关于json反序列化为实体的泛型擦除问题
关于json反序列化为实体的泛型擦除问题
1. 问题背景
生产中,使用配置文件将json中数据对应赋值到实体的某个字段上,其中主要问题在于数据类型是什么?json数据中无法很好区分,这块设计的是反射拿到具体的数据类型进行赋值。但,如果是嵌套类型怎么办,比如将某段json字段值赋值到
Map<String, Class>中呢?会有泛型擦除问题
2. 问题复现
2.1 使用Map.class反射后直接赋值
Code
实体的代码
public class Test implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Map<String, Price> prices;
}
public class Price implements Serializable{
@JSONField(name="o")
private Double origanl_price;
@JSONField(name="p")
private Double price;
@JSONField(name="u")
private String union;
@JSONField(name="c")
private String currency;
}
测试案例
public static void mapJsonToFields3(T t, JSONObject json) {
try {
// 获取当前类的全部字段
for (Field field : ReflectUtil.listField(t.getClass())) {
// 。。。。。。。 其它类型
// 判断是否是map类型
if (field.getType() == Map.class) {
// 将 json转换为 Map对象,并将其设置为字段的值
field.set(t, JSON.toJavaObject((JSONObject) json, field.getType()));
}
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Test
public void test04() throws IllegalAccessException {
String jsonString = "{\"US\":{\"o\":62.0,\"p\":20.0,\"u\":\"$\",\"c\":\"USD\"}}";
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(jsonString);
Test test= new Test();
JsonMapper.mapJsonToFields3(test, jsonObject);
Map<String, Price> prices = test.getPrices();
Price usPrice = prices.get("US");
System.out.println(usPrice);
}
代码目的就是将JSON数据映射到t对象的Map类型的字段上
Debug
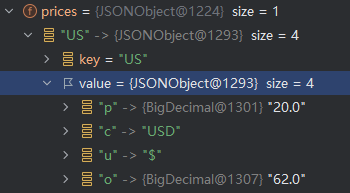
不难看出,对象中的prices这个类型竟然是JSONObject,对于外层实体test来说是毫无影响的,结果反正复制上了,序列化什么的无所谓啦,后面写sql的时候转一下json还是没问题的。但是如果后续代码中使用到了prices中的某个变量的话,这样是读不出来的,会报错
我的数据类型不是Map吗?为什么JSONObject可以存进来?
请看JSONObject实现的接口
public class JSONObject extends JSON implements Map<String, Object>, Cloneable, Serializable, InvocationHandler, Wrapper
3. 解决方案
3.1 临时救急版
示例代码
@Test
public void test2() {
String jsonString = "{\"US\":{\"o\":370.0,\"p\":370.0,\"u\":\"$\"}}";
Map<String, Price> prices = JSON.parseObject(jsonString, new TypeReference<Map<String, Price>>() {});
prices.forEach((k, v) -> {
System.out.println(k + ": " + v);
});
}
OutPut
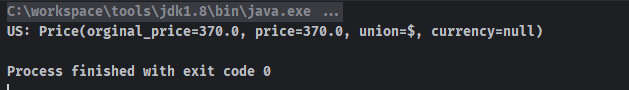
使用TypeReference来告诉JSON,我应该怎么序列化数据,弊端就是不够通用,结果还是没问题的
3.2 加一个注解试试,参数就是需要反序列化的class
3.2.1 示例代码
实体定义
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface InternalClass {
Class<?> value();
}
public class Test implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@InternalClass(Price.class)
private Map<String, Price> prices;
}
public class Price implements Serializable{
@JSONField(name="o")
private Double origanl_price;
@JSONField(name="p")
private Double price;
@JSONField(name="u")
private String union;
@JSONField(name="c")
private String currency;
}
测试案例
public static void mapJsonToFields(Object target, JSONObject jsonObject) throws IllegalAccessException {
Class<?> clazz = target.getClass();
for (Field field : clazz.getDeclaredFields()) {
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(InternalClass.class)) {
InternalClass annotation = field.getAnnotation(InternalClass.class);
Class<?> valueType = annotation.value();
field.setAccessible(true);
Map<String, ?> map = (Map<String, ?>) JSON.parseObject(
jsonObject.toJSONString(),
Map.class
);
Map<String, Object> typedMap = new java.util.HashMap<>();
for (Map.Entry<String, ?> entry : map.entrySet()) {
String key = entry.getKey();
JSONObject valueJson = (JSONObject) entry.getValue();
Object value = JSON.toJavaObject(valueJson, valueType);
typedMap.put(key, value);
}
field.set(target, typedMap);
}
}
}
@Test
public void test05() throws IllegalAccessException {
String jsonString = "{\"US\":{\"o\":62.0,\"p\":20.0,\"u\":\"$\",\"c\":\"USD\"}}";
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(jsonString);
GoodsTest goods = new GoodsTest();
JsonMapper.mapJsonToFields(goods, jsonObject);
Map<String, Price> prices = goods.getPrices();
Price usPrice = prices.get("US");
System.out.println(usPrice);
}
这样的话可以找到注解的值,然后根据这个class来进行反序列化
3.2.2 Debug
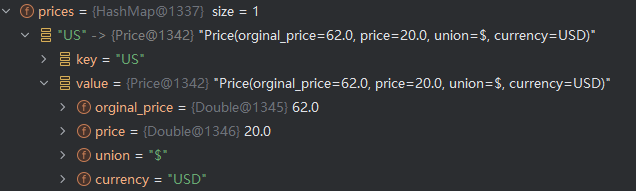
看看这个和第一版就知道了,完全可行。但是这个注解其实是多余的,在map的v位置的泛型,我们也是可以拿到对应的class的,于是就诞生出了版本3
3.3 再往里解析试试
3.3.1 实例代码
测试案例
public static void mapJsonToFields2(Test t, JSONObject json) {
try {
for (Field field : ReflectUtil.listField(t.getClass())) {
// ~~~~
if (field.getType() == Map.class) {
Type genericType = field.getGenericType();
if (genericType instanceof ParameterizedType) {
ParameterizedType parameterizedType = (ParameterizedType) genericType;
// 拿到了value的类型
Type valueType = parameterizedType.getActualTypeArguments()[1];
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
JSONObject mapJson = json.getJSONObject(field.getName());
if (mapJson != null) {
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : mapJson.entrySet()) {
String key = entry.getKey();
JSONObject valueJson = (JSONObject) entry.getValue();
// value起作用,哈哈哈哈
Object value = JSON.toJavaObject(valueJson, (Class<?>) valueType);
map.put(key, value);
}
}
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(t, map);
}
}
// ~
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Test
public void test03() throws IllegalAccessException {
String jsonString = "{\"prices\":{\"US\":{\"o\":62.0,\"p\":20.0,\"u\":\"$\",\"c\":\"USD\"}}}";
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(jsonString);
GoodsTest goods = new GoodsTest();
JsonMapper.mapJsonToFields2(goods, jsonObject);
Map<String, Price> prices = goods.getPrices();
Price usPrice = prices.get("US");
System.out.println(usPrice);
}
3.3.2 Debug
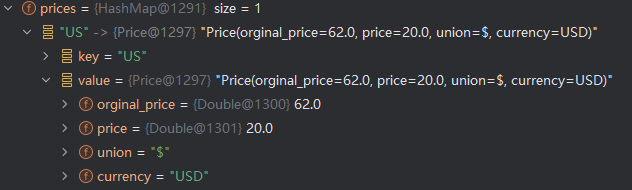
这个结果也是可行的,但是同样还有一个问题,如果套娃了怎么办?Price中又嵌套了一个?我只能说,设计数据结构的那个,打一架吧,把内层这个抽出来不好吗?(其实可以上递归,但,懒得写了🐶)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号