SQL学习
一、分区表
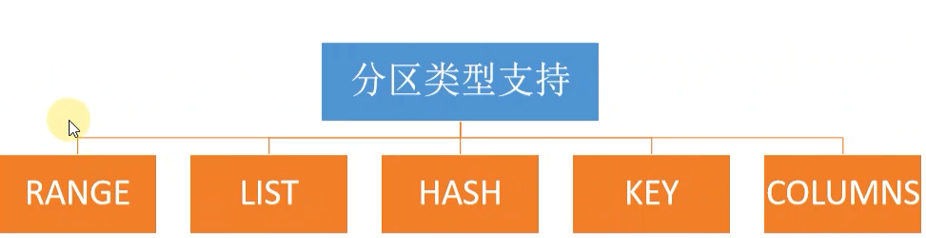
1.1、分区的类型
1.2、分区表的原数据
(root@localhost) [dbt3]> use information_schema; Reading table information for completion of table and column names You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A (root@localhost) [information_schema]> desc PARTITIONS; +-------------------------------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------------------------------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | TABLE_CATALOG | varchar(512) | NO | | | | | TABLE_SCHEMA | varchar(64) | NO | | | | | TABLE_NAME | varchar(64) | NO | | | | | PARTITION_NAME | varchar(64) | YES | | NULL | | | SUBPARTITION_NAME | varchar(64) | YES | | NULL | | | PARTITION_ORDINAL_POSITION | bigint(21) unsigned | YES | | NULL | | | SUBPARTITION_ORDINAL_POSITION | bigint(21) unsigned | YES | | NULL | | | PARTITION_METHOD | varchar(18) | YES | | NULL | | | SUBPARTITION_METHOD | varchar(12) | YES | | NULL | | | PARTITION_EXPRESSION | longtext | YES | | NULL | | | SUBPARTITION_EXPRESSION | longtext | YES | | NULL | | | PARTITION_DESCRIPTION | longtext | YES | | NULL | | | TABLE_ROWS | bigint(21) unsigned | NO | | 0 | | | AVG_ROW_LENGTH | bigint(21) unsigned | NO | | 0 | | | DATA_LENGTH | bigint(21) unsigned | NO | | 0 | | | MAX_DATA_LENGTH | bigint(21) unsigned | YES | | NULL | | | INDEX_LENGTH | bigint(21) unsigned | NO | | 0 | | | DATA_FREE | bigint(21) unsigned | NO | | 0 | | | CREATE_TIME | datetime | YES | | NULL | | | UPDATE_TIME | datetime | YES | | NULL | | | CHECK_TIME | datetime | YES | | NULL | | | CHECKSUM | bigint(21) unsigned | YES | | NULL | | | PARTITION_COMMENT | varchar(80) | NO | | | | | NODEGROUP | varchar(12) | NO | | | | | TABLESPACE_NAME | varchar(64) | YES | | NULL | | +-------------------------------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 25 rows in set (0.00 sec)
1.3、分区规则
分区列必须是唯一索引的组成部分
二、表结构范式
范式:数据库范式是一个可以帮助避免数据异常,和数据管理时候出现其他问题的技术,他由各阶段的表转化组成:第一范式、第二范式、第三范式;
范式的目的:
消除数据冗余;
使数据的更改更容易,而且避免这样做的时候出现异常;
更容易执行一致性约束;
产生一个更容易理解的结构;

三、SQL语句
用于排序的内存
(root@localhost) [db1]> show variables like 'sort_buffer_size'; +------------------+--------+ | Variable_name | Value | +------------------+--------+ | sort_buffer_size | 262144 | +------------------+--------+ 1 row in set (0.06 sec)
配置文件配置sort_buffer_size大小
#session memory
sort_buffer_size=32M
3.1、Group by
SELECT DATE_FORMAT(o_orderDATE, '%Y%m'), sum(o_totalprice) FROM orders GROUP BY DATE_FORMAT(o_orderDATE, '%Y%m');
每个员工,每个月的订单总量,及平均值
SELECT DATE_FORMAT(o_orderDATE, '%Y-%m'), count(1), o_clerk, sum(o_totalprice), avg(o_totalprice) FROM orders GROUP BY DATE_FORMAT(o_orderDATE, '%Y-%m'), o_clerk;
查询过程中,查看系统产生基于磁盘的表
(root@localhost) [dbt3]> show status like '%tmp%'; +-------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +-------------------------+-------+ | Created_tmp_disk_tables | 0 | | Created_tmp_files | 25 | | Created_tmp_tables | 7 | +-------------------------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
将排序临时数据表空间的设置写入配置文件,空间足够,表将不在写入磁盘
tmp_table_size=32M
3.2、count(*)
(root@localhost) [db1]> select * from f; +------+ | aa | +------+ | 1 | | 3 | | 5 | | NULL | +------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) (root@localhost) [db1]> select count(1),count(*),count(100),count(aa) from f; +----------+----------+------------+-----------+ | count(1) | count(*) | count(100) | count(aa) | +----------+----------+------------+-----------+ | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 | +----------+----------+------------+-----------+ 1 row in set (0.01 sec)
3.3、group_concat函数,将分组以外的列,列出来
SELECT
o_clerk,
GROUP_CONCAT(o_orderstatus)
FROM
orders
GROUP BY
o_clerk;
默认使用逗号分割,可以自己定义
SELECT o_clerk, GROUP_CONCAT(o_orderstatus SEPARATOR ':') FROM orders GROUP BY o_clerk;
3.4、子查询
select * from orders where o_orderpriority in ('5-LOW','2-HIGH');
3.5、SQL中设置变量
set @a:=0; select @a:=@a+1,emp_no,birth_date,first_name,last_name from employees limit 10;
四、Prepared Statement
MySQL 5.7 provides support for server-side prepared statements. This support takes advantage of the efficient client/server binary protocol. Using prepared statements with placeholders(占位符) for parameter(参数) values has the following benefits:
-
Less overhead for parsing the statement each time it is executed. Typically, database applications process large volumes of almost-identical(几乎相同) statements, with only changes to literal or variable values in clauses such as
WHEREfor queries and deletes,SETfor updates, andVALUESfor inserts. -
Protection against SQL injection attacks. The parameter values can contain unescaped SQL quote and delimiter characters.
减少每次语句执行的语法分析。典型的,数据库应用程序处理大量几乎相同的语句,Prepare可以只更改字符值或者变量值,比如查询或者删除的WHERE子句,或者update中的SET变量,insert语句中的VALUES值;
防范SQL注入攻击,存储过程的定义的值可以包含未转义的SQL引号和分隔符;
The first example shows how to create a prepared statement by using a string literal to supply the text of the statement:
(root@localhost) [(none)]> prepare stmt1 from 'select sqrt(pow(?,2)+pow(?,2)) as hypotenuse'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) Statement prepared (root@localhost) [(none)]> set @a=3; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) (root@localhost) [(none)]> set @b=4; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) (root@localhost) [(none)]> execute stmt1 using @a,@b; +------------+ | hypotenuse | +------------+ | 5 | +------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
(root@localhost) [(none)]> DEALLOCATE PREPARE stmt1;
SQL语句作为变量
SET @s = 'select * from employees where 1=1'; SET @s = concat(@s, ' and gender="m"'); SET @s = concat(@s, ' and birth_date >= "1960-01-01"'); PREPARE stmt FROM @s; EXECUTE stmt; DEALLOCATE PREPARE stmt;
五、一个简单的SQL注入
select * from employees where emp_no=10001 or 1=1;
可以查到全部的表记录
用存储过程避免SQL注入
(root@localhost) [employees]> set @s='select * from employees where emp_no=?'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) (root@localhost) [employees]> set @a='10001 or 1=1'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) (root@localhost) [employees]> prepare stmt from @s; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) Statement prepared (root@localhost) [employees]> execute stmt using @a; +--------+------------+------------+-----------+--------+------------+ | emp_no | birth_date | first_name | last_name | gender | hire_date | +--------+------------+------------+-----------+--------+------------+ | 10001 | 1953-09-02 | Georgi | Facello | M | 1986-06-26 | +--------+------------+------------+-----------+--------+------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
六、DML语句
insert,插入如果有重复的语句
insert into t6 values(2) on DUPLICATE key update id=id+10;
七、临时表
创建临时表
(root@localhost) [db1]> create temporary table a(id int); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
临时表是会话级别的,回话退出,表就不存在了;

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号