排序算法
一、总纲
常见排序算法:冒泡排序(Bubble Sort)、选择排序(Selection Sort)、插入排序(Insertion Sort)、快速排序(Quick Sort)、归并排序(Merge Sort)、堆排序(Heap Sort)、希尔排序(Shell Sort)、计数排序(Counting Sort)、桶排序(Bucket Sort)、基数排序(Radix Sort)
按照算法的特点可以归类为插入排序、选择排序、交换排序。
时间复杂度:常数阶O(1),对数阶O(log2n),线性阶O(n), 线性对数阶O(nlog2n),平方阶O(n2),立方阶O(n3),..., k次方阶O(nk),指数阶O(2n)。可以参考👉🏻https://blog.csdn.net/zolalad/article/details/11848739
空间复杂度:排序过程为了完成排序额外申请的空间;
稳定性:是指值相等的元素在排序过程中是否会交换顺序,如果会交换顺序则为不稳定排序算法;
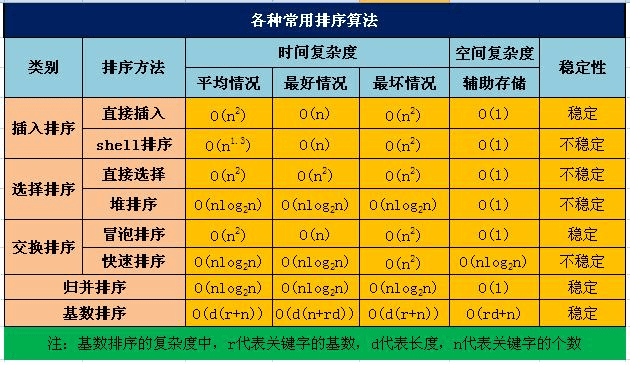
二、算法实现
下面是这几种排序算法的Java测试用例:
1. 冒泡排序(Bubble Sort)
冒泡排序
public class BubbleSort {
public static void sort(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
}
// 测试用例
int[] arr = new int[]{3, 9, 1, 4, 7, 8, 5, 6, 2};
BubbleSort.sort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]2. 选择排序(Selection Sort)
选择排序
public class SelectionSort {
public static void sort(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
if (minIndex != i) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[minIndex];
arr[minIndex] = temp;
}
}
}
}
// 测试用例
int[] arr = new int[]{3, 9, 1, 4, 7, 8, 5, 6, 2};
SelectionSort.sort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]3. 插入排序(Insertion Sort)
插入排序
public class InsertionSort {
public static void sort(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int key = arr[i];
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j--;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
}
// 测试用例
int[] arr = new int[]{3, 9, 1, 4, 7, 8, 5, 6, 2};
InsertionSort.sort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]4. 快速排序(Quick Sort)
快速排序
public class QuickSort {
public static void sort(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
int pivot = partition(arr, low, high);
sort(arr, low, pivot - 1);
sort(arr, pivot + 1, high);
}
}
private static int partition(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
int pivot = arr[high];
int i = low - 1;
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
if (arr[j] < pivot) {
i++;
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
int temp = arr[i + 1];
arr[i + 1] = arr[high];
arr[high] = temp;
return i + 1;
}
}
// 测试用例
int[] arr = new int[]{3, 9, 1, 4, 7, 8, 5, 6, 2};
QuickSort.sort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]5. 归并排序(Merge Sort)
归并排序
public class MergeSort {
public static void sort(int[] arr, int left, int right) {
if (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
sort(arr, left, mid);
sort(arr, mid + 1, right);
merge(arr, left, mid, right);
}
}
private static void merge(int[] arr, int left, int mid, int right) {
int[] temp = new int[right - left + 1];
int i = left, j = mid + 1, k = 0;
while (i <= mid && j <= right) {
if (arr[i] < arr[j]) {
temp[k++] = arr[i++];
} else {
temp[k++] = arr[j++];
}
}
while (i <= mid) {
temp[k++] = arr[i++];
}
while (j <= right) {
temp[k++] = arr[j++];
}
for (int m = 0; m < temp.length; m++) {
arr[left + m] = temp[m];
}
}
}
// 测试用例
int[] arr = new int[]{3, 9, 1, 4, 7, 8, 5, 6, 2};
MergeSort.sort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]6. 堆排序(Heap Sort)
堆排序
public class HeapSort {
public static void sort(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(arr, n, i);
}
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
int temp = arr[0];
arr[0] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
heapify(arr, i, 0);
}
}
private static void heapify(int[] arr, int n, int i) {
int largest = i;
int left = 2 * i + 1;
int right = 2 * i + 2;
if (left < n && arr[left] > arr[largest]) {
largest = left;
}
if (right < n && arr[right] > arr[largest]) {
largest = right;
}
if (largest != i) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[largest];
arr[largest] = temp;
heapify(arr, n, largest);
}
}
}
// 测试用例
int[] arr = new int[]{3, 9, 1, 4, 7, 8, 5, 6, 2};
HeapSort.sort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]7. 希尔排序(Shell Sort)
Shell排序
public class ShellSort {
public static void sort(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
for (int gap = n / 2; gap > 0; gap /= 2) {
for (int i = gap; i < n; i++) {
int temp = arr[i];
int j;
for (j = i; j >= gap && arr[j - gap] > temp; j -= gap) {
arr[j] = arr[j - gap];
}
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}
// 测试用例
int[] arr = new int[]{3, 9, 1, 4, 7, 8, 5, 6, 2};
ShellSort.sort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]8. 计数排序(Counting Sort)
计数排序
public class CountingSort {
public static void sort(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
int max = Arrays.stream(arr).max().getAsInt();
int[] count = new int[max + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
count[arr[i]]++;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= max; i++) {
count[i] += count[i - 1];
}
int[] output = new int[n];
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
output[count[arr[i]] - 1] = arr[i];
count[arr[i]]--;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = output[i];
}
}
}
// 测试用例
int[] arr = new int[]{3, 9, 1, 4, 7, 8, 5, 6, 2};
CountingSort.sort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]9. 桶排序(Bucket Sort)
桶排序
public class BucketSort {
public static void sort(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
int max = Arrays.stream(arr).max().getAsInt();
int[] bucket = new int[max + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
bucket[arr[i]]++;
}
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < bucket[i]; j++) {
arr[index++] = i;
}
}
}
}
// 测试用例
int[] arr = new int[]{3, 9, 1, 4, 7, 8, 5, 6, 2};
BucketSort.sort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]


