linux下wrk的安装
wrk是linux下开源的性能测试工具,并且只能在linux下运行,下面介绍下安装教程(以ubantu18.04环境为例):
1.预先安装git,如:apt install git
2.从git上拉取wrk:git clone https://github.com/wg/wrk.git wrk
3.cd wrk
4.apt-get install build-essential -y
5.make
6.把生成的 wrk 移到一个 PATH 目录下面, 比如 : sudo cp wrk /usr/local/bin
注意编译的时间可能比较长,耐心等待即可
CentOs/RedHat/Fedora 下的安装:
-
sudo yum groupinstall 'Development Tools'
-
sudo yum install openssl-devel
-
sudo yum install git
-
git clone https://github.com/wg/wrk.git wrk
-
cd wrk
-
make
-
# 把生成的 wrk 移到一个 PATH 目录下面, 比如
-
sudo cp wrk /usr/local/bin
mac 下快捷安装:
brew install wrk
基本使用:
wrk -t12 -c400 -d30s http://127.0.0.1:8080/index.html
使用 12 个线程运行 30 秒, 400 个 http 并发
命令行选项
-
使用方法: wrk <选项> <被测HTTP服务的URL>
-
Options:
-
-c, --connections <N> 跟服务器建立并保持的 TCP 连接数量
-
-d, --duration <T> 压测时间
-
-t, --threads <N> 使用多少个线程进行压测
-
-s, --script <S> 指定 Lua 脚本路径
-
-H, --header <H> 为每一个 HTTP 请求添加 HTTP 头
-
--latency 在压测结束后,打印延迟统计信息
-
--timeout <T> 超时时间
-
-v, --version 打印正在使用的 wrk 的详细版本信息
-
-
<N>代表数字参数,支持国际单位 (1k, 1M, 1G)
-
<T>代表时间参数,支持时间单位 (2s, 2m, 2h)
做一次简单压测,分析下结果:
-
wrk -t8 -c200 -d30s --latency "http://www.bing.com"
-
-
输出:
-
Running 30s test @ http://www.bing.com
-
8 threads and 200 connections
-
Thread Stats Avg Stdev Max +/- Stdev
-
Latency 46.67ms 215.38ms 1.67s 95.59%
-
Req/Sec 7.91k 1.15k 10.26k 70.77%
-
Latency Distribution
-
50% 2.93ms
-
75% 3.78ms
-
90% 4.73ms
-
99% 1.35s
-
1790465 requests in 30.01s, 684.08MB read
-
Requests/sec: 59658.29
-
Transfer/sec: 22.79MB
以上使用 8 个线程 200 个连接,对 bing 首页进行了 30 秒的压测,并要求在压测结果中输出响应延迟信息。以下对压测结果进行简单注释:
-
Running 30s test @ http://www.bing.com (压测时间30s)
-
8 threads and 200 connections (共8个测试线程,200个连接)
-
Thread Stats Avg Stdev Max +/- Stdev
-
(平均值) (标准差)(最大值)(正负一个标准差所占比例)
-
Latency 46.67ms 215.38ms 1.67s 95.59%
-
(延迟)
-
Req/Sec 7.91k 1.15k 10.26k 70.77%
-
(处理中的请求数)
-
Latency Distribution (延迟分布)
-
50% 2.93ms
-
75% 3.78ms
-
90% 4.73ms
-
99% 1.35s (99分位的延迟)
-
1790465 requests in 30.01s, 684.08MB read (30.01秒内共处理完成了1790465个请求,读取了684.08MB数据)
-
Requests/sec: 59658.29 (平均每秒处理完成59658.29个请求)
-
Transfer/sec: 22.79MB (平均每秒读取数据22.79MB)
可以看到,wrk 使用方便,结果清晰。并且因为非阻塞 IO 的使用,可以在普通的测试机上创建出大量的连接,从而达到较好的压测效果。
lua脚本压测
在基本压测中, 每次发送的请求都是一样的,很多时候我们压测的请求体是每个请求都不一样, 这时候就要写lua基本来压测
使用 POST 方法压测
-
wrk.method = "POST"
-
wrk.body = "foo=bar&baz=quux"
-
wrk.headers["Content-Type"] = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"
wrk -t2 -d30s -c1k -s xxx.lua http://192.168.17.1/
每个 request 的参数都不一样
-
request = function()
-
uid = math.random(1, 10000000)
-
path = "/test?uid=" .. uid
-
return wrk.format(nil, path)
-
end
解释一下 wrk.format 这个函数
-
wrk.format 这个函数的作用,根据参数和全局变量 wrk 生成一个 http 请求
-
函数签名: function wrk.format(method, path, headers, body)
-
method:http方法,比如GET/POST等
-
path: url上的路径(含函数)
-
headers: http header
-
body: http body
每个线程先登录然后压测
-
token = nil
-
path = "/authenticate"
-
-
request = function()
-
return wrk.format("GET", path)
-
end
-
-
response = function(status, headers, body)
-
if not token and status == 200 then
-
token = headers["X-Token"]
-
path = "/resource"
-
wrk.headers["X-Token"] = token
-
end
-
end
发送 json
-
request = function()
-
local headers = { }
-
headers['Content-Type'] = "application/json"
-
body = {
-
mobile={"1533899828"},
-
params={code=math.random(1000,9999)}
-
}
-
-
local cjson = require("cjson")
-
body_str = cjson.encode(body)
-
return wrk.format('POST', nil, headers, body_str)
-
end
若运行的时候报错找不到cjson, 可以安装 luarocks install lua-cjson
wrk lua脚本说明
wrk 压测脚本有3个生命周期, 分别是 启动阶段,运行阶段和结束阶段,每个线程都有自己的lua运行环境
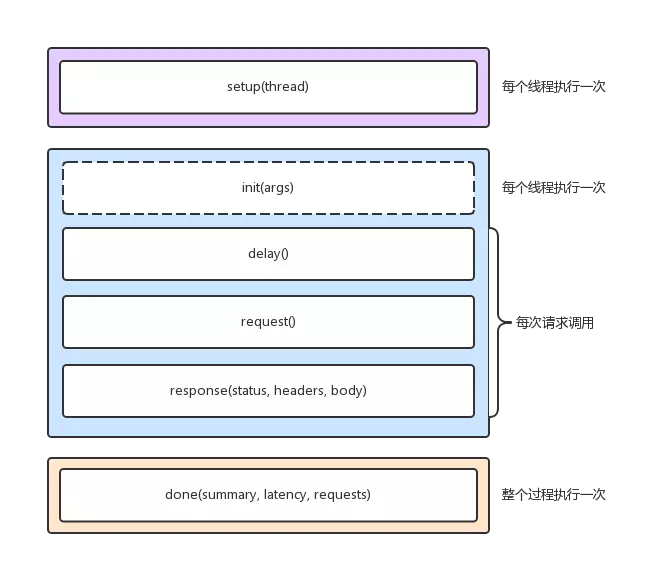
启动阶段
-
function setup(thread)
-
在脚本文件中实现setup方法,wrk就会在测试线程已经初始化但还没有启动的时候调用该方法。wrk会为每一个测试线程调用一次setup方法,并传入代表测试线程的对象thread作为参数。setup方法中可操作该thread对象,获取信息、存储信息、甚至关闭该线程。
-
-- thread提供了1个属性,3个方法
-
-- thread.addr 设置请求需要打到的ip
-
-- thread:get(name) 获取线程全局变量
-
-- thread:set(name, value) 设置线程全局变量
-
-- thread:stop() 终止线程
运行阶段
-
function init(args)
-
-- 每个线程仅调用1次,args 用于获取命令行中传入的参数, 例如 --env=pre
-
-
function delay()
-
-- 每次请求调用1次,发送下一个请求之前的延迟, 单位为ms
-
-
function request()
-
-- 每次请求调用1次,返回http请求
-
-
function response(status, headers, body)
-
-- 每次请求调用1次,返回 http 响应
init由测试线程调用,只会在进入运行阶段时,调用一次。支持从启动wrk的命令中,获取命令行参数;
delay在每次发送request之前调用,如果需要delay,那么delay相应时间; request用来生成请求;
每一次请求都会调用该方法,所以注意不要在该方法中做耗时的操作; reponse在每次收到一个响应时调用;
为提升性能,如果没有定义该方法,那么wrk不会解析headers和body; 结束阶段
结束阶段
-
function done(summary, latency, requests)
-
-
latency.min -- minimum value seen
-
latency.max -- maximum value seen
-
latency.mean -- average value seen
-
latency.stdev -- standard deviation
-
latency:percentile(99.0) -- 99th percentile value
-
latency(i) -- raw value and count
-
-
summary = {
-
duration = N, -- run duration in microseconds
-
requests = N, -- total completed requests
-
bytes = N, -- total bytes received
-
errors = {
-
connect = N, -- total socket connection errors
-
read = N, -- total socket read errors
-
write = N, -- total socket write errors
-
status = N, -- total HTTP status codes > 399
-
timeout = N -- total request timeouts
-
}
-
}
该方法在整个测试过程中只会调用一次,可从参数给定的对象中,获取压测结果,生成定制化的测试报告。
线程变量
-
wrk = {
-
scheme = "http",
-
host = "localhost",
-
port = nil,
-
method = "GET",
-
path = "/",
-
headers = {},
-
body = nil,
-
thread = <userdata>,
-
}
-
-
-- 生成整个request的string,例如:返回
-
-- GET / HTTP/1.1
-
-- Host: tool.lu
-
function wrk.format(method, path, headers, body)
-
-- method: http方法, 如GET/POST/DELETE 等
-
-- path: url的路径, 如 /index, /index?a=b&c=d
-
-- headers: 一个header的table
-
-- body: 一个http body, 字符串类型
-
-
-- 获取域名的IP和端口,返回table,例如:返回 `{127.0.0.1:80}`
-
function wrk.lookup(host, service)
-
-- host:一个主机名或者地址串(IPv4的点分十进制串或者IPv6的16进制串)
-
-- service:服务名可以是十进制的端口号,也可以是已定义的服务名称,如ftp、http等
-
-
-- 判断addr是否能连接,例如:`127.0.0.1:80`,返回 true 或 false
-
function wrk.connect(addr)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号