0138. Copy List with Random Pointer (M)
Copy List with Random Pointer (M)
题目
A linked list is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer which could point to any node in the list or null.
Return a deep copy of the list.
The Linked List is represented in the input/output as a list of n nodes. Each node is represented as a pair of [val, random_index] where:
val: an integer representingNode.valrandom_index: the index of the node (range from0ton-1) where random pointer points to, ornullif it does not point to any node.
Example 1:
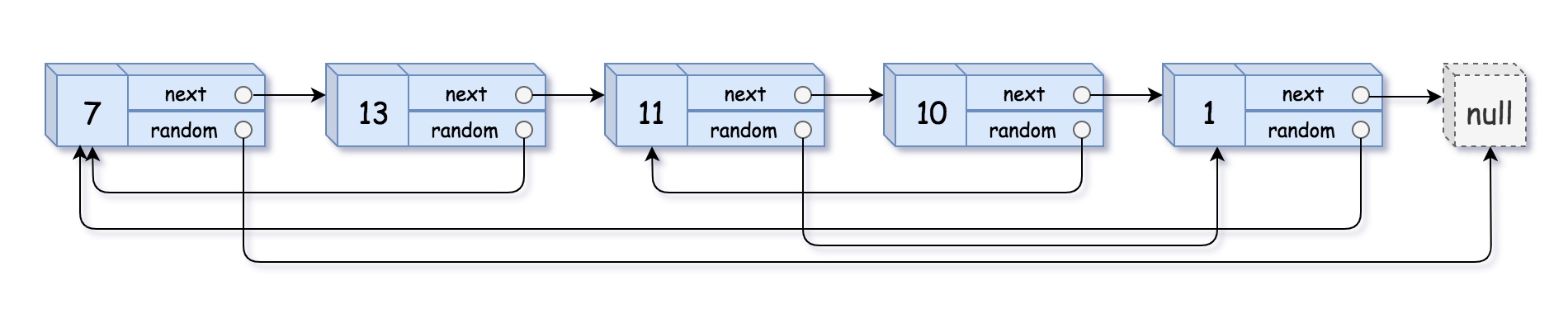
Input: head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Output: [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Example 2:
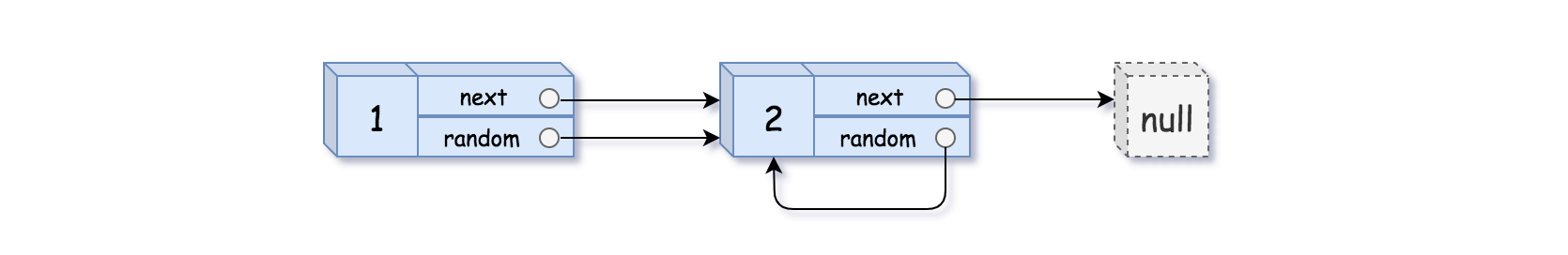
Input: head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
Output: [[1,1],[2,1]]
Example 3:
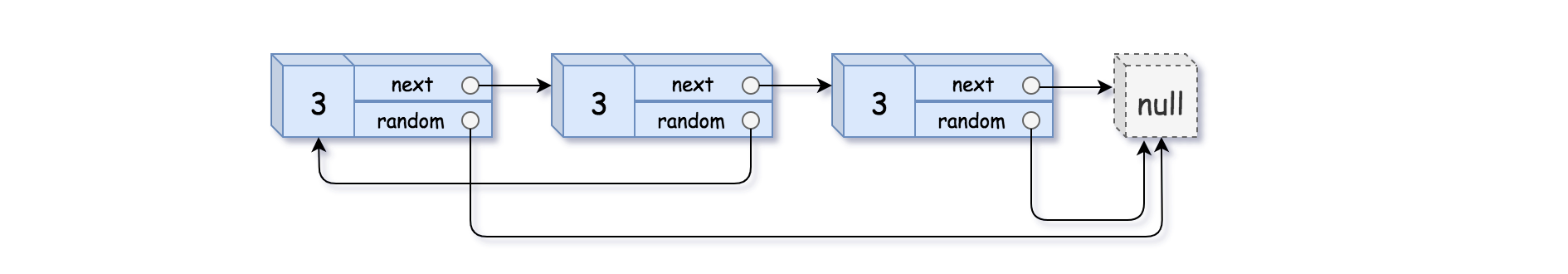
Input: head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Output: [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Example 4:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Explanation: Given linked list is empty (null pointer), so return null.
Constraints:
-10000 <= Node.val <= 10000Node.randomis null or pointing to a node in the linked list.- Number of Nodes will not exceed 1000.
题意
给定一个链表,该链表中有next和random两个域,next指向链表的下一个结点,random指向链表中随机一个结点或为null。要求返回该链表的一个深拷贝。
思路
拷贝next容易,难在拷贝random。问题的关键在于如何建立新旧链表对应结点之间的关系。
一种非常巧妙地方法是,每次拷贝一个结点A'后,将其插入到旧链表对应结点A之后,以此建立对应关系A->A',即A.next = A'。如果有A.random = B,且A'.random = B',根据之前建立的对应关系还能得到B.next = B',所以很容易发现A'.random = A.random.next。拷贝完所有的random后,只要再将新旧链表拆分出来即可。

也可以使用HashMap来绑定新旧结点,这样更加直观一点。
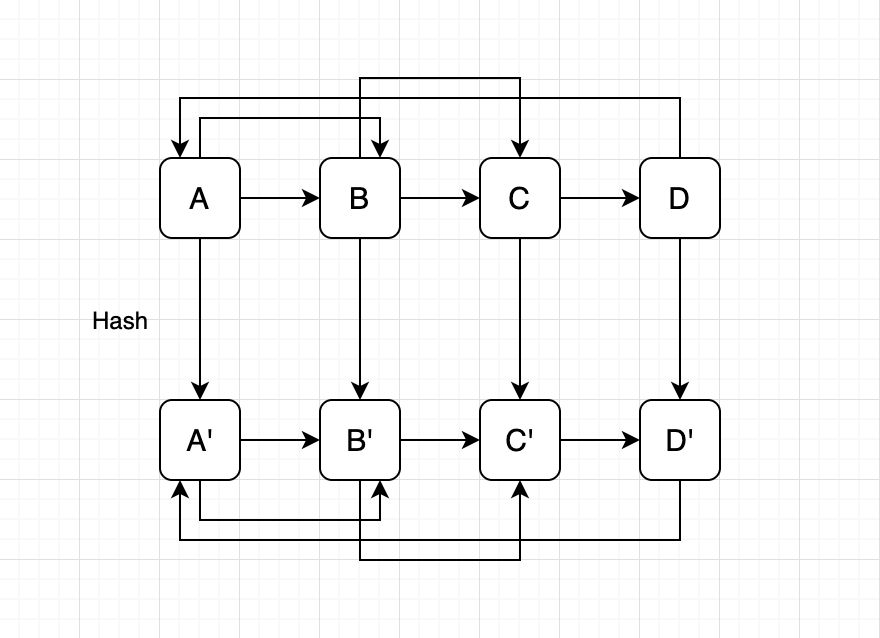
代码实现
Java
链表交叉
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
// 将新结点交叉插入到旧链表中
Node p = head;
while (p != null) {
Node temp = new Node(p.val);
temp.next = p.next;
p.next = temp;
p = temp.next;
}
// 生成新链表的random域
p = head;
while (p != null) {
Node q = p.next;
q.random = p.random == null ? null : p.random.next; // null单独处理
p = q.next;
}
// 拆分新旧链表
p = head;
Node dummy = new Node(0);
Node cur = dummy;
while (p != null) {
cur.next = p.next;
cur = cur.next;
p.next = cur.next;
p = p.next;
cur.next = null;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
Hash
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
Map<Node, Node> hash = new HashMap<>();
Node p = head;
Node dummy = new Node(0);
Node cur = dummy;
// 生成hash对应关系
while (p != null) {
cur.next = new Node(p.val);
cur = cur.next;
hash.put(p, cur);
p = p.next;
}
// 根据对应关系生成新链表的random域
p = head;
while (p != null) {
hash.get(p).random = p.random == null ? null : hash.get(p.random); // null单独处理
p = p.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
JavaScript
/**
* @param {Node} head
* @return {Node}
*/
var copyRandomList = function (head) {
let p = head
while (p) {
p.next = new Node(p.val, p.next, null)
p = p.next.next
}
p = head
while (p) {
p.next.random = p.random ? p.random.next : null
p = p.next.next
}
const dummy = new Node(0, null, null)
p = dummy
while (head) {
p.next = head.next
p = p.next
head.next = head.next.next
head = head.next
}
return dummy.next
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号