谈原型模式还有JAVA的克隆还有Transient....
本来是只想看下Transient是什么?
Variables may be marked
transient to indicate that they are not part of the persistent state of an object. 即指明变量不是对象的持久化的一部分。
然后想说写段代码看看实际效果吧,怎么持久呢?对象流... 接着就想到Java的克隆方式。
java的克隆方式有两种:
1、 覆写Object的protected的clone方法。
光覆写还是不行的,使用的时候会报错 java.lang.CloneNotSupportedException。
所以需要实现下Cloneable接口,告诉下JVM。
2、 通过对象流转换。
需要对象实现一下java.io.Serializable
想着想着就想起一种叫做Prototype的设计模式。
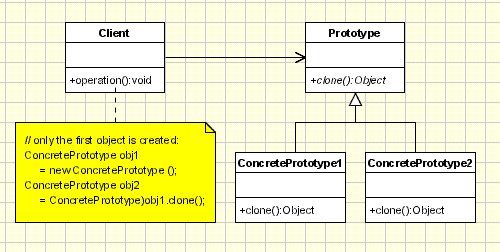
它的定义是:
Specify the kinds of objects to create using a prototypical instance, and create new Object by copying this prototype.
这种模式最主要的使用场景就是低开销的创建一个独立的和原型一模一样的对象。
下面练习代码融合了对原型模式的描述、以及java的两种克隆方法(含深度克隆),还是transient的测试。
prototype角色
public interface Prototype extends Serializable, Cloneable{
public Object cloneByIO();
}
public Object cloneByIO();
}
ConcretePrototype角色
18行起,如果使用浅拷贝。后面打印时,克隆对象的name会随着原型的改变而改变就不独立了。所以类的成员也需要实现原型接口。
66行:由于使用了transient,所以rho,theta为0
1 public class ConcretePrototype implements Prototype{
2 private int x, y;
3 private transient float rho, theta;
4 private Name name;
5
6 public ConcretePrototype(String name ) {
7 x = 1;
8 y = 2;
9 rho =1f;
10 theta = 2f;
11 this.name = new Name(name);;
12 }
13
14 public void changeName(String name){
15 this.name.name = name;
16 }
17
18 public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException{
19 // 浅克隆
20 // return super.clone();
21
22 // 深度克隆
23 ConcretePrototype obj = (ConcretePrototype) super.clone();
24 obj.name = (Name) this.name.clone();
25 return obj;
26 }
27
28 public ConcretePrototype cloneByIO(){
29 ConcretePrototype result = null;
30 //保持到对象流
31 try {
32 ByteArrayOutputStream o = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
33 ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(o);
34 out.writeObject(this);
35 ByteArrayInputStream i = new ByteArrayInputStream(o.toByteArray());
36 ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(i);
37 result = (ConcretePrototype) in.readObject();
38 } catch (IOException e) {
39 e.printStackTrace();
40 }catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
41 e.printStackTrace();
42 }
43 return result;
44 }
45
46 public void println(){
47 System.out.println("name " + name.name +" x = " + x + " y = " + y + " rho = " + rho + " theta = " + theta);
48 }
49
50
51 public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
52 // 测试数据
53 ConcretePrototype originalObj = new ConcretePrototype("original");
54 System.out.println("被克隆对象:");
55 originalObj.println();
56
57 // 使用覆写的克隆方法
58 ConcretePrototype changedObj= (ConcretePrototype) originalObj.clone();
59 // 使用对象流方式的克隆方法
60 ConcretePrototype changedObj2= originalObj.cloneByIO();
61
62 originalObj.changeName("changed");
63 System.out.println("克隆对象:");
64 changedObj.println();
65 System.out.println("对象流克隆对象:");
66 changedObj2.println();
67 }
68
69 }
70
71 class Name implements Prototype {
72 String name = "";
73
74 Name(String name){
75 this.name = name;
76 }
77
78 public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException{
79 return super.clone();
80 }
81
82 @Override
83 public Object cloneByIO() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
84 return null;
85 }
86 }
2 private int x, y;
3 private transient float rho, theta;
4 private Name name;
5
6 public ConcretePrototype(String name ) {
7 x = 1;
8 y = 2;
9 rho =1f;
10 theta = 2f;
11 this.name = new Name(name);;
12 }
13
14 public void changeName(String name){
15 this.name.name = name;
16 }
17
18 public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException{
19 // 浅克隆
20 // return super.clone();
21
22 // 深度克隆
23 ConcretePrototype obj = (ConcretePrototype) super.clone();
24 obj.name = (Name) this.name.clone();
25 return obj;
26 }
27
28 public ConcretePrototype cloneByIO(){
29 ConcretePrototype result = null;
30 //保持到对象流
31 try {
32 ByteArrayOutputStream o = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
33 ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(o);
34 out.writeObject(this);
35 ByteArrayInputStream i = new ByteArrayInputStream(o.toByteArray());
36 ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(i);
37 result = (ConcretePrototype) in.readObject();
38 } catch (IOException e) {
39 e.printStackTrace();
40 }catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
41 e.printStackTrace();
42 }
43 return result;
44 }
45
46 public void println(){
47 System.out.println("name " + name.name +" x = " + x + " y = " + y + " rho = " + rho + " theta = " + theta);
48 }
49
50
51 public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
52 // 测试数据
53 ConcretePrototype originalObj = new ConcretePrototype("original");
54 System.out.println("被克隆对象:");
55 originalObj.println();
56
57 // 使用覆写的克隆方法
58 ConcretePrototype changedObj= (ConcretePrototype) originalObj.clone();
59 // 使用对象流方式的克隆方法
60 ConcretePrototype changedObj2= originalObj.cloneByIO();
61
62 originalObj.changeName("changed");
63 System.out.println("克隆对象:");
64 changedObj.println();
65 System.out.println("对象流克隆对象:");
66 changedObj2.println();
67 }
68
69 }
70
71 class Name implements Prototype {
72 String name = "";
73
74 Name(String name){
75 this.name = name;
76 }
77
78 public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException{
79 return super.clone();
80 }
81
82 @Override
83 public Object cloneByIO() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
84 return null;
85 }
86 }


