第三天:spring面向切面的编程
一:spring面向切面的编程
Spring提供2个代理模式,一个是jdk代理,另一个cglib代理
1.若目标对象实现了若干接口,spring使用JDK的java.lang.reflect.Proxy类代理。
2.若目标对象没有实现任何接口,spring使用CGLIB库生成目标对象的子类。
注意:开发时尽量使用接口的编程,
(1)对接口创建代理优于对类创建代理,因为会产生更加松耦合的系统。
(2)标记为final的方法不能够被通知。spring是为目标类产生子类。任何需要被通知的方法都被复写,将通知织入。final方法是不允许重写的。
(3) spring只支持方法连接点,不支持属性的连接点

(1)配置:
要进行AOP编程,首先我们要在spring的配置文件中引入aop命名空间:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd">
</beans>
Spring提供了两种切面使用方式,实际工作中我们可以选用其中一种:
l 基于XML配置方式进行AOP开发。
l 基于注解方式进行AOP开发。
SpringAOP编程,需要引入的jar包
* cglib-3.2.4.jar
cglib代理
* aopalliance-1.0.jar
* aspectjtools-1.8.4.jar
* spring-aop-4.3.6.RELEASE.jar
spring的面向切面编程,提供AOP(面向切面编程)实现
* spring-aspects-4.3.6.RELEASE.jar
spring提供对AspectJ框架的整合
(2)基于XML方式的配置:测试代码
结构:

l IuserService接口
public interface IUserService {
public void saveUser(String name,String password);
public void updateUser(String name,String password);
public void deleteUser(String name);
public String findUser();
}
l UserServiceImpl实现类
public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService {
public void saveUser(String name, String password) {
System.out.println("【新增】用户名:"+name+",密码:"+password);
}
public void updateUser(String name, String password) {
System.out.println("【修改】用户名:"+name+",密码:"+password);
}
public void deleteUser(String name) {
System.out.println("【删除】用户名:"+name);
}
public String findUser() {
System.out.println("【查询】用户");
return "小强";
}
}
l 测试类App.java
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//直接访问目标对象
//使用代理对象访问目标对象,当在spring的容器中添加<aop>
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/offcn/e_xml/a_before/beans.xml");
IUserService userService = (IUserService)ac.getBean("userServiceImpl");
userService.saveUser("超级强", "123");
userService.updateUser("超级强", "123");
userService.deleteUser("超级强");
String str = userService.findUser();
System.out.println("str:"+str);
}
}
【1】前置通知
l 切面类Security
/**切面*/
public class Security {
/**通知*/
/**
* 任何通知方法可以将第一个参数定义为org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint类型 (
* 环绕通知需要定义第一个参数为ProceedingJoinPoint类型, 它是 JoinPoint 的一个子类)。
* JoinPoint 接口提供了一系列有用的方法,
* 比如 getArgs()(返回方法参数)、
* getThis()(返回代理对象)、
* getTarget()(返回目标)、
* getSignature()(返回正在被通知的方法相关信息)、
* toString() (打印出正在被通知的方法的有用信息)。
*/
public void checkSecurity(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("正在执行验证...");
Object [] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
if(args!=null && args.length>0){
for(Object o:args){
System.out.println("参数:"+o);
}
}
System.out.println("代理对象:"+joinPoint.getThis().getClass());
System.out.println("目标对象:"+joinPoint.getTarget().getClass());
System.out.println("访问目标对象方法的名称:"+joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("spring容器中定义切入点的表达式:"+joinPoint.toString());
}
}
l Spring容器(beans.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 创建目标对象 -->
<bean id="userServiceImpl" class="com.offcn.a_before.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="security" class="com.offcn.a_before.Security"></bean>
<!-- spring的aop编程,所有的操作(切面、通知、切入点)都要放置到aop:config -->
<aop:config>
<!--
定义个切面,此时切面的类具有了灵魂
id:惟一标识
ref:注入对象
-->
<aop:aspect id="aa" ref="security">
<!--
声明切入点
id:切入点的惟一标识
expression:切入点的表达式语言,指定项目中哪个类哪个方法作为切入点
-->
<aop:pointcut id="save" expression="execution(* com.offcn.a_before.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(..))" />
<aop:pointcut id="update" expression="execution(* com.offcn.a_before.UserServiceImpl.updateUser(..))" />
<!--
定义通知(切入点要做的事情)
前置通知:在访问目标对象方法之前,先执行通知定义的方法
特点:如果代理对象(切面)中的方法(通知)抛出异常,此时不会执行目标对象
* pointcut-ref:注入切入点,这样才能让切入点关联通知
* method:指定切面中定义的通知的方法
-->
<aop:before pointcut-ref="save" method="checkSecurity"/>
<aop:before pointcut-ref="update" method="checkSecurity"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
【2】后置通知
l 切面类Security
/**切面*/
public class Security {
/**通知*/
/**
* 任何通知方法可以将第一个参数定义为org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint类型 (
* 环绕通知需要定义第一个参数为ProceedingJoinPoint类型, 它是 JoinPoint 的一个子类)。
* JoinPoint 接口提供了一系列有用的方法,
* 比如 getArgs()(返回方法参数)、
* getThis()(返回代理对象)、
* getTarget()(返回目标)、
* getSignature()(返回正在被通知的方法相关信息)、
* toString() (打印出正在被通知的方法的有用信息)。
*/
public void checkSecurity(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object returnValue){
System.out.println("正在执行验证...");
Object [] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
if(args!=null && args.length>0){
for(Object o:args){
System.out.println("参数:"+o);
}
}
System.out.println("代理对象:"+joinPoint.getThis().getClass());
System.out.println("目标对象:"+joinPoint.getTarget().getClass());
System.out.println("访问目标对象方法的名称:"+joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("spring容器中定义切入点的表达式:"+joinPoint.toString());
System.out.println("目标对象方法的返回值:"+returnValue);
}
}
l Spring容器(beans.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 创建目标对象 -->
<bean id="userServiceImpl" class="com.offcn.b_afterreturning.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<!-- 声明切面 (无灵魂)-->
<bean id="security" class="com.offcn.b_afterreturning.Security"></bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="aa" ref="security">
<aop:pointcut id="save" expression="execution(* com.offcn.b_afterreturning.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(..))" />
<aop:pointcut id="find" expression="execution(* com.offcn.b_afterreturning.UserServiceImpl.findUser(..))" />
<!--
后置通知:在访问目标对象方法之后,再执行通知定义的方法
特点:1:如果在目标对象中抛出异常,此时不会执行通知
2:因为是先执行目标对象中的方法,再执行通知,所以能不能在通知中获取目标对象的方法的返回值?能
第一步:在spring容器中定义:returning="returnValue"
第二步:在通知的方法中的第二个参数,可以指定Object类型,
例如public void checkSecurity(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object returnValue){
总结: 参数一定要放在到第二个参数的位置
参数一定一个Object类型
参数的属性名称一定要与spring容器中定义的returning相一致
-->
<aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="save" method="checkSecurity" returning="returnValue"/>
<aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="find" method="checkSecurity" returning="returnValue"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
【3】异常通知
l 切面类Security
/**切面*/
public class Security {
/**通知*/
/**
* 任何通知方法可以将第一个参数定义为org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint类型 (
* 环绕通知需要定义第一个参数为ProceedingJoinPoint类型, 它是 JoinPoint 的一个子类)。
* JoinPoint 接口提供了一系列有用的方法,
* 比如 getArgs()(返回方法参数)、
* getThis()(返回代理对象)、
* getTarget()(返回目标)、
* getSignature()(返回正在被通知的方法相关信息)、
* toString() (打印出正在被通知的方法的有用信息)。
*/
public void checkSecurity(JoinPoint joinPoint,Throwable throwingValue){
System.out.println("正在执行验证...");
Object [] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
if(args!=null && args.length>0){
for(Object o:args){
System.out.println("参数:"+o);
}
}
System.out.println("代理对象:"+joinPoint.getThis().getClass());
System.out.println("目标对象:"+joinPoint.getTarget().getClass());
System.out.println("访问目标对象方法的名称:"+joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("spring容器中定义切入点的表达式:"+joinPoint.toString());
System.out.println("目标对象方法抛出的异常是:"+throwingValue);
}
}
l Spring容器(beans.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 创建目标对象 -->
<bean id="userServiceImpl" class="com.offcn.c_afterthrowing.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<!-- 声明切面 (无灵魂)-->
<bean id="security" class="com.offcn.c_afterthrowing.Security"></bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="aa" ref="security">
<aop:pointcut id="save" expression="execution(* com.offcn.c_afterthrowing.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(..))" />
<aop:pointcut id="find" expression="execution(* com.offcn.c_afterthrowing.UserServiceImpl.findUser(..))" />
<!--
异常通知:在访问目标对象方法之后,前提是目标对象方法中抛出异常,此时才会执行通知定义的方法
特点:1:只有目标对象方法中抛出异常,此时才会执行通知
2:在通知的方法中捕获异常
第一步:在spring容器中定义
第二步:在通知的方法中的第二个参数的位置,可以指定,例如public void checkSecurity(JoinPoint joinPoint,Throwable throwingValue){
* 要求一:获取目标对象抛出的异常的参数要放置在第二个参数的位置
* 要求二:类型必须指定Throwable类型
* 要求三:Throwable对应的属性值要和spring容器中定义的throwing="throwingValue"值要相匹配
-->
<aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="save" method="checkSecurity" throwing="throwingValue"/>
<aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="find" method="checkSecurity" throwing="throwingValue"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
【4】环绕通知 ProceedingJoinPoint
l 切面类Security
/**切面*/
public class Security {
/**通知*/
/**
* 普通通知类型:
* 任何通知方法可以将第一个参数定义为org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint类型 (
* 环绕通知需要定义第一个参数为ProceedingJoinPoint类型, 它是 JoinPoint 的一个子类)。
* JoinPoint 接口提供了一系列有用的方法,
* 比如 getArgs()(返回方法参数)、
* getThis()(返回代理对象)、
* getTarget()(返回目标)、
* getSignature()(返回正在被通知的方法相关信息)、
* toString() (打印出正在被通知的方法的有用信息)。
*
* 环绕通知类型
* 通知的第一个参数必须是 ProceedingJoinPoint类型。
* 在通知体内,调用 ProceedingJoinPoint的proceed()方法会导致 后台的连接点方法执行。
* proceed 方法也可能会被调用并且传入一个 Object[]对象-该数组中的值将被作为方法执行时的参数。
*
* 环绕通知将通知的方法的返回值要定义成Object类型,只有这样才能将目标对象方法的返回值,传递给客户端
*/
public Object checkSecurity(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){
//如果调用joinPoint.proceed();方法放置在通知的最前面,此时就相当于后置通知
System.out.println("环绕通知:在目标执行前调用:"+joinPoint.getTarget().getClass());
Object value = null;
try {
value = joinPoint.proceed();
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
/*System.out.println("正在执行验证...");
Object [] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
if(args!=null && args.length>0){
for(Object o:args){
System.out.println("参数:"+o);
}
}
System.out.println("代理对象:"+joinPoint.getThis().getClass());
System.out.println("目标对象:"+joinPoint.getTarget().getClass());
System.out.println("访问目标对象方法的名称:"+joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("spring容器中定义切入点的表达式:"+joinPoint.toString());*/
// //如果调用joinPoint.proceed();方法放置在通知的最后,此时就相当于前置通知
// Object value = null;
// try {
// value = joinPoint.proceed();
// } catch (Throwable e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
System.out.println("环绕通知:在目标执行后调用:"+joinPoint.getTarget().getClass()+" 获取返回结果:"+value);
return value;
}
}
l Spring容器(beans.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 创建目标对象 -->
<bean id="userServiceImpl" class="com.offcn.e_around.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<!-- 声明切面 (无灵魂)-->
<bean id="security" class="com.offcn.e_around.Security"></bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="aa" ref="security">
<aop:pointcut id="save" expression="execution(* com.offcn.e_around.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(..))" />
<aop:pointcut id="find" expression="execution(* com.offcn.e_around.UserServiceImpl.findUser(..))" />
<!--
环绕通知:
最后一种通知是环绕通知。环绕通知在一个目标对象方法执行之前和之后执行。
它使得通知有机会 在一个方法执行之前和执行之后运行。而且它可以决定这个方法在什么时候执行,如何执行,甚至是否执行。
环绕通知经常在某线程安全的环境下,你需要在一个方法执行之前和之后共享某种状态的时候使用。
请尽量使用最简单的满足你需求的通知。(比如如果简单的前置通知也可以适用的情况下不要使用环绕通知)。
-->
<aop:around pointcut-ref="save" method="checkSecurity"/>
<aop:around pointcut-ref="find" method="checkSecurity"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
(3)基于注解方式的配置:测试代码
首先为了在Spring配置中使用@AspectJ切面,你首先必须启用Spring对@AspectJ切面配置的支持,并确保自动代理 (蓝色部分):
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd”>
<!--启用Spring对@AspectJ的支持 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
<!-- 声明切面对象 -->
<bean id="security" class="com.offcn.service.Security" />
<!-- 创建接口实现类对象 -->
<bean id="userManager" class="com.offcn.service.UserManagerImpl" />
</beans>
结构:

l IuserService接口
public interface IUserService {
public void saveUser(String name,String password);
public void updateUser(String name,String password);
public void deleteUser(String name);
public String findUser();
}
l UserServiceImpl实现类
public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService {
public void saveUser(String name, String password) {
System.out.println("【新增】用户名:"+name+",密码:"+password);
}
public void updateUser(String name, String password) {
System.out.println("【修改】用户名:"+name+",密码:"+password);
}
public void deleteUser(String name) {
System.out.println("【删除】用户名:"+name);
}
public String findUser() {
System.out.println("【查询】用户");
return "小强";
}
}
l 测试类App.java
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//直接访问目标对象
//使用代理对象访问目标对象,当在spring的容器中添加<aop>
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/offcn/a_before/beans.xml");
IUserService userService = (IUserService)ac.getBean("userServiceImpl");
userService.saveUser("超级强", "123");
userService.updateUser("超级强", "123");
userService.deleteUser("超级强");
String str = userService.findUser();
System.out.println("str:"+str);
}
}
【1】前置通知
l 切面类Security
/**切面*/
@Aspect //表示在spring容器中定义:<aop:aspect id="aa" ref="security">
public class Security {
/**
* 声明定义目标对象方法的切入点(指的是方法)
* 要求:1、方法的修饰符任意
* 2、要求方法没有返回值
* 3、方法的名称任意(一个类中,不允许出现同名方法,表明的切入点的id惟一)
* 4、方法没有参数
* 5、方法体为空
*/
//相当于spring容器中定义:<aop:pointcut id="save" expression="execution(* com.offcn.a_before.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(..))" />
@Pointcut(value="execution(* com.offcn.a_before.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(..))")
public void save(){};
@Pointcut(value="execution(* com.offcn.a_before.UserServiceImpl.updateUser(..))")
public void update(){};
/**通知*/
/**
* 任何通知方法可以将第一个参数定义为org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint类型 (
* 环绕通知需要定义第一个参数为ProceedingJoinPoint类型, 它是 JoinPoint 的一个子类)。
* JoinPoint 接口提供了一系列有用的方法,
* 比如 getArgs()(返回方法参数)、
* getThis()(返回代理对象)、
* getTarget()(返回目标)、
* getSignature()(返回正在被通知的方法相关信息)、
* toString() (打印出正在被通知的方法的有用信息)。
*/
//相当于spring容器中定义:<aop:before pointcut-ref="save" method="checkSecurity"/><aop:before pointcut-ref="update" method="checkSecurity"/>
@Before(value="save() || update()")
public void checkSecurity(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("正在执行验证...");
Object [] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
if(args!=null && args.length>0){
for(Object o:args){
System.out.println("参数:"+o);
}
}
System.out.println("代理对象:"+joinPoint.getThis().getClass());
System.out.println("目标对象:"+joinPoint.getTarget().getClass());
System.out.println("访问目标对象方法的名称:"+joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("spring容器中定义切入点的表达式:"+joinPoint.toString());
if(true){
throw new RuntimeException("抛出运行时异常!");
}
}
}
l Spring容器(beans.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 启用Spring对@AspectJ切面配置的支持 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
<!-- 创建目标对象 -->
<bean id="userServiceImpl" class="com.offcn.a_before.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<!-- 声明切面 (无灵魂)-->
<bean id="security" class="com.offcn.a_before.Security"></bean>
</beans>
【2】后置通知
l 切面类Security
/**切面*/
@Aspect //表示在spring容器中定义:<aop:aspect id="aa" ref="security">
public class Security {
/**
* 声明定义目标对象方法的切入点(指的是方法)
* 要求:1、方法的修饰符任意
* 2、要求方法没有返回值
* 3、方法的名称任意(一个类中,不允许出现同名方法,表明的切入点的id惟一)
* 4、方法没有参数
* 5、方法体为空
*/
//相当于spring容器中定义:<aop:pointcut id="save" expression="execution(* com.offcn.a_before.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(..))" />
@Pointcut(value="execution(* com.offcn.b_afterreturning.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(..))")
public void save(){};
@Pointcut(value="execution(* com.offcn.b_afterreturning.UserServiceImpl.findUser(..))")
public void find(){};
/**通知*/
/**
* 任何通知方法可以将第一个参数定义为org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint类型 (
* 环绕通知需要定义第一个参数为ProceedingJoinPoint类型, 它是 JoinPoint 的一个子类)。
* JoinPoint 接口提供了一系列有用的方法,
* 比如 getArgs()(返回方法参数)、
* getThis()(返回代理对象)、
* getTarget()(返回目标)、
* getSignature()(返回正在被通知的方法相关信息)、
* toString() (打印出正在被通知的方法的有用信息)。
*/
//相当于spring容器中定义:<aop:before pointcut-ref="save" method="checkSecurity"/><aop:before pointcut-ref="update" method="checkSecurity"/>
@AfterReturning(value="save() || find()",returning="returnValue")
public void checkSecurity(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object returnValue){
System.out.println("正在执行验证...");
Object [] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
if(args!=null && args.length>0){
for(Object o:args){
System.out.println("参数:"+o);
}
}
System.out.println("代理对象:"+joinPoint.getThis().getClass());
System.out.println("目标对象:"+joinPoint.getTarget().getClass());
System.out.println("访问目标对象方法的名称:"+joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("spring容器中定义切入点的表达式:"+joinPoint.toString());
System.out.println("目标对象方法的返回值:"+returnValue);
// if(true){
// throw new RuntimeException("抛出运行时异常!");
// }
}
}
l Spring容器(beans.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 启用Spring对@AspectJ切面配置的支持 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
<!-- 创建目标对象 -->
<bean id="userServiceImpl" class="com.offcn.b_afterreturning.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<!-- 声明切面 (无灵魂)-->
<bean id="security" class="com.offcn.b_afterreturning.Security"></bean>
</beans>
【3】异常通知
l 切面类Security
/**切面*/
@Aspect //表示在spring容器中定义:<aop:aspect id="aa" ref="security">
public class Security {
/**
* 声明定义目标对象方法的切入点(指的是方法)
* 要求:1、方法的修饰符任意
* 2、要求方法没有返回值
* 3、方法的名称任意(一个类中,不允许出现同名方法,表明的切入点的id惟一)
* 4、方法没有参数
* 5、方法体为空
*/
//相当于spring容器中定义:<aop:pointcut id="save" expression="execution(* com.offcn.a_before.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(..))" />
@Pointcut(value="execution(* com.offcn.c_afterthrowing.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(..))")
public void save(){};
@Pointcut(value="execution(* com.offcn.c_afterthrowing.UserServiceImpl.findUser(..))")
public void find(){};
/**通知*/
/**
* 任何通知方法可以将第一个参数定义为org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint类型 (
* 环绕通知需要定义第一个参数为ProceedingJoinPoint类型, 它是 JoinPoint 的一个子类)。
* JoinPoint 接口提供了一系列有用的方法,
* 比如 getArgs()(返回方法参数)、
* getThis()(返回代理对象)、
* getTarget()(返回目标)、
* getSignature()(返回正在被通知的方法相关信息)、
* toString() (打印出正在被通知的方法的有用信息)。
*/
//相当于spring容器中定义:<aop:before pointcut-ref="save" method="checkSecurity"/><aop:before pointcut-ref="update" method="checkSecurity"/>
@AfterThrowing(value="save() || find()",throwing="throwingValue")
public void checkSecurity(JoinPoint joinPoint,Throwable throwingValue){
System.out.println("正在执行验证...");
Object [] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
if(args!=null && args.length>0){
for(Object o:args){
System.out.println("参数:"+o);
}
}
System.out.println("代理对象:"+joinPoint.getThis().getClass());
System.out.println("目标对象:"+joinPoint.getTarget().getClass());
System.out.println("访问目标对象方法的名称:"+joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("spring容器中定义切入点的表达式:"+joinPoint.toString());
System.out.println("目标对象抛出的异常:"+throwingValue);
}
}
l Spring容器(beans.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 启用Spring对@AspectJ切面配置的支持 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
<!-- 创建目标对象 -->
<bean id="userServiceImpl" class="com.offcn.c_afterthrowing.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<!-- 声明切面 (无灵魂)-->
<bean id="security" class="com.offcn.c_afterthrowing.Security"></bean>
</beans>
【4】环绕通知
l 切面类Security
/**切面*/
@Aspect //表示在spring容器中定义:<aop:aspect id="aa" ref="security">
public class Security {
/**
* 声明定义目标对象方法的切入点(指的是方法)
* 要求:1、方法的修饰符任意
* 2、要求方法没有返回值
* 3、方法的名称任意(一个类中,不允许出现同名方法,表明的切入点的id惟一)
* 4、方法没有参数
* 5、方法体为空
*/
//相当于spring容器中定义:<aop:pointcut id="save" expression="execution(* com.offcn.a_before.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(..))" />
@Pointcut(value="execution(* com.offcn.e_around.UserServiceImpl.saveUser(..))")
public void save(){};
@Pointcut(value="execution(* com.offcn.e_around.UserServiceImpl.findUser(..))")
public void find(){};
/**通知*/
/**
* 任何通知方法可以将第一个参数定义为org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint类型 (
* 环绕通知需要定义第一个参数为ProceedingJoinPoint类型, 它是 JoinPoint 的一个子类)。
* JoinPoint 接口提供了一系列有用的方法,
* 比如 getArgs()(返回方法参数)、
* getThis()(返回代理对象)、
* getTarget()(返回目标)、
* getSignature()(返回正在被通知的方法相关信息)、
* toString() (打印出正在被通知的方法的有用信息)。
*/
//相当于spring容器中定义:<aop:before pointcut-ref="save" method="checkSecurity"/><aop:before pointcut-ref="update" method="checkSecurity"/>
@Around(value="save() || find()")
public Object checkSecurity(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("正在执行验证...");
Object [] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
if(args!=null && args.length>0){
for(Object o:args){
System.out.println("参数:"+o);
}
}
System.out.println("代理对象:"+joinPoint.getThis().getClass());
System.out.println("目标对象:"+joinPoint.getTarget().getClass());
System.out.println("访问目标对象方法的名称:"+joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("spring容器中定义切入点的表达式:"+joinPoint.toString());
//调用proceed,放置到最后,此时相当于前置通知
Object value = null;
try {
value = joinPoint.proceed();
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return value;
}
}
l Spring容器(beans.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 启用Spring对@AspectJ切面配置的支持 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
<!-- 创建目标对象 -->
<bean id="userServiceImpl" class="com.offcn.e_around.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<!-- 声明切面 (无灵魂)-->
<bean id="security" class="com.offcn.e_around.Security"></bean>
</beans>
总结:
1:spring的5种类型,目的在访问目标对象方法之前或者之后,先执行通知定义的方法,这种编程就是aop方式的编程思想,即面向切面的编程。
* 应用(spring提供的声明式事务处理),后面讲
2:对于环绕通知来说:
Object value = joinPoint.proceed();就类似于jdk代理和cglib代理的Object returnValue = method.invoke(this.targetObject, args);,此时效果是一样的
二、综合案例:
#账号信息表
create table account
(
accountid varchar(18) primary key, #账号
balance double(10,2) #余额
)
#存款信息表(存款的过程)
create table inaccount
(
accountid varchar(18), #账号
inbalance double(10,2) #存款金额
)
完成业务要求
需求:向8888的账号存款200元钱
1:向存款信息表中的8888账号存款200元,存放一条记录
2:使用8888的账号查询账号信息表,获取8888账号对应的余额
3:更新8888账号的余额(余额=存款的金额+新增的金额)
4:更新账号信息表,对8888的账号,将余额更新最新的余额
结构:

l Account.java
//账号信息
public class Account {
private String accountid; //账号
private Double balance; //余额
public String getAccountid() {
return accountid;
}
public void setAccountid(String accountid) {
this.accountid = accountid;
}
public Double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(Double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
}
l InAccount.java
//存款信息
public class InAccount {
private String accountid; //账号
private Double inbalance; //存款金额
public String getAccountid() {
return accountid;
}
public void setAccountid(String accountid) {
this.accountid = accountid;
}
public Double getInbalance() {
return inbalance;
}
public void setInbalance(Double inbalance) {
this.inbalance = inbalance;
}
}
l IAccountDao.java接口
public interface IAccountDao {
Account findAccountById(String accountid);
void updateAccount(Account account);
}
l IInAccountDao.java接口
public interface IInAccountDao {
void save(InAccount inAccount);
}
l AccountDaoImpl.java实现类
/**账号DAO*/
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
/**2:使用8888的账号查询账号信息表,获取8888账号对应的余额*/
@Override
public Account findAccountById(String accountid) {
String sql = "select accountid,balance from account where accountid=?";
Object [] args = {accountid};
RowMapper<Account> rowMapper = new RowMapper<Account>() {
@Override
public Account mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
Account account = new Account();
account.setAccountid(rs.getString("accountid"));
account.setBalance(rs.getDouble("balance"));
return account;
}
};
Account account = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, args, rowMapper);
return account;
}
/**4:更新账号信息表,对8888的账号,将余额更新最新的余额*/
@Override
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
try {
String sql = "update account set balance=? where accountid=?";
Object [] args = {account.getBalance(),account.getAccountid()};
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException("抛出运行时异常!");
}
}
}
l InAccountDaoImpl.java实现类
public class InAccountDaoImpl implements IInAccountDao {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
/**1:向存款信息表中的8888账号存款200元,存放一条记录*/
@Override
public void save(InAccount inAccount) {
String sql = "insert into inaccount(accountid,inbalance) values (?,?)";
Object [] args = {inAccount.getAccountid(),inAccount.getInbalance()};
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, args);
}
}
l IAccountService.java接口
public interface IAccountService {
void saveAccount(InAccount inAccount);
}
l AccountServiceImpl.java实现类
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
private IInAccountDao inAccountDao;
private IAccountDao accountDao;
public void setInAccountDao(IInAccountDao inAccountDao) {
this.inAccountDao = inAccountDao;
}
public void setAccountDao(IAccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
/**向8888的账号存款200元钱*/
@Override
public void saveAccount(InAccount inAccount) {
//1:向存款信息表中的8888账号存款200元,存放一条记录
inAccountDao.save(inAccount);
//2:使用8888的账号查询账号信息表,获取8888账号对应的余额
String accountid = inAccount.getAccountid();
Account account = accountDao.findAccountById(accountid);
//3:更新8888账号的余额(余额=存款的金额+新增的金额)
Double balance = account.getBalance()+inAccount.getInbalance();
account.setBalance(balance);
//4:更新账号信息表,对8888的账号,将余额更新最新的余额
accountDao.updateAccount(account);
}
}
l Spring容器beans.xml的配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd
<!-- 配置DBCP连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/0403_demo02?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="123"></property>
<!-- 连接池启动时的初始值 -->
<property name="initialSize" value="1"/>
<!-- 连接池的最大值 -->
<property name="maxActive" value="500"/>
<!-- 最大空闲值.当经过一个高峰时间后,连接池可以慢慢将已经用不到的连接慢慢释放一部分,一直减少到maxIdle为止 -->
<property name="maxIdle" value="2"/>
<!-- 最小空闲值.当空闲的连接数少于该值时,连接池就会预申请一些连接,以避免洪峰来时再申请而造成的性能开销 -->
<property name="minIdle" value="1"/>
</bean>
<!-- 创建spring提供的Jdbc模板,用来操作数据库 -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 创建Service -->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.offcn.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="inAccountDao" ref="inAccountDao"></property>
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 创建Dao -->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.offcn.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="inAccountDao" class="com.offcn.dao.impl.InAccountDaoImpl">
<property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
l 测试类App.java
@RunWith(value=SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(value="classpath:beans.xml")
public class App {
@Resource(name="accountService")
private IAccountService accountService;
/**需求:向8888的账号存款200元钱*/
@Test
public void saveAccount(){
InAccount inAccount = new InAccount();
inAccount.setAccountid("8888");
inAccount.setInbalance(200d);
accountService.saveAccount(inAccount);
}
}
三、Spring事务处理
1:事务的概念
事务处理:
* 声明式事务管理(*****)
如果你并不需要细粒度的事务控制,你可以使用声明式事务,在Spring中,你只需要在Spring配置文件中做一些配置,即可将操作纳入到事务管理中,解除了和代码的耦合, 这是对应用代码影响最小的选择,从这一点再次验证了Spring关于AOP的概念。当你不需要事务管理的时候,可以直接从Spring配置文件中移除该设置
* 事务管理器:
事务是一组操作的执行单元,相对于数据库操作来讲,事务管理的是一组SQL指令,比如增加,修改,删除等,事务的一致性,要求,这个事务内的操作必须全部执行成功,如果在此过程种出现了差错,比如有一条SQL语句没有执行成功,那么这一组操作都将全部回滚
仅用四个词解释事务(ACID)
atomic(原子性):要么都发生,要么都不发生。
consistent(一致性):数据应该不被破坏。
Isolate(隔离性):用户间操作不相混淆
Durable(持久性):永久保存,例如保存到数据库中等
Spring提供了两种事务管理方式
编程式事务管理
编写程序式的事务管理可以清楚的定义事务的边界,可以实现细粒度的事务控制,比如你可以通过程序代码来控制你的事务何时开始,何时结束等,与后面介绍的声明式事务管理相比,它可以实现细粒度的事务控制。
声明式事务管理(*****)
如果你并不需要细粒度的事务控制,你可以使用声明式事务,在Spring中,你只需要在Spring配置文件中做一些配置,即可将操作纳入到事务管理中,解除了和代码的耦合, 这是对应用代码影响最小的选择,从这一点再次验证了Spring关于AOP的概念。当你不需要事务管理的时候,可以直接从Spring配置文件中移除该设置
之前手工方式控制事务:例如:

如果使用spring的声明式事务处理,这些方法都是可以省略的。
2:spring提供的事务管理器
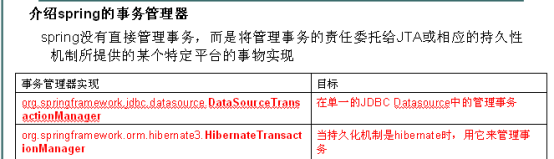
介绍spring的事务管理器
spring没有直接管理事务,而是将管理事务的责任委托给JTA或相应的持久性机制所提供的某个特定平台的事物实现

3:传播行为
传播行为:定义关于客户端和被调用方法的事物边界
例如一个操作:

声明对应的传播行为
事务的传播级别定义的是事务的控制范围,主要是父子事务之间的相互影响关系;事务的隔离级别定义的是事务读写的控制范围,主要是两个事务之间的相互影响关系。
传播级别:

总结:
REQUIRED(默认值):也是项目应用最多的传播行为,因为他表示如果业务方法存在一个事务中,则直接使用这个事务。如果业务方法不存在事务,则开启一个新的事务。
保证一个业务方法在一个事务中完成。
4:隔离级别

脏读:一个事务读取了另一个事务改写但还未提交的数据,如果这些数据被回滚,则读到的数据是无效的。
不可重复读:在同一事务中,多次读取同一数据返回的结果有所不同。换句话说就是,后续读取可以读到另一事务已提交的更新数据。相反,“可重复读”在同一事务中多次读取数据时,能够保证所读数据一样,也就是,后续读取不能读到另一事务已提交的更新数据。
幻读(虚度):一个事务读取了几行记录后,另一个事务插入一些记录,幻读就发生了。再后来的查询中,第一个事务就会发现有些原来没有的记录。
总结:
开发时使用DEFAULT(默认值),表示数据库采用那个隔离级别,我们就使用哪种隔离级别
5:声明式事务处理(XML)
(1)在spring容器中定义:引入用于声明事务的tx命名空间
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 配置DBCP连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/0403_demo02?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="123"></property>
<!-- 连接池启动时的初始值 -->
<property name="initialSize" value="1"/>
<!-- 连接池的最大值 -->
<property name="maxActive" value="500"/>
<!-- 最大空闲值.当经过一个高峰时间后,连接池可以慢慢将已经用不到的连接慢慢释放一部分,一直减少到maxIdle为止 -->
<property name="maxIdle" value="2"/>
<!-- 最小空闲值.当空闲的连接数少于该值时,连接池就会预申请一些连接,以避免洪峰来时再申请而造成的性能开销 -->
<property name="minIdle" value="1"/>
</bean>
<!-- 创建spring提供的Jdbc模板,用来操作数据库 -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 创建Service -->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.offcn.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="inAccountDao" ref="inAccountDao"></property>
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 创建Dao -->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.offcn.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="inAccountDao" class="com.offcn.dao.impl.InAccountDaoImpl">
<property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 添加声明式事务处理(XML)begin -->
<!--
声明事务管理器
(相当于切面,也就是说在切面的类中定义的是事务控制)
-->
<bean id="trManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--
tx:advice:定义通知(通知关联事务,通知的方法要放置到切面的类中)
* id:通知方法的在容器中的惟一标识
* transaction-manager:事务管理,指定对哪个事务进行管理
tx:method:对切入点方法的细化
* name:表示切入点中的方法名称
* 实例:
* name="saveAccount":表示业务层的saveAccount的方法 (1)
* name="save*":表示业务层的以save开头的方法(2)
* name="*":表示业务层的所有的方法(3)
* 执行的优先级:(1)>(2)>(3)
* isolation="DEFAULT":事务的隔离级别,数据库用什么隔离级别,该方法就使用什么隔离级别
* propagation="REQUIRED":如果业务方法存在一个事务中,直接使用这个事务,如果业务方法运行不存在一个事务,自己会开启一个新的事务
* read-only="false":可写数据库,比如增、删、改的操作
read-only=”true”:只读数据库,比如查询的操作
-->
<tx:advice id="trManagerAdvice" transaction-manager="trManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="save*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="update*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="delete*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="*" read-only="true"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- 定义切入点点,而且使得切入点要关联通知 -->
<aop:config>
<!--
aop:pointcut:定义切入点,(业务层的方法就是切入点)
-->
<aop:pointcut id="servicePointCut" expression="execution(* com.offcn.service..*.*(..))" />
<!--
aop:advisor:配置切入点要关联通知(事务控制业务层的方法)
-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="trManagerAdvice" pointcut-ref="servicePointCut"/>
</aop:config>
<!-- 添加声明式事务处理(XML) end-->
</beans>
测试再次测试我们的练习,发现事务可以被控制。
* 即如果没有错误,则提交
如果出现错误,则回滚
(2)Spring事务控制的原理:
Spring事务的本质其实就是数据库对事务的支持,没有数据库的事务支持,spring是无法提供事务功能的。对于纯JDBC操作数据库,想要用到事务,可以按照以下步骤进行:
- 获取连接 Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection()
- 开启事务con.setAutoCommit(true/false);
- 执行CRUD
- 提交事务/回滚事务 con.commit() / con.rollback();
- 关闭连接 conn.close();
使用Spring的事务管理功能后,我们可以不再写步骤 2 和 4 的代码,而是由Spirng 自动完成。
在控制层访问业务的方法时,实质上产生一个代理对象$Proxy,在代理对象中对业务层的方法用事务进行控制,这样就将业务层的方法用一个事务做了控制
实质上代理产生的代码(因为在容器中进行配置)进行事务控制:这个配置再次验证spring关于aop的思想,即在业务层的方法之前,创建一个代理类,由代理类控制事务的提交和回滚。
例如:

(3)测试代码
结构:
l Account.java
//账号信息
public class Account {
private String accountid; //账号
private Double balance; //余额
public String getAccountid() {
return accountid;
}
public void setAccountid(String accountid) {
this.accountid = accountid;
}
public Double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(Double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
}
l InAccount.java
//存款信息
public class InAccount {
private String accountid; //账号
private Double inbalance; //存款金额
public String getAccountid() {
return accountid;
}
public void setAccountid(String accountid) {
this.accountid = accountid;
}
public Double getInbalance() {
return inbalance;
}
public void setInbalance(Double inbalance) {
this.inbalance = inbalance;
}
}
l IAccountDao.java接口
public interface IAccountDao {
Account findAccountById(String accountid);
void updateAccount(Account account);
}
l IInAccountDao.java接口
public interface IInAccountDao {
void save(InAccount inAccount);
}
l AccountDaoImpl.java实现类
/**账号DAO*/
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
/**2:使用8888的账号查询账号信息表,获取8888账号对应的余额*/
@Override
public Account findAccountById(String accountid) {
String sql = "select accountid,balance from account where accountid=?";
Object [] args = {accountid};
RowMapper<Account> rowMapper = new RowMapper<Account>() {
@Override
public Account mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
Account account = new Account();
account.setAccountid(rs.getString("accountid"));
account.setBalance(rs.getDouble("balance"));
return account;
}
};
Account account = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, args, rowMapper);
return account;
}
/**4:更新账号信息表,对8888的账号,将余额更新最新的余额*/
@Override
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
try {
//故意抛出报错
String sql = "update account set balancexxxxxxxxxxxx=? where accountid=?";
Object [] args = {account.getBalance(),account.getAccountid()};
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException("Dao层抛出运行时异常!");
}
}
}
l InAccountDaoImpl.java实现类
public class InAccountDaoImpl implements IInAccountDao {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
/**1:向存款信息表中的8888账号存款200元,存放一条记录*/
@Override
public void save(InAccount inAccount) {
String sql = "insert into inaccount(accountid,inbalance) values (?,?)";
Object [] args = {inAccount.getAccountid(),inAccount.getInbalance()};
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, args);
}
}
l IAccountService.java接口
public interface IAccountService {
void saveAccount(InAccount inAccount);
}
l AccountServiceImpl.java实现类
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
private IInAccountDao inAccountDao;
private IAccountDao accountDao;
public void setInAccountDao(IInAccountDao inAccountDao) {
this.inAccountDao = inAccountDao;
}
public void setAccountDao(IAccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
/**向8888的账号存款200元钱*/
@Override
public void saveAccount(InAccount inAccount) {
try {
//1:向存款信息表中的8888账号存款200元,存放一条记录
inAccountDao.save(inAccount);
//2:使用8888的账号查询账号信息表,获取8888账号对应的余额
String accountid = inAccount.getAccountid();
Account account = accountDao.findAccountById(accountid);
//3:更新8888账号的余额(余额=存款的金额+新增的金额)
Double balance = account.getBalance()+inAccount.getInbalance();
account.setBalance(balance);
//4:更新账号信息表,对8888的账号,将余额更新最新的余额
accountDao.updateAccount(account);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException("Service层抛出运行时异常!");
}
}
}
l Spring容器beans.xml的配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 配置DBCP连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/0403_demo02?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="123"></property>
<!-- 连接池启动时的初始值 -->
<property name="initialSize" value="1"/>
<!-- 连接池的最大值 -->
<property name="maxActive" value="500"/>
<!-- 最大空闲值.当经过一个高峰时间后,连接池可以慢慢将已经用不到的连接慢慢释放一部分,一直减少到maxIdle为止 -->
<property name="maxIdle" value="2"/>
<!-- 最小空闲值.当空闲的连接数少于该值时,连接池就会预申请一些连接,以避免洪峰来时再申请而造成的性能开销 -->
<property name="minIdle" value="1"/>
</bean>
<!-- 创建spring提供的Jdbc模板,用来操作数据库 -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 创建Service -->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.offcn.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="inAccountDao" ref="inAccountDao"></property>
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 创建Dao -->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.offcn.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="inAccountDao" class="com.offcn.dao.impl.InAccountDaoImpl">
<property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 添加声明式事务处理(XML)begin -->
<!--
声明事务管理器
(相当于切面,也就是说在切面的类中定义的是事务控制)
-->
<bean id="trManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--
tx:advice:定义通知(通知关联事务,通知的方法要放置到切面的类中)
* id:通知方法的在容器中的惟一标识
* transaction-manager:事务管理,指定对哪个事务进行管理
tx:method:对切入点方法的细化
* name:表示切入点中的方法名称
* 实例:
* name="saveAccount":表示业务层的saveAccount的方法 (1)
* name="save*":表示业务层的以save开头的方法(2)
* name="*":表示业务层的所有的方法(3)
* 执行的优先级:(1)>(2)>(3)
* isolation="DEFAULT":事务的隔离级别,数据库用什么隔离级别,该方法就使用什么隔离级别
* propagation="REQUIRED":如果业务方法存在一个事务中,直接使用这个事务,如果业务方法运行不存在一个事务,自己会开启一个新的事务
* read-only="false":可写数据库,比如增、删、改的操作,需要对数据库进行可写,查询的操作,需要只读
-->
<tx:advice id="trManagerAdvice" transaction-manager="trManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="save*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="update*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="delete*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="*" read-only="true"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- 定义切入点点,而且使得切入点要关联通知 -->
<aop:config>
<!--
aop:pointcut:定义切入点,(业务层的方法就是切入点)
-->
<aop:pointcut id="servicePointCut" expression="execution(* com.offcn.service..*.*(..))" />
<!--
aop:advisor:配置切入点要关联通知(事务控制业务层的方法)
-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="trManagerAdvice" pointcut-ref="servicePointCut"/>
</aop:config>
<!-- 添加声明式事务处理(XML) end-->
</beans>
l 测试类App.java
@RunWith(value=SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(value="classpath:beans.xml")
public class App {
@Resource(name="accountService")
private IAccountService accountService;
/**需求:向8888的账号存款200元钱*/
@Test
public void saveAccount(){
InAccount inAccount = new InAccount();
inAccount.setAccountid("8888");
inAccount.setInbalance(200d);
accountService.saveAccount(inAccount);
}
}
6:声明式事务处理(注解)
(1)在spring的配置文件中的定义:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 注解:配置组件的自动扫描,扫描范围的类都可以定义注解 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.offcn"/>
<!-- 配置DBCP连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/0403_demo02?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="123"></property>
<!-- 连接池启动时的初始值 -->
<property name="initialSize" value="1"/>
<!-- 连接池的最大值 -->
<property name="maxActive" value="500"/>
<!-- 最大空闲值.当经过一个高峰时间后,连接池可以慢慢将已经用不到的连接慢慢释放一部分,一直减少到maxIdle为止 -->
<property name="maxIdle" value="2"/>
<!-- 最小空闲值.当空闲的连接数少于该值时,连接池就会预申请一些连接,以避免洪峰来时再申请而造成的性能开销 -->
<property name="minIdle" value="1"/>
</bean>
<!-- 创建spring提供的Jdbc模板,用来操作数据库 -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 添加声明式事务处理(注解的方式)begin -->
<bean id="trManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 注解需要在业务层的类的上面或者方法的上面添加一个注解@Transcational -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="trManager"/>
<!-- 添加声明式事务处理(注解的方式) end-->
</beans>
(2)在业务层的类中定义:
/**
* @Transcational注解
* * 放置到类的上面,默认对类中的所有方法都有效,而且默认是可写的操作
* * 放置到方法的上面:此时方法级别的事务,会覆盖类级别的事务
*
* 注解方式总结:
1:在业务层的类上面定义:@Transactional(readOnly=true),表示业务层的所有方法都只读。
* 2:在业务层类的方法上定义@Transactional(isolation=Isolation.DEFAULT,propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly=false):表示方法可写,例如新增、删除、修改的方法上:
* 3:查询的方法无需定义@Transactional,因为表示只读即可
*
* 相当于spring容器中定义:
* <tx:advice id="trManagerAdvice" transaction-manager="trManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="save*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="update*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="delete*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="*" read-only="true"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- 定义切入点点,而且使得切入点要关联通知 -->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="servicePointCut" expression="execution(* com.offcn.service..*.*(..))" />
<aop:advisor advice-ref="trManagerAdvice" pointcut-ref="servicePointCut"/>
</aop:config>
*
*/
@Service("accountService")
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.DEFAULT,propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
@Resource(name="inAccountDao")
private IInAccountDao inAccountDao;
@Resource(name="accountDao")
private IAccountDao accountDao;
/**向8888的账号存款200元钱*/
@Override
@Transactional(isolation=Isolation.DEFAULT,propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly=false)
public void saveAccount(InAccount inAccount) {
//1:向存款信息表中的8888账号存款200元,存放一条记录
inAccountDao.save(inAccount);
//2:使用8888的账号查询账号信息表,获取8888账号对应的余额
String accountid = inAccount.getAccountid();
Account account = accountDao.findAccountById(accountid);
//3:更新8888账号的余额(余额=存款的金额+新增的金额)
Double balance = account.getBalance()+inAccount.getInbalance();
account.setBalance(balance);
//4:更新账号信息表,对8888的账号,将余额更新最新的余额
accountDao.updateAccount(account);
}
}
(3)总结:
1)方法级别的事务,会覆盖类级别的事务
2)注解@Transactional放置到类的上面,默认对类中的所有方法都有效,如果不添加任何属性,此时默认是可写的操作,即类中的所有方法都可写。
3) 在业务层的类上面定义:@Transactional(readOnly=true),此时表示业务层类上的所有方法都是只读操作
4)@Transactional(isolation=Isolation.DEFAULT,propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly=false)放到方法上,表示该方法是可写的的操作,例如新增、修改、删除的方法。此时查询的方法无需定义@Transactional
(4)测试代码
结构:

l Account.java
//账号信息
public class Account {
private String accountid; //账号
private Double balance; //余额
public String getAccountid() {
return accountid;
}
public void setAccountid(String accountid) {
this.accountid = accountid;
}
public Double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(Double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
}
l InAccount.java
//存款信息
public class InAccount {
private String accountid; //账号
private Double inbalance; //存款金额
public String getAccountid() {
return accountid;
}
public void setAccountid(String accountid) {
this.accountid = accountid;
}
public Double getInbalance() {
return inbalance;
}
public void setInbalance(Double inbalance) {
this.inbalance = inbalance;
}
}
l IAccountDao.java接口
public interface IAccountDao {
Account findAccountById(String accountid);
void updateAccount(Account account);
}
l IInAccountDao.java接口
public interface IInAccountDao {
void save(InAccount inAccount);
}
l AccountDaoImpl.java实现类
/**账号DAO*/
@Repository("accountDao")
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
@Resource(name="jdbcTemplate")
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
/**2:使用8888的账号查询账号信息表,获取8888账号对应的余额*/
@Override
public Account findAccountById(String accountid) {
String sql = "select accountid,balance from account where accountid=?";
Object [] args = {accountid};
RowMapper<Account> rowMapper = new RowMapper<Account>() {
@Override
public Account mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
Account account = new Account();
account.setAccountid(rs.getString("accountid"));
account.setBalance(rs.getDouble("balance"));
return account;
}
};
Account account = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, args, rowMapper);
return account;
}
/**4:更新账号信息表,对8888的账号,将余额更新最新的余额*/
@Override
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
try {
String sql = "update account set balancexxxxxxxxxxxx=? where accountid=?";
Object [] args = {account.getBalance(),account.getAccountid()};
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException("抛出运行时异常!");
}
}
}
l InAccountDaoImpl.java实现类
@Repository("inAccountDao")
public class InAccountDaoImpl implements IInAccountDao {
@Resource(name="jdbcTemplate")
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
/**1:向存款信息表中的8888账号存款200元,存放一条记录*/
@Override
public void save(InAccount inAccount) {
String sql = "insert into inaccount(accountid,inbalance) values (?,?)";
Object [] args = {inAccount.getAccountid(),inAccount.getInbalance()};
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, args);
}
}
l IAccountService.java接口
public interface IAccountService {
void saveAccount(InAccount inAccount);
}
l AccountServiceImpl.java实现类
/**
* @Transcational注解
* * 放置到类的上面,默认对类中的所有方法都有效,而且默认是可写的操作
* * 放置到方法的上面:此时方法级别的事务,会覆盖类级别的事务
*
* 注解方式总结:
1:在业务层的类上面定义:@Transactional(readOnly=true),表示业务层的所有方法都只读。
* 2:在业务层类的方法上定义@Transactional(isolation=Isolation.DEFAULT,propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly=false):表示方法可写,例如新增、删除、修改的方法上:
* 3:查询的方法无需定义@Transactional,因为表示只读即可
*
* 相当于spring容器中定义:
* <tx:advice id="trManagerAdvice" transaction-manager="trManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="save*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="update*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="delete*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="*" read-only="true"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- 定义切入点点,而且使得切入点要关联通知 -->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="servicePointCut" expression="execution(* com.offcn.service..*.*(..))" />
<aop:advisor advice-ref="trManagerAdvice" pointcut-ref="servicePointCut"/>
</aop:config>
*
*/
@Service("accountService")
@Transactional(readOnly=true)
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
@Resource(name="inAccountDao")
private IInAccountDao inAccountDao;
@Resource(name="accountDao")
private IAccountDao accountDao;
/**向8888的账号存款200元钱*/
@Override
@Transactional(isolation=Isolation.DEFAULT,propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly=false)
public void saveAccount(InAccount inAccount) {
//1:向存款信息表中的8888账号存款200元,存放一条记录
inAccountDao.save(inAccount);
//2:使用8888的账号查询账号信息表,获取8888账号对应的余额
String accountid = inAccount.getAccountid();
Account account = accountDao.findAccountById(accountid);
//3:更新8888账号的余额(余额=存款的金额+新增的金额)
Double balance = account.getBalance()+inAccount.getInbalance();
account.setBalance(balance);
//4:更新账号信息表,对8888的账号,将余额更新最新的余额
accountDao.updateAccount(account);
}
}
l Spring容器beans.xml的配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 注解:配置组件的自动扫描,扫描范围的类都可以定义注解 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.offcn"/>
<!-- 配置DBCP连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/0403_demo02?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="123"></property>
<!-- 连接池启动时的初始值 -->
<property name="initialSize" value="1"/>
<!-- 连接池的最大值 -->
<property name="maxActive" value="500"/>
<!-- 最大空闲值.当经过一个高峰时间后,连接池可以慢慢将已经用不到的连接慢慢释放一部分,一直减少到maxIdle为止 -->
<property name="maxIdle" value="2"/>
<!-- 最小空闲值.当空闲的连接数少于该值时,连接池就会预申请一些连接,以避免洪峰来时再申请而造成的性能开销 -->
<property name="minIdle" value="1"/>
</bean>
<!-- 创建spring提供的Jdbc模板,用来操作数据库 -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 添加声明式事务处理(注解的方式)begin -->
<bean id="trManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 注解需要在业务层的类的上面或者方法的上面添加一个注解@Transcational -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="trManager"/>
<!-- 添加声明式事务处理(注解的方式) end-->
</beans>
l 测试类App.java
@RunWith(value=SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(value="classpath:beans.xml")
public class App {
@Resource(name="accountService")
private IAccountService accountService;
/**需求:向8888的账号存款200元钱*/
@Test
public void saveAccount(){
InAccount inAccount = new InAccount();
inAccount.setAccountid("8888");
inAccount.setInbalance(200d);
accountService.saveAccount(inAccount);
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号