获得计算机的网络信息
《网络程序设计》上机实验报告1
获得计算机的网络信息
[实验目的]
了解如何获得计算机的基本网络信息。
[实验要求]
给出实验中主要的程序代码以及运行结果,并把编译、运行过程中出现的问题以及解决方法填入实验报告中,按时上交。
[实验学时] 2 学时。
[实验内容]
1、获得计算机的MAC地址
实验中主要的程序代码
//#include "stdafx.h"
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include < windows.h >
#include < wincon.h >
#include < stdlib.h >
#include < stdio.h >
#include < time.h >
// 因为是通过NetAPI来获取网卡信息,所以需要包含其题头文件nb30.h#include < nb30.h >
//#include < nb30.h >
#pragma comment(lib,"Netapi32.lib")
typedef struct _ASTAT_{
ADAPTER_STATUS adapt;
NAME_BUFFER NameBuff[30];
}ASTAT, * PASTAT;
ASTAT Adapter;
// 定义一个存放返回网卡信息的变量
// 输入参数:lana_num为网卡编号,一般地,从0开始,但在Windows 2000中并不一定是连续分配的
void getmac_one(int lana_num)
{
NCB ncb;
UCHAR uRetCode;
memset(&ncb, 0, sizeof(ncb));
ncb.ncb_command = NCBRESET;
ncb.ncb_lana_num = lana_num;
// 指定网卡号
// 首先对选定的网卡发送一个NCBRESET命令,以便进行初始化
uRetCode = Netbios(&ncb);
printf("The NCBRESET return code is: 0x%x \n", uRetCode);
memset(&ncb, 0, sizeof(ncb));
ncb.ncb_command = NCBASTAT;
ncb.ncb_lana_num = lana_num; // 指定网卡号
strcpy((char*)ncb.ncb_callname, "* ");
ncb.ncb_buffer = (unsigned char*)&Adapter;
// 指定返回的信息存放的变量
ncb.ncb_length = sizeof(Adapter);
// 接着,可以发送NCBASTAT命令以获取网卡的信息
uRetCode = Netbios(&ncb);
printf("The NCBASTAT return code is: 0x%x \n", uRetCode);
if (uRetCode == 0){
// 把网卡MAC地址格式化成常用的16进制形式,如0010-A4E4-5802
printf("The Ethernet Number[%d] is: %02X%02X-%02X%02X-%02X%02X\n",
lana_num,
Adapter.adapt.adapter_address[0],
Adapter.adapt.adapter_address[1],
Adapter.adapt.adapter_address[2],
Adapter.adapt.adapter_address[3],
Adapter.adapt.adapter_address[4],
Adapter.adapt.adapter_address[5]);
}}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
NCB ncb;
UCHAR uRetCode;
LANA_ENUM lana_enum;
memset(&ncb, 0, sizeof(ncb));
ncb.ncb_command = NCBENUM;
ncb.ncb_buffer = (unsigned char*)&lana_enum;
ncb.ncb_length = sizeof(lana_enum);
// 向网卡发送NCBENUM命令,以获取当前机器的网卡信息,如有多少个网卡、每张网卡的编号等
uRetCode = Netbios(&ncb);
printf("The NCBENUM return code is: 0x%x \n", uRetCode);
if (uRetCode == 0){
printf("Ethernet Count is : %d\n\n", lana_enum.length);
// 对每一张网卡,以其网卡编号为输入编号,获取其MAC地址
for (int i = 0; i < lana_enum.length; ++i)
getmac_one(lana_enum.lana[i]);
}
return 0;
}
实验中主要的运行结果
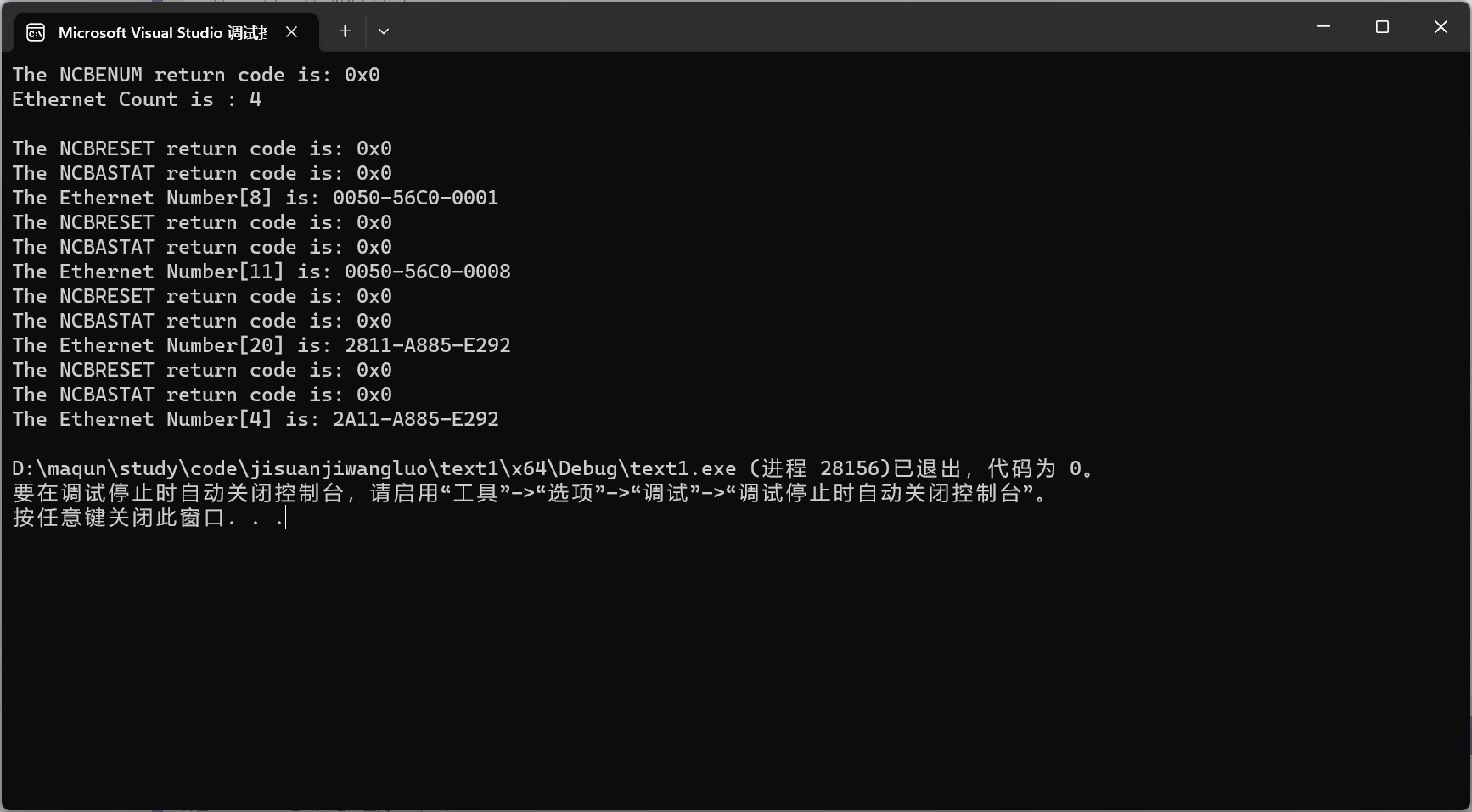
2.获得计算机的IP地址
实验中主要的程序代码
#define _WINSOCK_DEPRECATED_NO_WARNINGS
#include <winsock2.h>
#include <ws2tcpip.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
#pragma comment(lib, "ws2_32.lib")
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
// 声明和初始化变量
WSADATA wsaData;
int iResult; DWORD dwError; int i = 0;
struct hostent* remoteHost;
char host_name[256];
struct in_addr addr;
char** pAlias;
//初始化Windows Sockets
iResult = WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2, 2), &wsaData);
if (iResult != 0)
{
printf("WSAStartup failed: %d\n", iResult);
return 1;
}
//查找主机名
iResult = gethostname(host_name, sizeof(host_name));
if (iResult != 0)
{
printf("gethostname failed: %d\n", iResult);
return 1;
}
//根据主机名获得主机信息
remoteHost = gethostbyname(host_name);
printf("Calling gethostbyname with %s\n", host_name);
// 对返回结果进行判断
if (remoteHost == NULL){
dwError = WSAGetLastError();
if (dwError != 0){
if (dwError == WSAHOST_NOT_FOUND){
printf("Host not found\n");
return 1;
}
else if (dwError == WSANO_DATA){
printf("No data record found\n");
return 1;
}
else{
printf("Function failed with error: %ld\n", dwError);
return 1;
}}}
else{
printf("Function returned:\n");
printf("\tOfficial name: %s\n", remoteHost->h_name);
for (pAlias = remoteHost->h_aliases; *pAlias != 0; pAlias++){
printf("\tAlternate name #%d: %s\n", ++i, *pAlias);
}
printf("\tAddress type: ");
switch (remoteHost->h_addrtype){
case AF_INET:
printf("AF_INET\n");
break;
case AF_NETBIOS:
printf("AF_NETBIOS\n");
break;
default:
printf(" %d\n", remoteHost->h_addrtype);
break;
}
printf("\tAddress length: %d\n", remoteHost->h_length);
// 如果返回的是IPv4的地址, 则输出 i = 0;
if (remoteHost->h_addrtype == AF_INET){
while (remoteHost->h_addr_list[i] != 0){
addr.s_addr = *(u_long*)remoteHost->h_addr_list[i++];
printf("\tIP Address #%d: %s\n", i, inet_ntoa(addr));
}}
else if (remoteHost->h_addrtype == AF_NETBIOS){
printf("NETBIOS address was returned\n");
}}
return 0;
}
实验中主要的运行结果
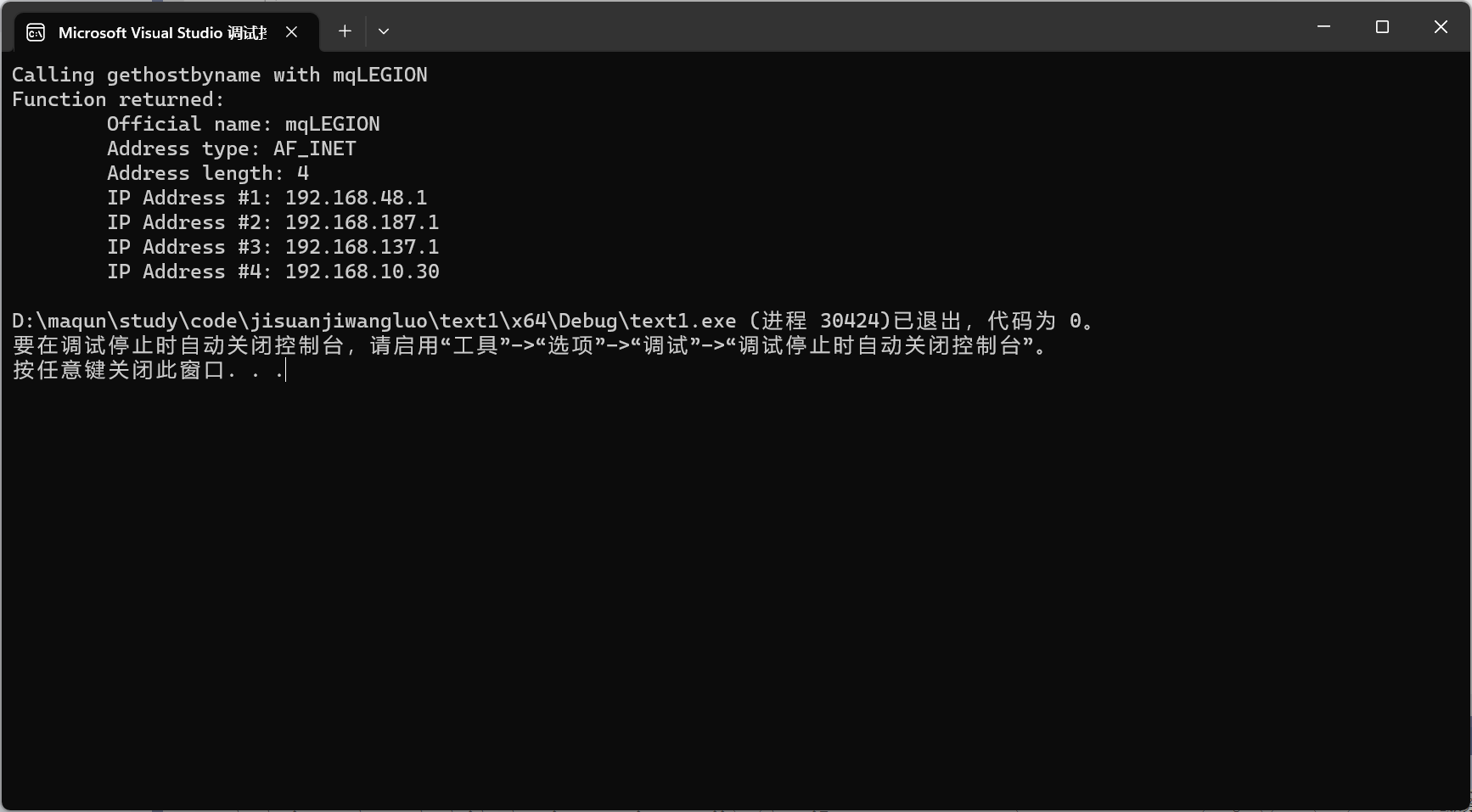
3.解析主机名称
实验中主要的程序代码
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("得到计算机名称和用户名称 \n");
const int MAX_BUFFER_LEN = 500;
char szBuffer[MAX_BUFFER_LEN];
DWORD dwNameLen;
dwNameLen = MAX_BUFFER_LEN;
if (!GetComputerName(szBuffer, &dwNameLen))
printf("Error %d\n", GetLastError());
else
printf("计算机名为: %s\n", szBuffer);
dwNameLen = MAX_BUFFER_LEN;
if (!GetUserName(szBuffer, &dwNameLen))
printf("Error %d\n", GetLastError());
else
printf("当前用户名为:%s\n", szBuffer);
return 0;
实验中主要的运行结果
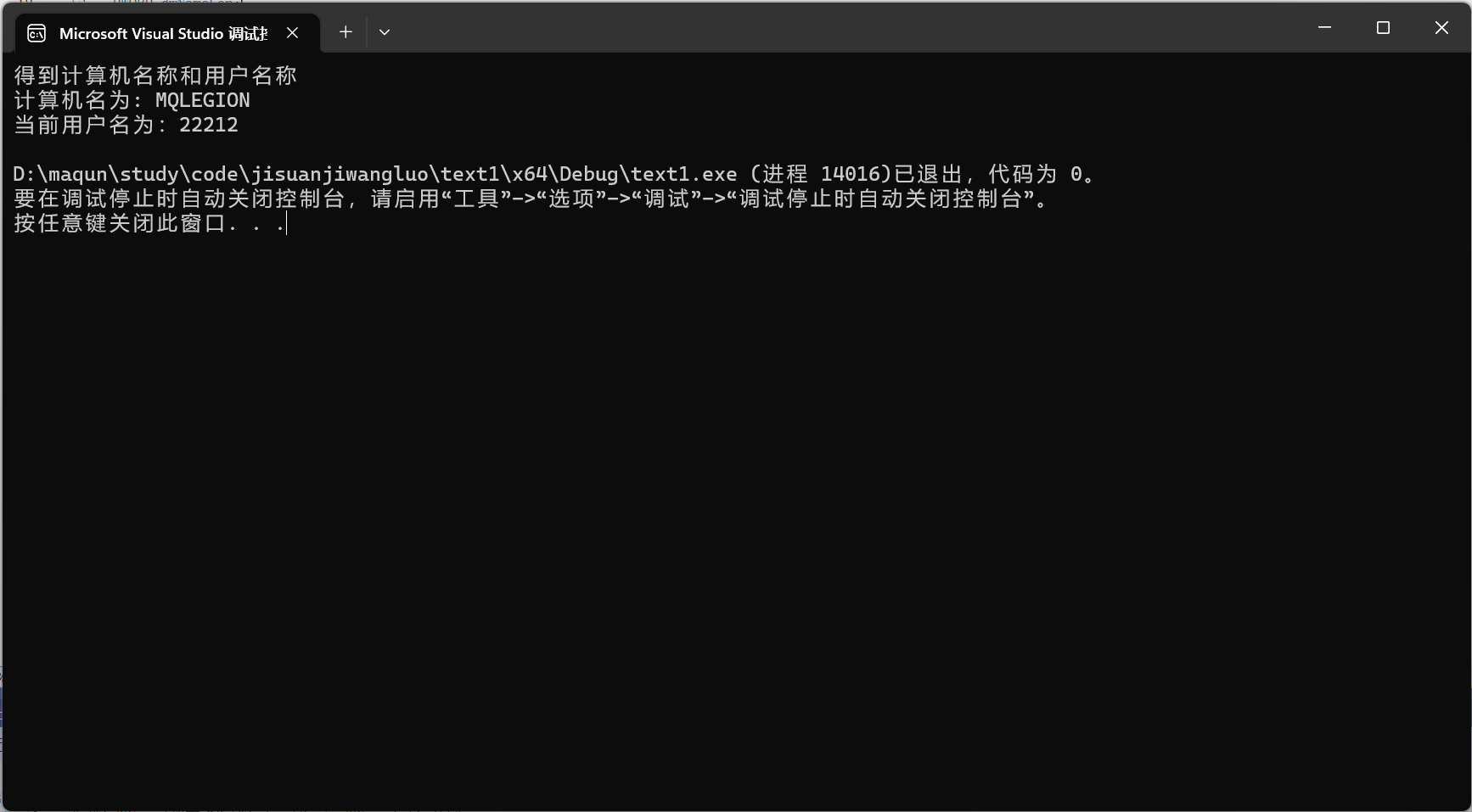
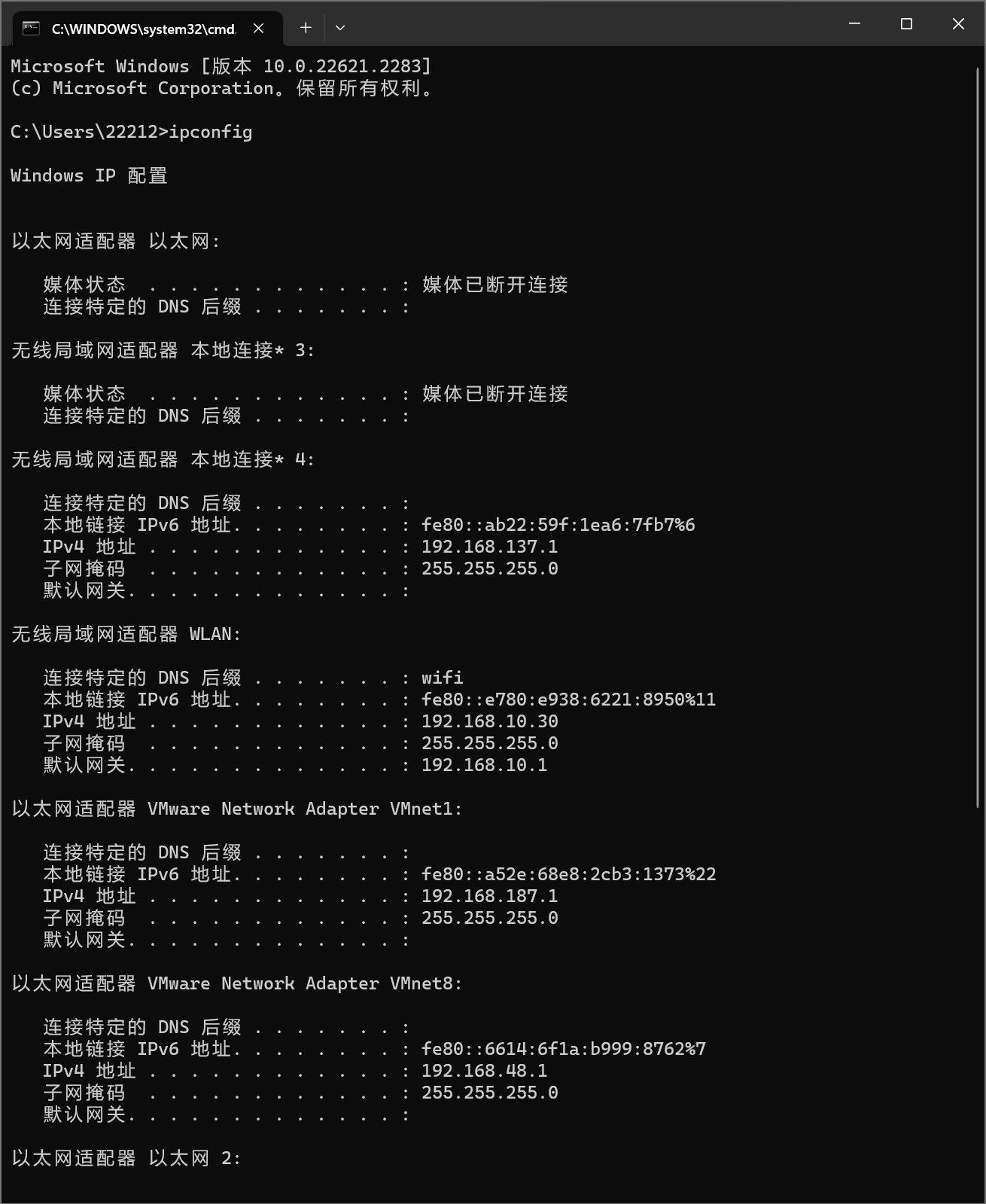
CMD命令 ipconfig查看本机的网路信息
[实验总结]
函数需要Platform SDK支持,需要ws2_32.lib 工程文件
#include <WinSock2.h>
#include <Ws2tcpip.h>
#pragma comment(lib,"ws2_32.lib")
gethostbyname( const char FAR *name ):根据主机名获取主机信息,返回
struct hostent FAR *;hostent 里有主机的IP地址
struct hostent {
char FAR * h_name; // 主机名
char FAR * FAR * h_aliases; // 别名
short h_addrtype; // 地址类型
short h_length; // 地址长度
char FAR * FAR * h_addr_list; // 地址列表
};
使用函数取出需要的内容并打印。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构