tensorflow训练线性回归模型
tensorflow安装
tensorflow安装过程不是很顺利,在这里记录一下
环境:Ubuntu
安装
sudo pip install tensorflow
如果出现错误
Could not findany downloads that satisfy the requirement tensorflow
执行
sudo pip install --upgrade pip
sudo pip install tensorflow
如果出现错误
Cannot uninstall 'six'.It is a distutils installed project and thus we cannot accurately determine which files belong to it which would lead to only a partial uninstall.
然后执行
sudo pip install six --upgrade --ignore-installed six
sudo pip install tensorflow
完整代码
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
#样本数据
x_train = np.linspace(-1,1,300)[:,np.newaxis]
noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.1, x_train.shape)
y_train = x_train * 3 + noise + 0.8
#线性模型
W = tf.Variable([0.1],dtype = tf.float32)
b = tf.Variable([0.1],dtype = tf.float32)
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
line_model = W * x + b
#损失模型
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
loss = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(line_model - y))
#创建优化器
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.001)
train = optimizer.minimize(loss)
#初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
# 绘制样本数据
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
ax.scatter(x_train, y_train)
plt.ion()
plt.show()
plt.pause(3)
#训练100次
for i in range(100):
#每隔10次打印1次成果
if i % 10 == 0:
print(i)
print('W:%s b:%s' % (sess.run(W),sess.run(b)))
print('loss:%s' % (sess.run(loss,{x:x_train,y:y_train})))
sess.run(train,{x:x_train,y:y_train})
print('---')
print('W:%s b:%s' % (sess.run(W),sess.run(b)))
print('loss:%s' % (sess.run(loss,{x:x_train,y:y_train})))
样本训练数据分布如下
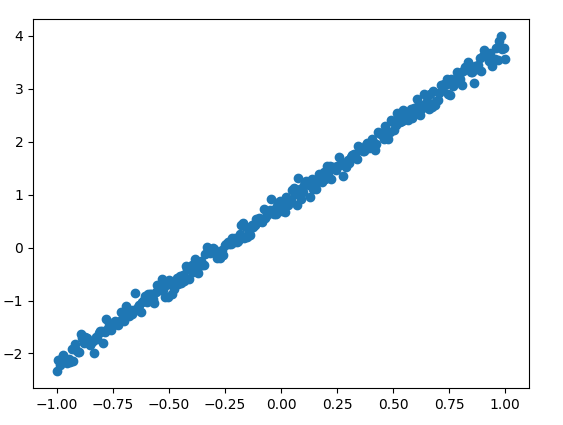
输出结果如下

结论
通过打印结果可以看到W已经非常接近初始给定的3,b也非常接近给定的0.8 (误差不可避免)
注:本文 代码+tensorboard功能 进阶,戳: https://www.cnblogs.com/maskerk/p/9973664.html
思考
-
与不用框架的神经网络学习( https://www.cnblogs.com/maskerk/p/9975510.html )相比,使用tensorflow进行迭代的时候,不会显式地处理 权重 和 偏差值 ,就是需要训练的参数。
-
在tensorflow框架下,只要定义成变量(tf.Variable)类型,在训练过程中,就会通过优化器顺藤摸瓜式的找到变量进行修改训练。
-
使用框架的话,套路居多,为什么这样做会变得模糊不清。所以要先看一下明白没有框架的代码是怎么运行的。再回头学框架的内容。

