0116. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node (M)
Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node (M)
题目
You are given a perfect binary tree where all leaves are on the same level, and every parent has two children. The binary tree has the following definition:
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
Example:
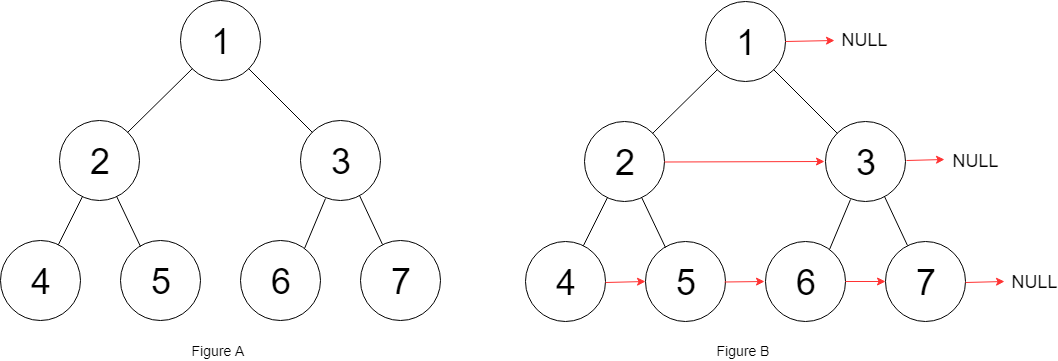
Input: {"$id":"1","left":{"$id":"2","left":{"$id":"3","left":null,"next":null,"right":null,"val":4},"next":null,"right":{"$id":"4","left":null,"next":null,"right":null,"val":5},"val":2},"next":null,"right":{"$id":"5","left":{"$id":"6","left":null,"next":null,"right":null,"val":6},"next":null,"right":{"$id":"7","left":null,"next":null,"right":null,"val":7},"val":3},"val":1}
Output: {"$id":"1","left":{"$id":"2","left":{"$id":"3","left":null,"next":{"$id":"4","left":null,"next":{"$id":"5","left":null,"next":{"$id":"6","left":null,"next":null,"right":null,"val":7},"right":null,"val":6},"right":null,"val":5},"right":null,"val":4},"next":{"$id":"7","left":{"$ref":"5"},"next":null,"right":{"$ref":"6"},"val":3},"right":{"$ref":"4"},"val":2},"next":null,"right":{"$ref":"7"},"val":1}
Explanation: Given the above perfect binary tree (Figure A), your function should populate each next pointer to point to its next right node, just like in Figure B.
Note:
- You may only use constant extra space.
- Recursive approach is fine, implicit stack space does not count as extra space for this problem.
题意
对于满二叉树的每一层,将当前层每一个结点的next域指向该层的右边一个结点;如果已经是当前层的最右结点,则指向null。(限制只能使用\(O(1)\)的额外空间,如果使用递归,则系统栈不计入额外空间)
思路
如果不限制额外空间大小,最简单的做法是层序遍历处理。
两种使用递归的方法:
- 递归参数有两个,分别是同一层上相邻的两个节点A和B,在完成连接 \(A.next = B\) 后,它们子树的连接只有三种情况:\(A.left.next = A.right\)、\(A.right.next=B.left\)、\(B.left.next=B.right\),所以只要递归处理这三种情况即可。当然这种递归方式存在重复连接的情况,因为同一个子树可能被多次递归访问。
- 递归参数只有一个,即当前子树的根节点x(x与它右边兄弟结点的连接已经处理完毕),如果x存在左子树,由满二叉树的性质,则x一定存在右子树,同时如果x存在兄弟结点y,则y也一定存在左子树。将x的左子树、右子树和y的左子树相连,就完成了本层递归,接着继续向x的左右子树递归即可。
另有一种只需要\(O(1)\)空间的迭代方法:
用head指向每一层的最左侧结点,用cur从左到右遍历(通过next连接)该层所有结点,在遍历过程中将每个结点的左右子结点与右兄弟结点的左子结点相连。迭代head处理所有层。
代码实现
Java
递归1
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
connect(root.left, root.right);
return root;
}
private void connect(Node x, Node y) {
if (x == null || y == null) {
return;
}
x.next = y;
// 分三种情况处理子树连接
connect(x.left, x.right);
connect(x.right, y.left);
connect(y.left, y.right);
}
}
递归 2
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
rConnect(root);
return root;
}
private void rConnect(Node x) {
if (x == null) {
return;
}
// 满二叉树的性质,如果存在左子树则必然存在右子树,且若存在兄弟结点,则兄弟结点也必存在左子树
if (x.left != null) {
x.left.next = x.right;
if (x.next != null) {
x.right.next = x.next.left;
}
}
rConnect(x.left);
rConnect(x.right);
}
}
层序遍历(O(1)额外空间)
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
Node head = root;
while (head.left != null) {
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
cur.left.next = cur.right;
if (cur.next != null) {
cur.right.next = cur.next.left;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
head = head.left;
}
return root;
}
}
层序遍历(非O(1)额外空间)
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
Queue<Node> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
Node[] level = q.toArray(new Node[size]);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (i != size - 1) {
level[i].next = level[i + 1];
}
Node cur = q.poll();
if (cur.left != null) q.offer(cur.left);
if (cur.right != null) q.offer(cur.right);
}
}
return root;
}
}
JavaScript
/**
* @param {Node} root
* @return {Node}
*/
var connect = function (root) {
let q = []
if (root) {
q.push(root)
}
while (q.length) {
let pre = null
let size = q.length
for (let i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
pre = q.shift()
} else {
let cur = q.shift()
pre.next = cur
pre = cur
}
if (pre.left) q.push(pre.left)
if (pre.right) q.push(pre.right)
}
}
return root
}
参考



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号