【2020牛客多校】2020牛客暑期多校训练营(第二场)I-Interval——最大流转对偶图求最短路
题意
给出一个区间 \([l ,r]\) ,允许进行如下操作:
- 将 \([l, r]\) 转为 \([l - 1, r]\) 或者 \([l + 1, r]\)
- 将 \([l, r]\) 转为 \([l, r - 1]\) 或者 \([l, r + 1]\)
且保证 \(l \leq r \space and \space l > 0 \space r \leq n\)
但是给出了一系列的限制 \(l, r, dir, c\) ,表示当前区间为 \([l, r]\) 时,限制当前的区间不能进行操作 \(1\)(dir = L)或者操作 \(2\) (dir = R),而启用这个限制则需要 \(c\) 的费用
你可以选择是否启用这个限制
询问最少需要花费多少来实现不能将区间 \([1, n]\) 转变为 \(l = r\) 的区间。
分析
从 \(1, n\) 能否转变为 \(l = r\) 可以通过最短路来求算。
但是无法求知当最短路无法到达时(即题目要求的不能转变)最少需要多少的限制条件,而这些条件又是什么。
所以采用最大流来解决
最大流
画出网格图
将所有可以转换的两个状态之间用边连接,如果有提供限制的,将流量限制为费用,如果没有限制的,则设置为 \(INF\)
对于整个矩阵而言,只需要一半的点用于建图,所以将汇点放在另外一半点中。所有 \(l = r\) 的点与汇点连接,而源点为 \([1, n]\)
对于样例可以得到如下图
样例:
3 4
1 3 L 10
1 3 R 3
1 2 L 1
1 2 R 1
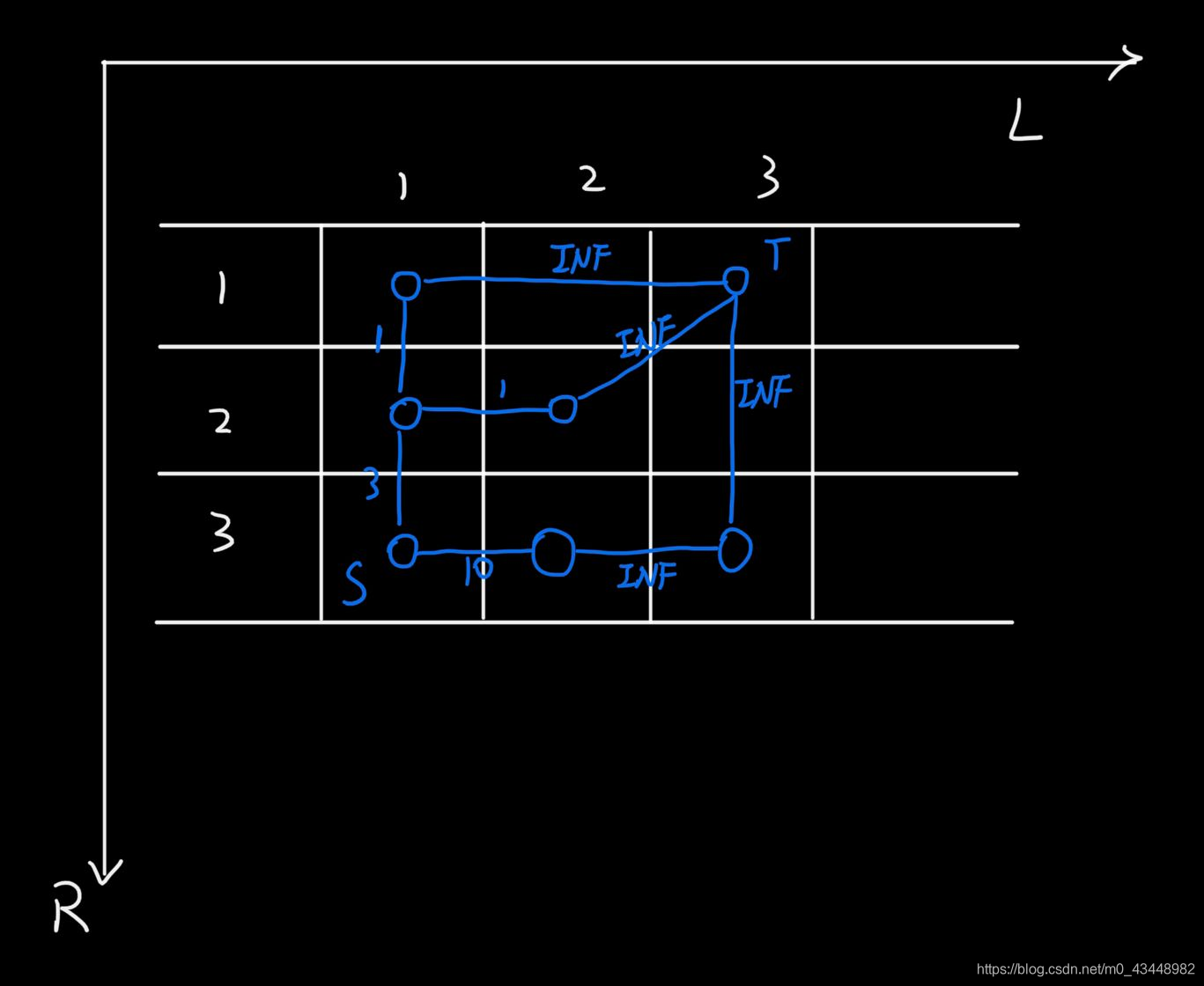
补充,图片漏画了\([2, 3] \rightarrow [2, 2]\)的连线,其流量为 \(INF\)
可以直接通过最大流求出答案
但是会TLE
对偶图
对偶图Wikipedia(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dual_graph)
通过对偶图,可以快速的将一张网格网络图求最大流转为求最短路
关于对偶图的解释请自行查阅资料
在原图上绘制对偶图得到
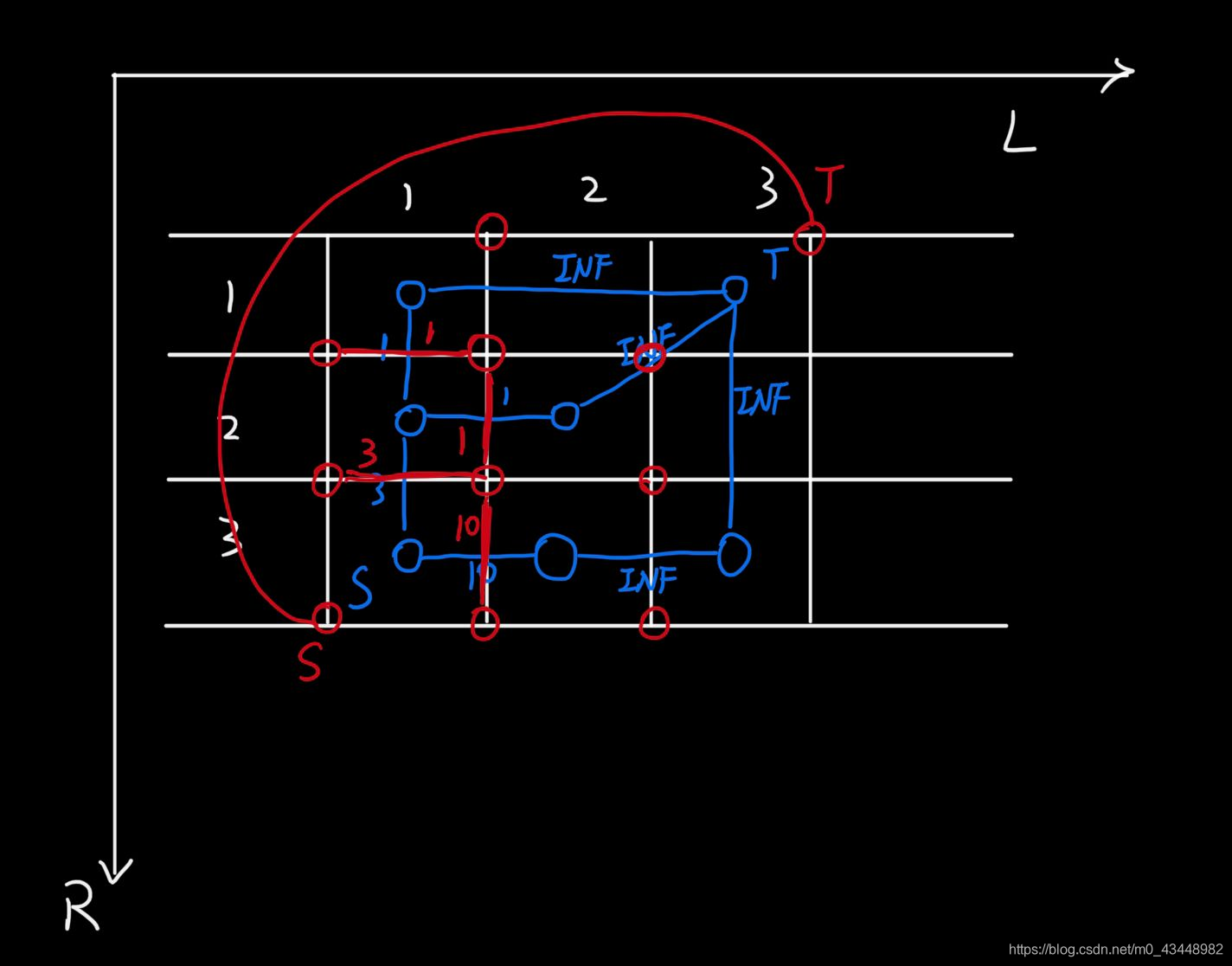
将对偶图中有用的元素将其分离出来得到
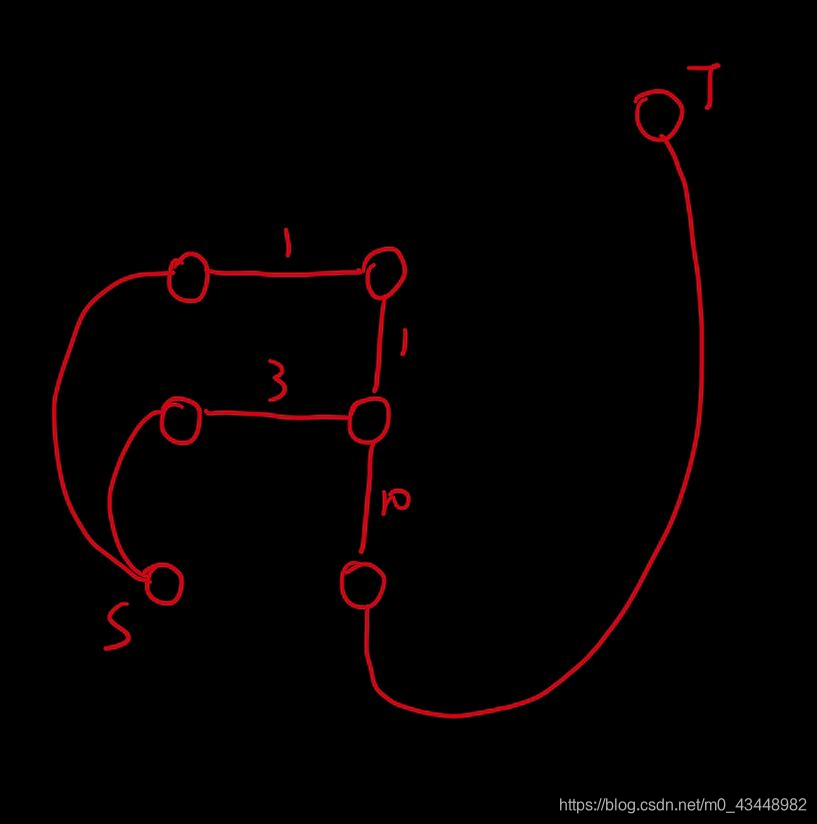
(图中未注明边权的边均为 \(0\))
可以通过最短路快速得到解
AC code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const int maxn = 510;
int n, m;
ll dis[maxn * maxn];
char si;
vector<pair<ll, int>> G[maxn * maxn];
void addedge(int u, int v, int cost) {
G[u].push_back({cost, v});
}
ll dijkstra(int s, int t) {
memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof(dis));
dis[s] = 0;
priority_queue<pair<ll, int>, vector<pair<ll, int>>, greater<pair<ll, int>>> q;
q.push({0ll, s});
while (!q.empty()) {
ll u = q.top().second, c = q.top().first;
q.pop();
if (dis[u] < c)continue;
for (auto i : G[u]) {
ll cc = i.first, v = i.second;
if (dis[v] > dis[u] + cc) {
dis[v] = dis[u] + cc;
q.push({dis[v], v});
}
}
}
return dis[t];
}
inline int id(int x, int y) {
return x * (n + 3) + y;
}
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
int u, v, w;
char c;
cin >> u >> v >> c >> w;
if (c == 'L') {
addedge(id(u, v), id(u, v + 1), w);
addedge(id(u, v + 1), id(u, v), w);
} else {
addedge(id(u, v), id(u - 1, v), w);
addedge(id(u - 1, v), id(u, v), w);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
addedge(id(0, 0), id(0, i), 0);
addedge(id(i, n + 1), id(n + 1, n + 1), 0);
}
dijkstra(id(0, 0), id(n + 1, n + 1));
if (dis[id(n + 1, n + 1)] >= 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f)
cout << -1 << endl;
else
cout << dis[id(n + 1, n + 1)] << endl;
}
signed main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
#ifdef ACM_LOCAL
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
int test_index_for_debug = 1;
char acm_local_for_debug;
while (cin >> acm_local_for_debug) {
if (acm_local_for_debug == '$') exit(0);
cin.putback(acm_local_for_debug);
if (test_index_for_debug > 20) {
throw runtime_error("Check the stdin!!!");
}
auto start_clock_for_debug = clock();
solve();
auto end_clock_for_debug = clock();
cout << "Test " << test_index_for_debug << " successful" << endl;
cerr << "Test " << test_index_for_debug++ << " Run Time: "
<< double(end_clock_for_debug - start_clock_for_debug) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "s" << endl;
cout << "--------------------------------------------------" << endl;
}
#else
solve();
#endif
return 0;
}


