LangChain的LCEL和Runnable你搞懂了吗
LangChain的LCEL估计行业内的朋友都听过,但是LCEL里的RunnablePassthrough、RunnableParallel、RunnableBranch、RunnableLambda又是什么意思?什么场景下用?
1、LCEL的定义和原理
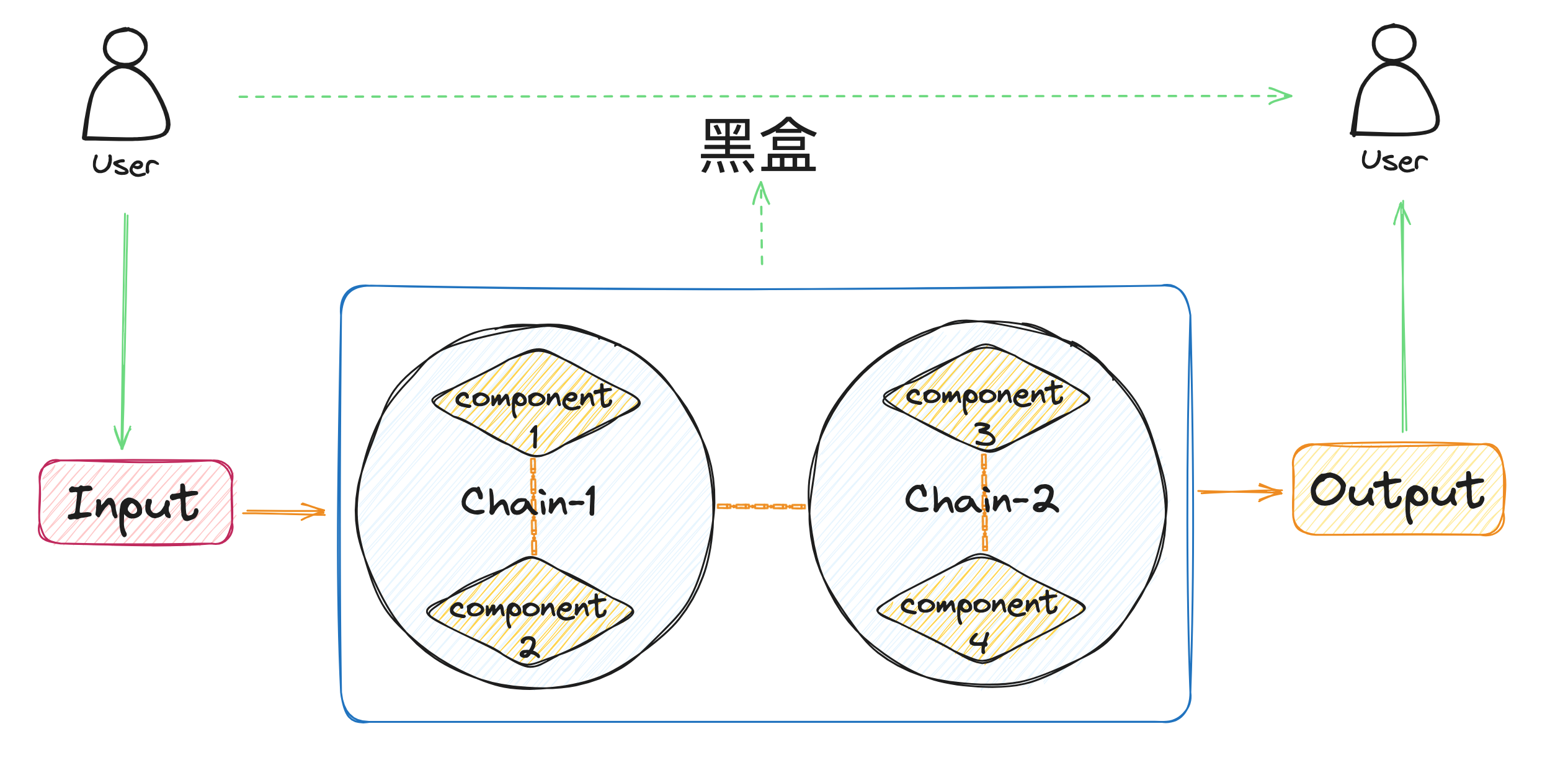
LangChain的核心是Chain,即对多个组件的一系列调用。
LCEL是LangChain 定义的表达式语言,是一种更加高效简洁的调用一系列组件的方式。
LCEL使用方式就是:以一堆管道符("|")串联所有实现了Runnable接口的组件。
比如这样:
prompt_tpl = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", "{parser_instructions}"),
("human", "列出{cityName}的{viewPointNum}个著名景点。"),
]
)
output_parser = CommaSeparatedListOutputParser()
parser_instructions = output_parser.get_format_instructions()
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo")
chain = prompt_tpl | model | output_parser
response = chain.invoke(
{"cityName": "南京", "viewPointNum": 3, "parser_instructions": parser_instructions}
)
所以LangChain为了让组件能以LCEL的方式快速简洁的被调用,计划将所有组件都实现Runnable接口。比如我们常用的PromptTemplate 、LLMChain 、StructuredOutputParser 等等。
管道符("|")在Python里就类似or运算(或运算),比如A|B,就是A.or(B)。
那对应到LangChain的Runnable接口里,这个or运算是怎么实现的呢?一起看到源码:
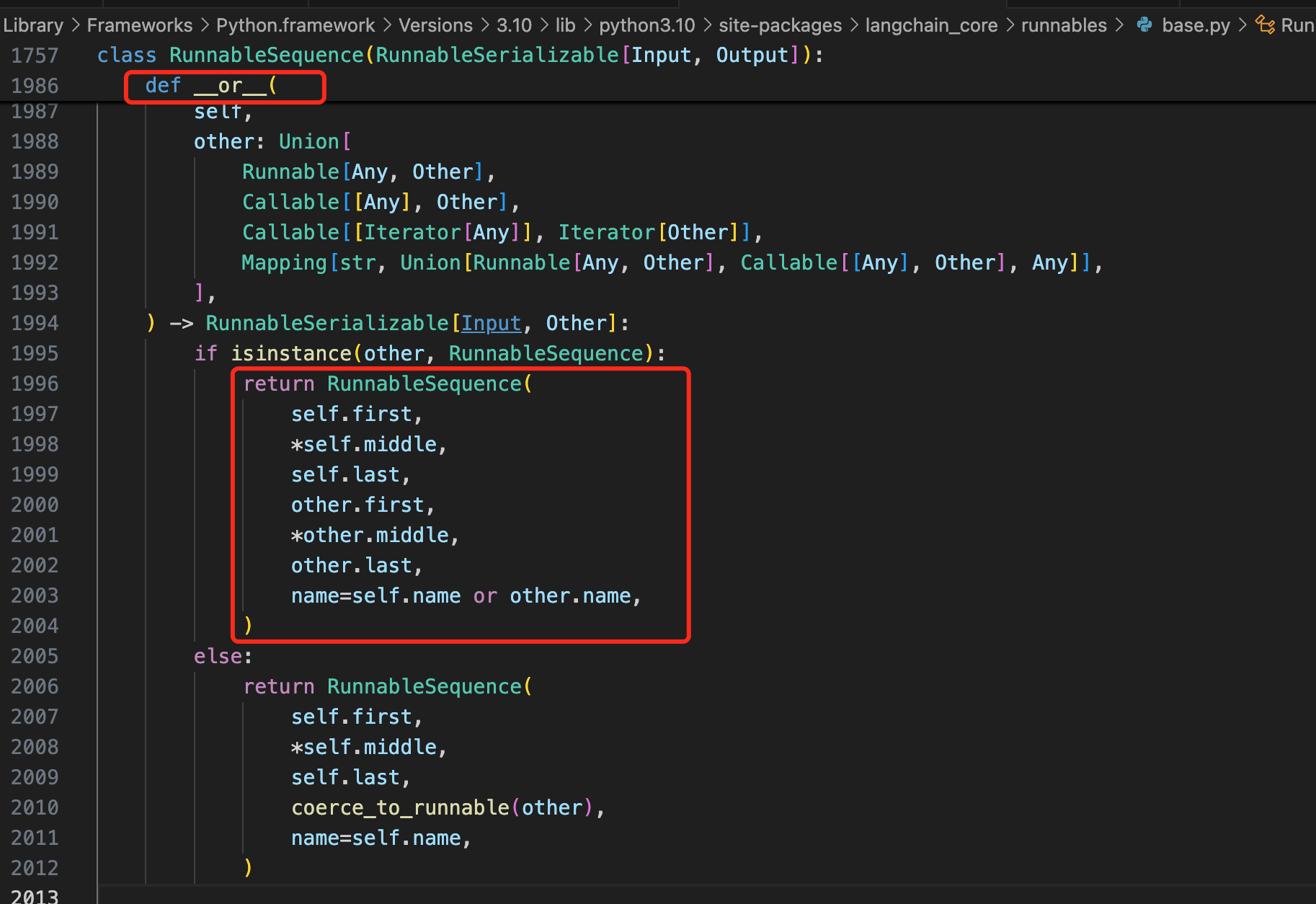
LangChain通过or将所有的Runnable串联起来,在通过invoke去一个个执行,上一个组件的输出,作为下一个组件的输入。
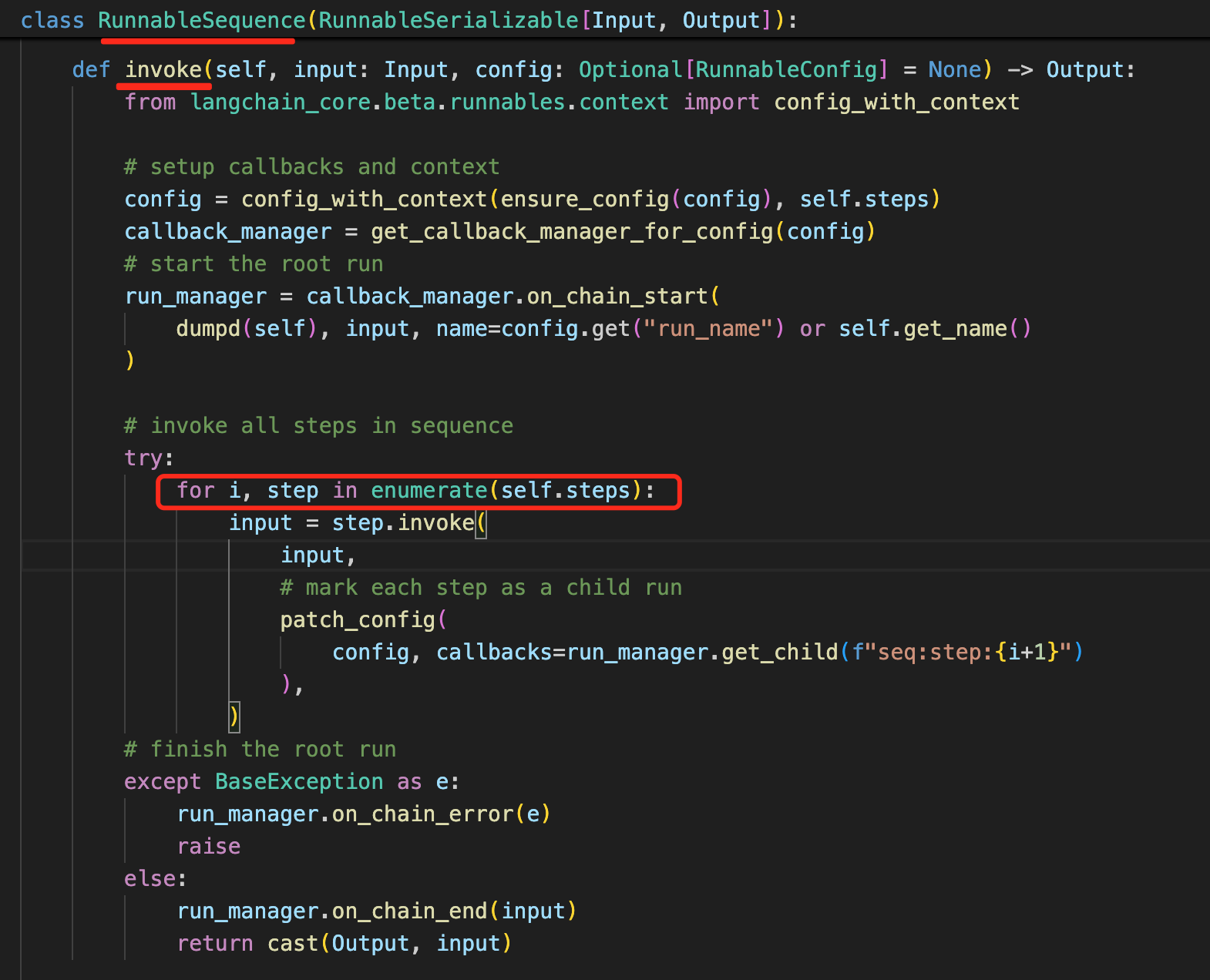
LangChain这风格怎么有点像神经网络呀,不得不说,这个世界到处都是相似的草台班子。嗨!
总结起来讲就是:LangChain的每个组件都实现了Runnable,通过LCEL方式,将多个组件串联到一起,最后一个个执行每个组件的invoke方法。上一个组件的输出是下一个组件的输入。
2、Runnable的含义和应用场景
2.1、RunnablePassthrough
定义
RunnablePassthrough 主要用在链中传递数据。RunnablePassthrough一般用在链的第一个位置,用于接收用户的输入。如果处在中间位置,则用于接收上一步的输出。
应用场景
比如,依旧使用上面的例子,接受用户输入的城市,如果输入城市是南京,则替换成北京,其余不变。代码如下。此处的{}和RunnablePassthrough.assign()是同一个语义。
chain = (
{
"cityName": lambda x: '北京' if x["cityName"] == '南京' else x["cityName"],
"viewPointNum": lambda x: x["viewPointNum"],
"parser_instructions": lambda x: x["parser_instructions"],
}
| prompt_tpl
| model
| output_parser
)
2.2、RunnableParallel
定义
RunnableParallel看名字里的Parallel就猜到一二,用于并行执行多个组件。通过RunnableParallel,可以实现部分组件或所有组件并发执行的需求。
应用场景
比如,同时要执行两个任务,一个列出城市著名景点,一个列出城市著名书籍。
prompt_tpl_1 = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", "{parser_instructions}"),
("human", "列出{cityName}的{viewPointNum}个著名景点。"),
]
)
prompt_tpl_2 = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", "{parser_instructions}"),
("human", "列出关于{cityName}历史的{viewPointNum}个著名书籍。"),
]
)
output_parser = CommaSeparatedListOutputParser()
parser_instructions = output_parser.get_format_instructions()
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo")
chain_1 = prompt_tpl_1 | model | output_parser
chain_2 = prompt_tpl_2 | model | output_parser
chain_parallel = RunnableParallel(view_point=chain_1, book=chain_2)
response = chain_parallel.invoke(
{"cityName": "南京", "viewPointNum": 3, "parser_instructions": parser_instructions}
)
2.3、RunnableBranch
定义
RunnableBranch主要用于多分支子链的场景,为链的调用提供了路由功能,这个有点类似于LangChain的路由链。我们可以创建多个子链,然后根据条件选择执行某一个子链。
应用场景
比如,有多个回答问题的链,先根据问题找到分类,然后在使用具体的链回答问题。
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo")
output_parser = StrOutputParser()
# 准备2条目的链:一条物理链,一条数学链
# 1. 物理链
physics_template = """
你是一位物理学家,擅长回答物理相关的问题,当你不知道问题的答案时,你就回答不知道。
具体问题如下:
{input}
"""
physics_chain = PromptTemplate.from_template(physics_template) | model | output_parser
# 2. 数学链
math_template = """
你是一个数学家,擅长回答数学相关的问题,当你不知道问题的答案时,你就回答不知道。
具体问题如下:
{input}
"""
math_chain = PromptTemplate.from_template(math_template) | model | output_parser
# 4. 其他链
other_template = """
你是一个AI助手,你会回答一下问题。
具体问题如下:
{input}
"""
other_chain = PromptTemplate.from_template(other_template) | model | output_parser
classify_prompt_template = """
请你对以下问题进行分类,将问题分类为"数学"、"物理"、"其它",不需要返回多个分类,返回一个即可。
具体问题如下:
{input}
分类结果:
"""
classify_chain = PromptTemplate.from_template(classify_prompt_template) | model | output_parser
answer_chain = RunnableBranch(
(lambda x: "数学" in x["topic"], math_chain),
(lambda x: "物理" in x["topic"], physics_chain),
other_chain
)
final_chain = {"topic": classify_chain, "input": itemgetter("input")} | RunnableLambda(print_info) | answer_chain
# final_chain.invoke({"input":"地球的半径是多少?"})
final_chain.invoke({"input":"对y=x求导的结果是多少?"})
2.4、RunnableLambda
定义
要说牛批还得是RunnableLambda,它可以将Python 函数转换为 Runnable对象。这种转换使得任何函数都可以被看作 LCEL 链的一部分,我们把自己需要的功能通过自定义函数 + RunnableLambda的方式包装一下,集成到 LCEL 链中,这样算是可以跟任何外部系统打通了。
应用场景
比如,在执行过程中,想在中间插入一段自定义功能(如 打印日志 等),可以通过自定义函数 + RunnableLambda的方式实现。
def print_info(info: str):
print(f"info: {info}")
return info
prompt_tpl_1 = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", "{parser_instructions}"),
("human", "列出{cityName}的{viewPointNum}个著名景点。"),
]
)
output_parser = CommaSeparatedListOutputParser()
parser_instructions = output_parser.get_format_instructions()
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo")
chain_1 = prompt_tpl_1 | model | RunnableLambda(print_info) | output_parser
response = chain_1.invoke(
{"cityName": "南京", "viewPointNum": 3, "parser_instructions": parser_instructions}
)
3、总结
本篇主要聊了LangChain的LCEL表达式,以及LangChain链的原理,以及常用的几个Runnable的定义和应用场景,希望对你有帮助。
近期我准备推出一个关于《助力开发者加持AI技术》的专栏,感兴趣的小伙伴可以加微信交流。
本篇完结!欢迎 关注、加微信(yclxiao)交流、二维码如下!!!
原文链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/l-EPH0hsmzQousPz8-MXcQ





【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 没有源码,如何修改代码逻辑?
· PowerShell开发游戏 · 打蜜蜂
· 在鹅厂做java开发是什么体验
· 百万级群聊的设计实践
· WPF到Web的无缝过渡:英雄联盟客户端的OpenSilver迁移实战