/test_api.py::TestApi::test_picture_text {'code': 200, 'result': [':', '自由', '心自由', '生活就自由', '到哪都有快乐'], 'msg': 'success'} PASSED
在Postman里的区别
get请求通过params传参
post请求通过data和json传参
下图是postman中的post的传参选择:
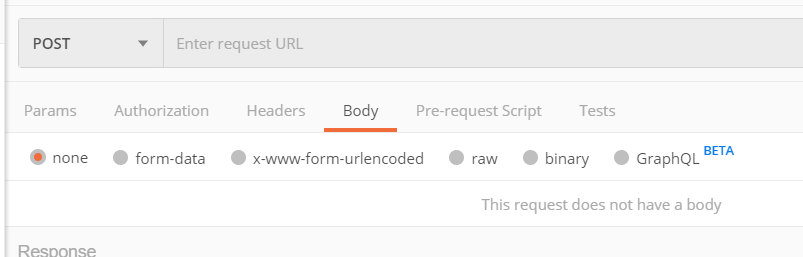
form-data: files,文件上传.data
x-www-form-urlencoded: data(表单)
文本raw传参: 除了json用json传参外,其他都是data(application/json)
二进制binary: application/octrent-stream, data
鉴权:(cookie鉴权、 session鉴权和 token鉴权)
鉴权:鉴定是否有访问接口的权限
session和token都可以通过cookie传输。
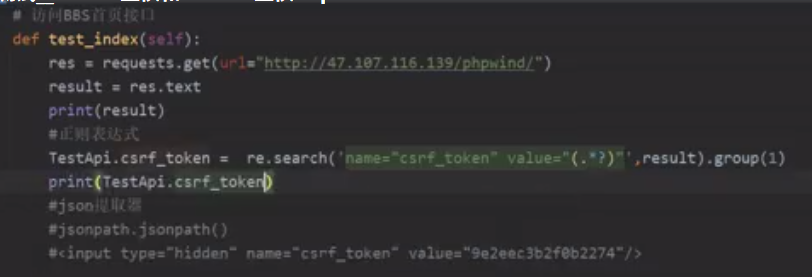
正则表达式:提取文本数据
Json提取器:提取json的数据
比如要提取下面的value值
例子:<input type="hidden" name="csrf_token" value="9e2eec3b2f0b2274">
import re # 正则表达式 re.search('name="csrf_token" value="(.*?)"', result).group(1)
==============================
session的好处:
requests.post(url)
和
requests.session().request(method='post',url)
上面两者效果是一样的,但是用session会让cookies自动关联,如果需要cookies时,就不需要再次传一次cookies。
所以在做接口时,用session效果会更好



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号