java调用sap中文乱码
背景:java中调用SAP接口,传参body,接口参数能传过去,但是SAP接收到的中文乱码,如图:
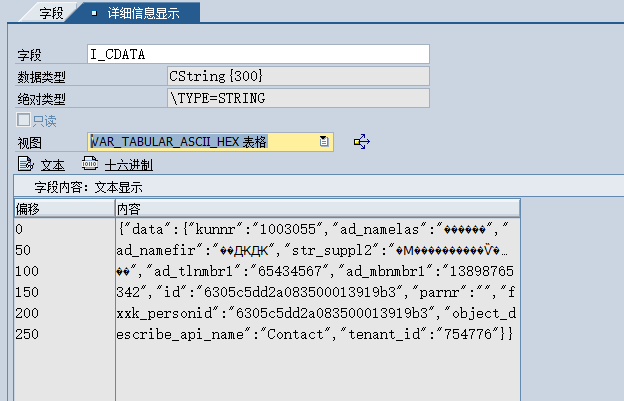
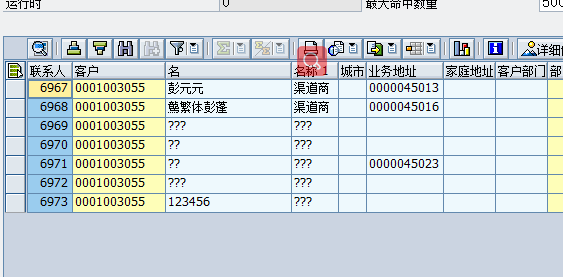
这里试了utf-8,GB2321,UTF-16LE,UTF-16BE等编码格式,SAP那边接收到的都是乱码,查遍了百度无果,方法几乎都一样,偶然看到一篇好几年前的帖子,破案了
原因:对方的SAP接口只支持接收繁体中文的编码格式UTF8,改成这个以后就好了
代码如下:
test:
String url="";
String jsonStr = "";
String httpOrgCreateTestRtn = HttpClientUtil.doPost(url, jsonStr, "utf-8");
//返回的数据要用utf-8接收,传的时候用utf8
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------调用
public static String doPost(String url,String jsonstr,String charset){
HttpClient httpClient = null;
HttpPost httpPost = null;
String result = null;
try{
httpClient = new SSLClient();
httpPost = new HttpPost(url);
httpPost.addHeader("content-type", "application/json;charset=UTF8");
httpPost.addHeader("Accept", "*/*");
httpPost.addHeader("Connection", "keep-alive");
System.out.println("jsonstrhttpPostEntity="+jsonstr);
StringEntity se=new StringEntity(jsonstr,"UTF8");
se.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF8");
se.setContentEncoding(new BasicHeader("Content-Type", "application/json"));
httpPost.setEntity(se);
System.out.println("httpPost="+httpPost);
System.out.println("httpPostEntitySE="+se);
HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
if(response != null){
HttpEntity resEntity = response.getEntity();
if(resEntity != null){
result = EntityUtils.toString(resEntity,charset);
}
}
}catch(Exception ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
--------------------------------------------------------------证书
package com.config;
import java.security.cert.CertificateException;
import java.security.cert.X509Certificate;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLContext;
import javax.net.ssl.TrustManager;
import javax.net.ssl.X509TrustManager;
import org.apache.http.conn.ClientConnectionManager;
import org.apache.http.conn.scheme.Scheme;
import org.apache.http.conn.scheme.SchemeRegistry;
import org.apache.http.conn.ssl.SSLSocketFactory;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.DefaultHttpClient;
/**
* 用于进行Https请求的HttpClient
* @ClassName: SSLClient
* @Description: TODO
* @author Devin <xxx>
* @date 2017年2月7日 下午1:42:07
*
*/
public class SSLClient extends DefaultHttpClient {
public SSLClient() throws Exception{
super();
SSLContext ctx = SSLContext.getInstance("TLS");
X509TrustManager tm = new X509TrustManager() {
@Override
public void checkClientTrusted(X509Certificate[] chain,
String authType) throws CertificateException {
}
@Override
public void checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] chain,
String authType) throws CertificateException {
}
@Override
public X509Certificate[] getAcceptedIssuers() {
return null;
}
};
ctx.init(null, new TrustManager[]{tm}, null);
SSLSocketFactory ssf = new SSLSocketFactory(ctx,SSLSocketFactory.ALLOW_ALL_HOSTNAME_VERIFIER);
ClientConnectionManager ccm = this.getConnectionManager();
SchemeRegistry sr = ccm.getSchemeRegistry();
sr.register(new Scheme("https", 443, ssf));
}
}

