2016012054+小学四则运算练习软件项目报告
作业源代码地址:https://git.coding.net/mal123/elementary_arithmetic2.git
1、需要实现的功能
·程序可接收一个输入参数n,然后随机产生n道加减乘除(分别使用符号+-*÷来表示)练习题,每个数字在 0 和 100 之间,运算符在3个到5个之间;
·每个练习题至少要包含2种运算符;同时,所出的练习题在运算过程中不得出现负数与非整数;
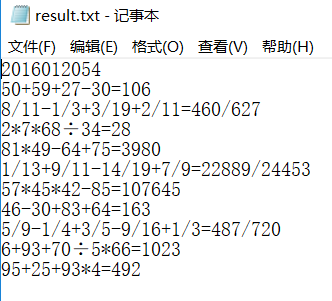
·练习题生成好后,将你的学号与生成的n道练习题及其对应的正确答案输出到文件“result.txt”中,不要输出额外信息,文件目录与程序目录一致。
·支持有括号的运算式,包括出题与求解正确答案。注意,算式中存在的括号必须大于2个,且不得超过运算符的个数。(附加)
·支持真分数的出题与运算(只需要涵盖加减法),注意在实现本功能时,需支持运算时分数的自动化简,且计算过程中与结果都须为真分数。(附加)
2、具体分析
项目的主要功能:
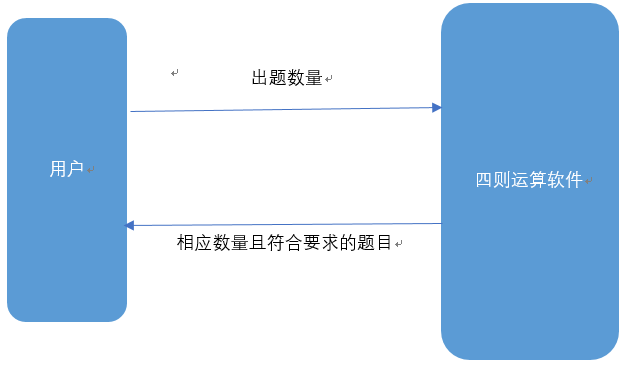
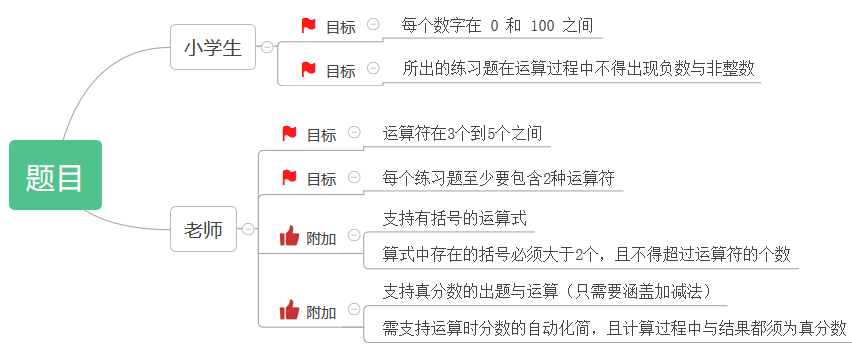
题目的具体要求:
面向用户:小学生、老师
针对小学生对于四则运算的掌握情况以及老师所要达到锻炼学生的目的,对于题目有如下要求:
二、功能设计
1、基本功能
·随机产生运算符(个数为3-5个),且至少有2种运算符。
·随机产生运算数(个数为运算符个数+1),且每个数字在0-100之间。
·计算题目:1.判断优先级 2.判断是否出现负数,小数,以及除数不能为0。
·根据用户输入的个数,产生相应的题目数量。(判断输入参数是否合法[int类型][1-1000之间])
·创建result.txt(在根目录下),将生成的题目写入result.txt中,并在第一行显示自己学号。
·能够在命令行进行测试。项目必须包含src文件夹,在src文件夹中必须包含名为Main.java文件,且Main.java中包含 public static void main(String[] args) 方法。
2、扩展功能
·随机产生括号,算式中存在的括号必须大于2个,且不得超过运算符的个数。(确保不会出现无意义的括号)
·支持真分数的出题与运算(只需要涵盖加减法),支持运算时分数的自动化简,且计算过程中与结果都须为真分数。
三、设计实现
考虑到时间的问题,所以我只对基本功能的实现进行了设计。具体的设计如下:
用例图:
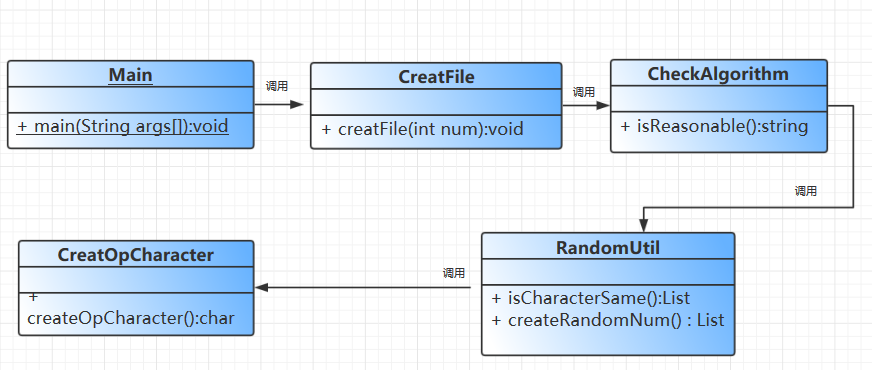
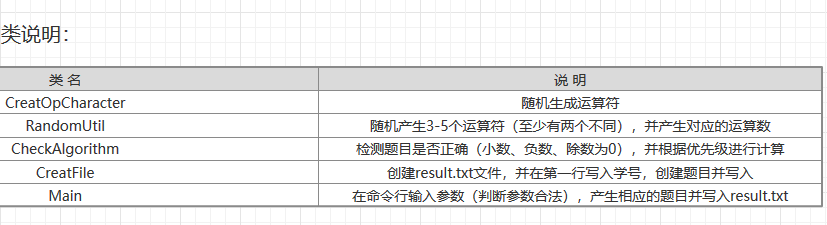
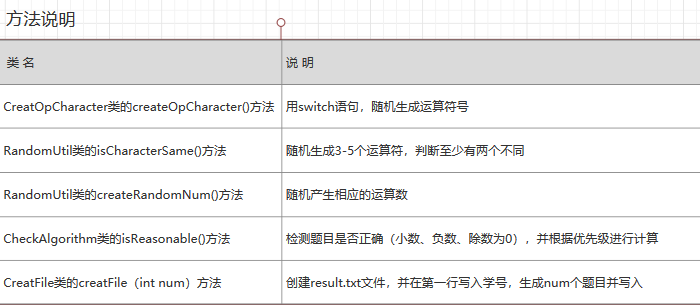 \
\
isReasonable()方法的流程图:
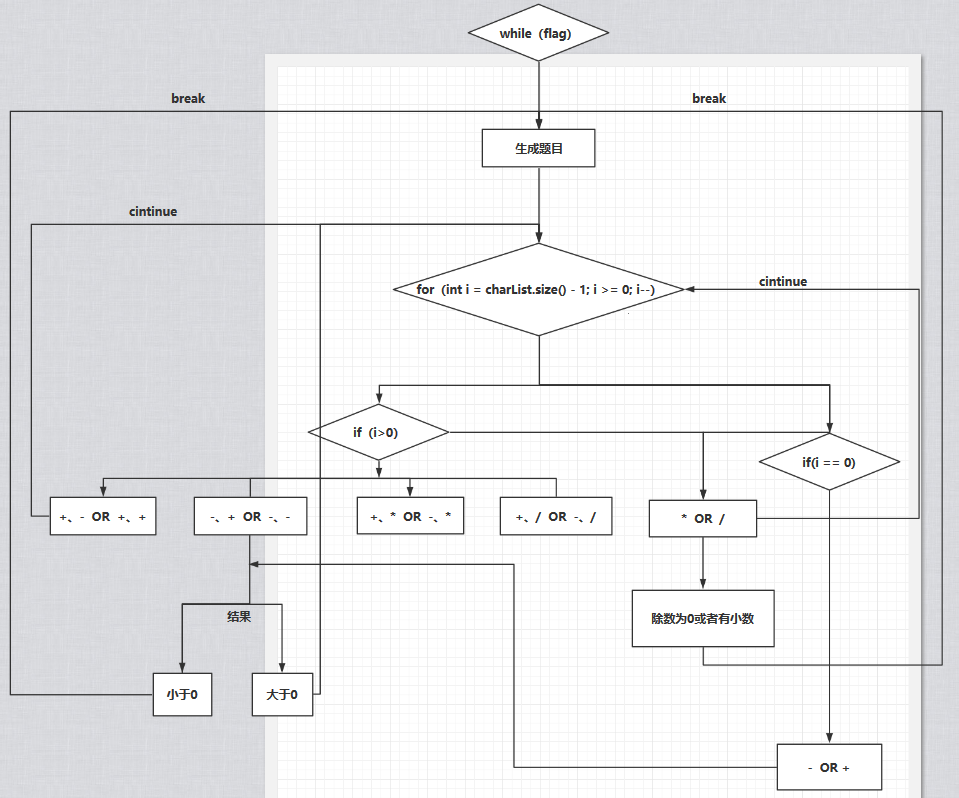
在完成基础功能的基础上,我对附加功能进行了设计,但由于之前实现方法的局限性,对于括号这一附加功能很难加进去,于是只对分数这一部分的运算进行了实现。
具体修改的如下:
用例图:
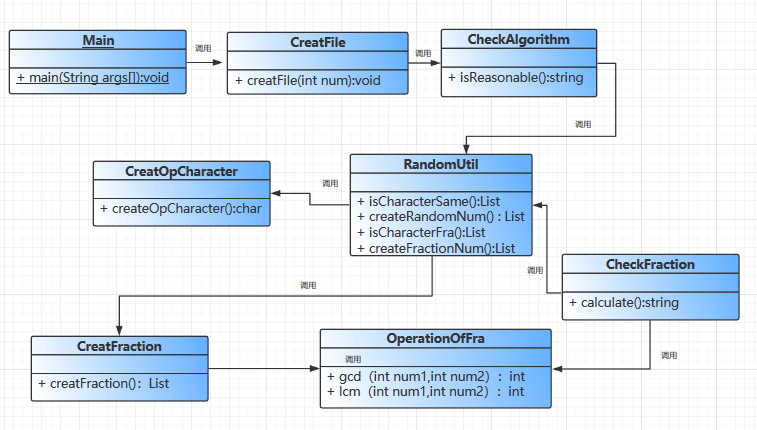
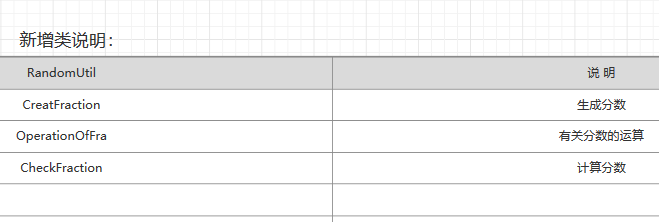
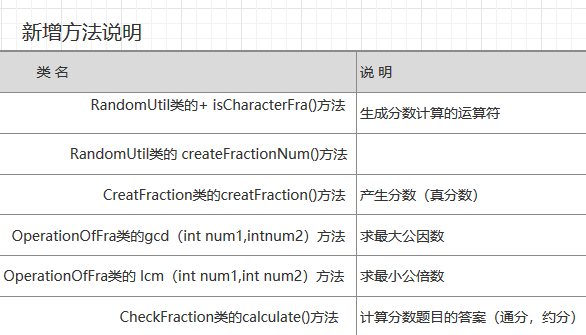
四、算法详解
1、生成题目:用switch语句随机生成运算符,并利用random方法随机生成合理数量的运算符和运算数。
2、解答题目:采用递归的算法,计算最大公因数,最小公倍数,利用list,if-else语句循环判断运算的优先级,和计算的合理性并进行计算。
五、测试运行
测试过程:
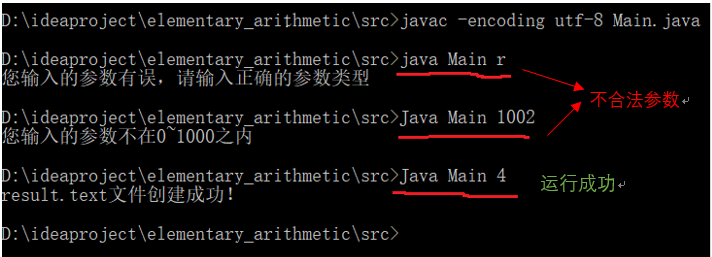
结果显示:

修改之后的结果显示:
六、代码展示
CreatFile类:
1 import java.io.*; 2 3 /** 4 * 创建TXT文件,写入数据 5 */ 6 public class CreatFile { 7 8 public void creatFile(int num) { 9 try { 10 File file = new File("../result.txt");//相对路径 11 if (file.exists()) { 12 file.delete(); 13 } 14 if (file.createNewFile()) { 15 FileOutputStream fileout = new FileOutputStream(file); 16 fileout.write("2016012054".getBytes());//在第一行写入学号 17 fileout.write("\r\n".getBytes());//换行 18 CheckAlgorithm checkAlgorithm = new CheckAlgorithm(); 19 CheckFraction checkFraction =new CheckFraction(); 20 //生成相应数量的题目,并写入 21 for (int i = num; i > 0; i--) { 22 String str = null; 23 if(i % 3 == 0){ 24 str = checkFraction.calculate();//分数类题目 25 }else { 26 str = checkAlgorithm.isReasonable();//整数类题目 27 } 28 byte[] b = str.getBytes(); 29 fileout.write(b); 30 fileout.write("\r\n".getBytes()); 31 } 32 fileout.close(); 33 } 34 35 System.out.println("result.text文件创建成功!"); 36 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 37 e.printStackTrace(); 38 } catch (IOException e) { 39 e.printStackTrace(); 40 } 41 } 42 }
CheckAlgorithm类
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.List; 3 4 /** 5 * 判断运算是否合理并计算结果 6 */ 7 public class CheckAlgorithm { 8 9 public String isReasonable() { 10 String str = ""; 11 boolean flag = true; 12 int result = 0; 13 List<Character> charList = new ArrayList<>(); 14 List<Integer> numList = new ArrayList<>(); 15 List<Character> charList1 = new ArrayList<>(); 16 List<Integer> numList1 = new ArrayList<>(); 17 //循环直到生成正确的题目位置 18 while (flag) { 19 result = 0; 20 charList1.clear(); 21 numList1.clear(); 22 charList.clear(); 23 numList.clear(); 24 RandomUtil creatRandom = new RandomUtil(); 25 charList = creatRandom.isCharacterSame(); 26 numList = creatRandom.createRandomNum(); 27 charList1.addAll(charList); 28 numList1.addAll(numList); 29 //循环计算每一步结果并判断是否合理 30 for (int i = charList.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { 31 // 有两个及以上运算符时 32 if (i > 0) { 33 //‘+’后面为同级运算时 34 if (charList.get(i) == '+' && ((charList.get(i - 1) == '+') || (charList.get(i - 1) == '-'))) { 35 result = numList.get(i + 1) + numList.get(i); 36 charList.remove(i); 37 numList.remove(i + 1); 38 numList.set(i, result); 39 continue; 40 } 41 //‘-’后面为同级运算时 42 if (charList.get(i) == '-' && ((charList.get(i - 1) == '+') || (charList.get(i - 1) == '-'))) { 43 result = numList.get(i + 1) - numList.get(i); 44 if (result <= 0) { 45 break; 46 } else { 47 charList.remove(i); 48 numList.remove(i + 1); 49 numList.set(i, result); 50 continue; 51 } 52 } 53 //‘+’或‘-’后面为优先级更高的运算时 54 if (((charList.get(i) == '+') || (charList.get(i) == '-')) && charList.get(i - 1) == '*') { 55 result = numList.get(i) * numList.get(i - 1); 56 57 char tempChar = charList.get(i); 58 charList.remove(i); 59 charList.remove(i - 1); 60 charList.add(tempChar); 61 62 int tempNum = numList.get(i + 1); 63 numList.remove(i + 1); 64 numList.remove(i); 65 numList.set(i - 1, result); 66 numList.add(tempNum); 67 continue; 68 } 69 70 if (((charList.get(i) == '+') || (charList.get(i) == '-')) && charList.get(i - 1) == '÷') { 71 if (numList.get(i - 1) != 0) { 72 result = numList.get(i) / numList.get(i - 1); 73 74 if (numList.get(i) % numList.get(i - 1) != 0) { 75 break; 76 } else { 77 char tempChar = charList.get(i); 78 charList.remove(i); 79 charList.remove(i - 1); 80 charList.add(tempChar); 81 82 int tempNum = numList.get(i + 1); 83 numList.remove(i + 1); 84 numList.remove(i); 85 numList.set(i - 1, result); 86 numList.add(tempNum); 87 continue; 88 } 89 } else { 90 break; 91 } 92 } 93 } 94 // 只有一个运算符时 95 //乘法运算 96 if (charList.get(i) == '*' || (i == 0 && charList.get(i) == '*')) { 97 result = numList.get(i + 1) * numList.get(i); 98 charList.remove(i); 99 numList.remove(i + 1); 100 numList.set(i, result); 101 if (i == 0) { 102 flag = false; 103 } 104 continue; 105 } 106 //除法运算 107 if (charList.get(i) == '÷' || (i == 0 && charList.get(i) == '÷')) { 108 if (numList.get(i) != 0) { 109 result = numList.get(i + 1) / numList.get(i); 110 if (numList.get(i + 1) % numList.get(i) == 0) { 111 charList.remove(i); 112 numList.remove(i + 1); 113 numList.set(i, result); 114 if (i == 0) { 115 flag = false; 116 } 117 continue; 118 } else { 119 break; 120 } 121 } else { 122 break; 123 } 124 } 125 126 //加减法 127 if (i == 0) { 128 if (charList.get(i) == '+') { 129 result = numList.get(i + 1) + numList.get(i); 130 flag = false; 131 continue; 132 } 133 if (charList.get(i) == '-') { 134 result = numList.get(i + 1) - numList.get(i); 135 if (result < 0) { 136 break; 137 } 138 flag = false; 139 continue; 140 } 141 142 } 143 } 144 } 145 //输出题目 146 for (int j = numList1.size() - 1; j >= 0; j--) { 147 if (j > 0) { 148 str += numList1.get(j); 149 str += charList1.get(j - 1); 150 } else { 151 str += numList1.get(j); 152 } 153 } 154 str += "=" + result; 155 return str; 156 } 157 }
OperationOfFra类
1 public class OperationOfFra { 2 3 //最大公因数 4 public int gcd(int a, int b) { 5 6 return a % b == 0 ? b : gcd(b, a % b); 7 } 8 9 // 最小公倍数 10 public int lcm(int n1, int n2) { 11 return n1 * n2 / gcd(n1, n2); 12 } 13 14 15 }
七、总结
在此次项目过程中,由于前期的设计不够合理,导致在代码编写阶段遇到了很多问题,只能一步一步debug,查找代码的纰漏,给自己造成了很大的麻烦。其次是这次项目当中涉及到一些我没有掌握的知识,例如如何向文件中写入数据,Main方法怎么在命令行获取参数等。在实现过程中,我意识到了很多自己的不足之处,也让我收获了许多新的知识。
为了使代码更加简洁,我将随机生成运算符和运算数、判断题目合理性、创建TXT文件并写入这些功能独立成一个模块,这样在主方法中只需要调用相应的方法就可以,而不需要知道具体代码的实现过程。
关于项目的设计,根据用户需求,我首先想到的是如何生成一道正确的四则运算,这样就可以利用循环,实现相应数量的题目。这其中,遇到最大的问题就是如何实现运算符优先级的判断,我想到的解决方案是利用List,进行循环判断,实现前两个运算符的判断,然后不断循环,直到计算出结果。后来我也有看其他同学的博客,看到他们用调度场算法,也意识到自己算法的弊端,由于时间原因,我还是采用了之前设计的方法,完成了作业。以后的学习中,也会吸取这次的经验,以最优化的方案完成作业。
八、PSP展示
|
PSP2.1 |
任务内容 |
计划共完成需要的时间(min) |
实际完成需要的时间(min) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
1*60 |
1*60 |
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间,并规划大致工作步骤 |
1*60 |
1*60 |
|
Development |
开发 |
21*60 |
21*60 |
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
4*60 |
4*60 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
20 |
20 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
10 |
10 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
30 |
30 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
1*60 |
1*60 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
11*60 |
11*60 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
1*60 |
1*60 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
2*60 |
2*60 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
6*60 |
6*60 |
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
30 |
30 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
30 |
30 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
5*60 |
5*60 |



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号