基于形态学处理的条形码数字分割和识别算法MATLAB仿真
1.算法理论概述
条形码数字的分割和识别是自动识别技术中的重要研究方向之一。本文将从专业角度详细介绍基于形态学处理的条形码数字分割和识别算法,包括实现步骤和数学公式的详细介绍。
一、算法概述
基于形态学处理的条形码数字分割和识别算法包括以下步骤:
图像预处理:对原始图像进行预处理,包括调整亮度和对比度、去除噪声和平滑处理等。
条形码检测:使用图像处理技术检测条形码的位置和方向,包括二值化、边缘检测、霍夫变换等。
条形码定位:利用条形码的边界信息进行定位,包括边界提取、形态学处理等。
条形码分割:将条形码分割成数字,包括字符定位、字符分割、字符识别等。
条形码识别:对数字进行识别和校验,包括数字识别、校验和计算等。
二、实现步骤
图像预处理
图像预处理的目的是提高图像质量,减少后续处理的误差和干扰。常用的图像预处理方法包括调整亮度和对比度、去除噪声和平滑处理等。其中,调整亮度和对比度可以使用直方图均衡化和灰度拉伸等方法实现;去除噪声可以使用中值滤波等方法实现;平滑处理可以使用高斯滤波等方法实现。
条形码检测
条形码检测的目的是确定条形码的位置和方向。首先需要将图像转换成二值图像,可以使用阈值分割、自适应阈值分割等方法实现。然后使用边缘检测算法,如Canny算法、Sobel算法等,提取图像中的边缘信息。最后使用霍夫变换,检测条形码的位置和方向。
条形码定位
条形码定位的目的是确定条形码的边界信息。首先需要对二值化后的图像进行边界提取,可以使用边缘检测算法或连通域标记算法实现。然后使用形态学处理,如膨胀、腐蚀等方法,扩大或缩小边界,使其更加接近条形码的实际边界。最后根据条形码的特征,如条形宽度和间距等,确定条形码的边界信息。
条形码分割
条形码分割的目的是将条形码分割成数字。首先需要根据条形码的特征,如字符宽度和间距等,进行字符定位。然后使用字符分割算法,如垂直投影法、水平投影法等,将字符分割成单个数字。最后使用字符识别算法,如模板匹配、神经网络等,对数字进行识别和校验。
条形码识别
条形码识别的目的是对数字进行识别和校验。首先需要对数字进行识别,可以使用模板匹配、神经网络等方法实现。然后根据条形码的校验位,计算数字的校验和,确认数字的正确性。
三、数学公式


2.算法运行软件版本
MATLAB2022a
3.算法运行效果图预览
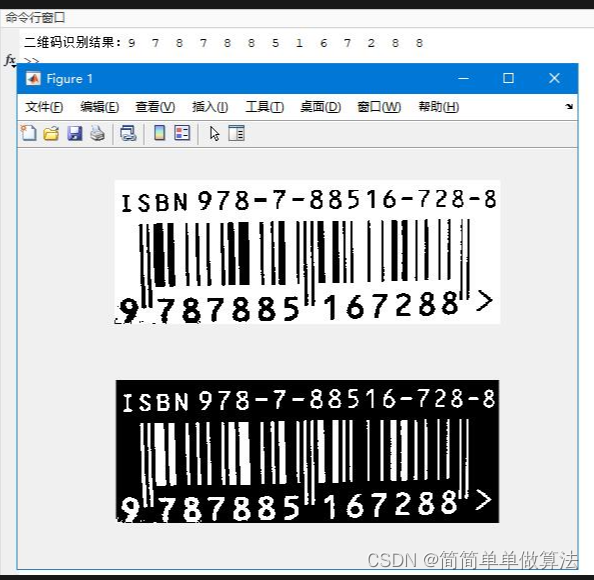

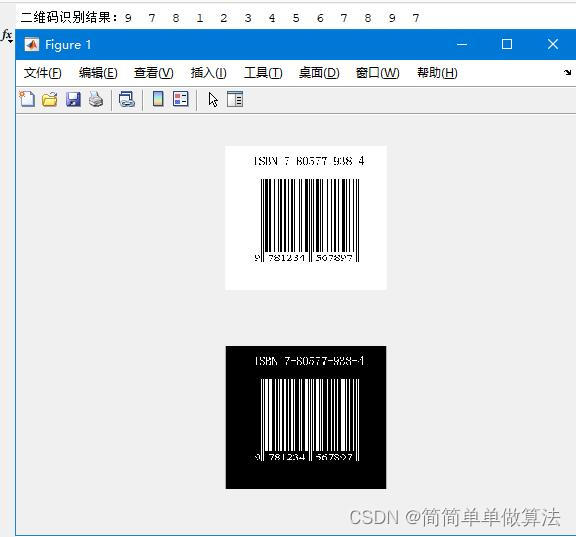
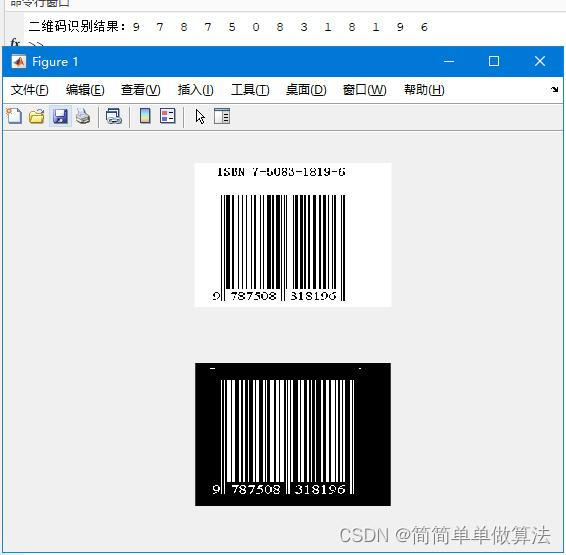
4.部分核心程序
% 寻找左边缘,为了保证鲁棒性,在已经确定的上下边界内全局搜索
for i=ImageTop:ImageBottom
for j=21:ImageWidth
if( (ImageArray(i,j-1)==0) && (ImageArray(i,j)==1) )
arLeftEdge(i) = j;
break;
end
end
end
[tempMax,iMax]=max(arLeftEdge);%获取左边缘的最大值
% 倾斜度不能大于1/10
iCount = 0;
for i=ImageTop:ImageBottom
if( abs(tempMax-arLeftEdge(i)) < abs(i-iMax)/6+1 )
iCount=iCount+1;
end
end
if( (iCount/(ImageBottom-ImageTop))<0.6 )
display('failure1!');%倾斜度太大,无法识别
return;
end
for n=0:28
for i=ImageTop:ImageBottom
for j=arLeftEdge(i)+1:ImageWidth
if( (ImageArray(i,j-1)==1) && (ImageArray(i,j)==0) )
arLeftEdge1(i) = j; break;
end
end
arDelta(i) = arLeftEdge1(i) - arLeftEdge(i);
end
tempArray=arDelta;
%排序
for i=ImageTop:ImageBottom-1
for j=ImageBottom:-1:i+1
if(tempArray(j)< tempArray(j-1))
tempSwap = tempArray(j);
tempArray(j)= tempArray(j-1);
tempArray(j-1) = tempSwap;
end
end
end
t0=floor(ImageTop+(ImageBottom-ImageTop)/2);
t1=t0+2;
t2=t0-2;
if(tempArray(t1)-tempArray(t2)>1) display('failure1!'); return;
else arWidth(2*n+1) = tempArray(t0);
end
%调整下一列边缘
for i=ImageTop:ImageBottom
if(abs(arDelta(i) - arWidth(2*n+1))>2)
arLeftEdge1(i) = arLeftEdge(i) + arWidth(2*n+1);
end
arLeftEdge(i)= arLeftEdge1(i);
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% 搜索空的右边缘
for i=ImageTop:ImageBottom
for j = arLeftEdge(i)+1:ImageWidth
if (ImageArray(i,j-1)==0) && (ImageArray(i,j)==1)
arLeftEdge1(i) = j;
break;
end
end
arDelta(i) = arLeftEdge1(i) - arLeftEdge(i);
end
tempArray = arDelta;
for i=ImageTop:ImageBottom-1
for j=ImageBottom:-1:i+1
if(tempArray(j)< tempArray(j-1))
tempSwap = tempArray(j);
tempArray(j)= tempArray(j-1);
tempArray(j-1) = tempSwap;
end
end
end
t0=floor(ImageTop+(ImageBottom-ImageTop)/2);
t1=t0+2;
t2=t0-2;
if(tempArray(t1)-tempArray(t2)>1) display('failure1!'); return;
else arWidth(2*n+2) = tempArray(t0);
end
%调整下一列边缘
for i=ImageTop:ImageBottom
if(abs(arDelta(i) - arWidth(2*n+2))>2)
arLeftEdge1(i) = arLeftEdge(i) + arWidth(2*n+2);
end
arLeftEdge(i)= arLeftEdge1(i);
end;
end
%% 搜索最后一个条的右边缘
for i=ImageTop:ImageBottom
for j = arLeftEdge(i)+1:ImageWidth
if (ImageArray(i,j-1)==1) && (ImageArray(i,j)==0)
arLeftEdge1(i) = j;
break;
end
end
arDelta(i) = arLeftEdge1(i) - arLeftEdge(i);
end


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号