10.ThinkPHP模型操作
## 模型定义
创建到指定模块
//只能该模块使用
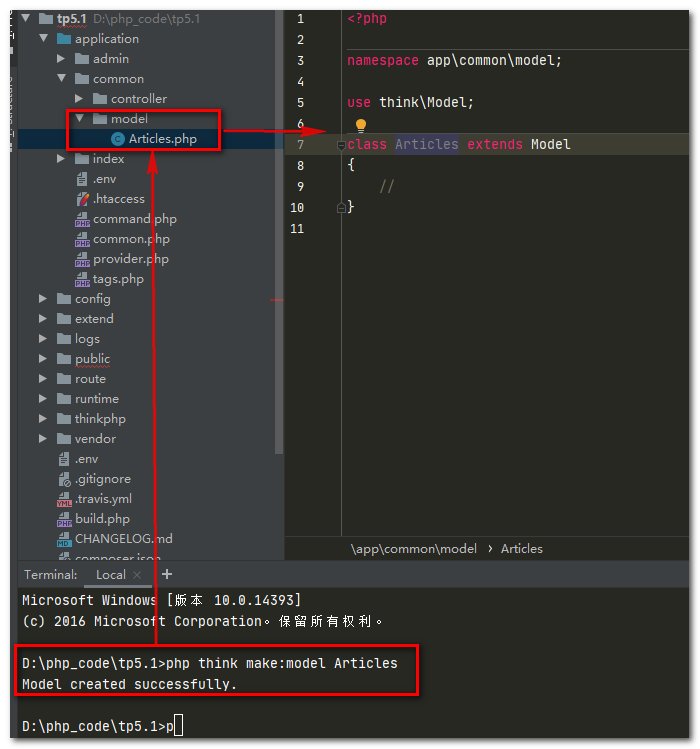
php think make:model 模块名/模型名(首字母大写)
创建到公共模块
//所有模块都能使用
php think make:model 模型名(首字母大写)
例:
模型设置
模型和数据表对应设置
模型会自动对应数据表,模型类的命名规则是除去表前缀的数据表名称,采用驼峰法命名,并且首字母大写,例如:
| 模型名 | 约定对应数据表(假设数据库的前缀定义是 think_) |
|---|---|
| User | think_user |
| UserType | think_user_type |
如果你的规则和上面的系统约定不符合,那么需要设置Model类的数据表名称属性,以确保能够找到对应的数据表。
模型自动对应的数据表名称都是遵循小写+下划线规范,如果你的表名有大写的情况,必须通过设置模型的table属性。
常用的模型设置
属性包括(以下属性都不是必须设置):
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| name | 模型名(默认为当前不含后缀的模型类名) |
| table | 数据表名(默认自动获取) |
| pk | 主键名(默认为id) |
| connection | 数据库连接(默认读取数据库配置) |
| query | 模型使用的查询类名称 |
| field | 模型对应数据表的字段列表(数组) |
设置例子:
# 非必须
protected $pk = 'uid'; # 设置主键名称
protected $table = 'think_user'; #设置当前模型对应的完整数据表名称
模型实例化方式
方式一:new
//直接创建模型类
$model = new Articles();
方式二:model()助手函数方法
//这种写法模型名大小写都可以
$model = model('articles');
注意:这种方式最好带上命令空间,否则有可能会找不到model类
如:
model('app\common\model\articles')
例:
模型中有如下定义
<?php
namespace app\common\model;
use think\Model;
class Articles extends Model
{
//设置主键
protected $pk = 'id';
//设置表名
protected $table = 'tp_articles';
public function test(){
return 'test...';
}
}
控制器
<?php
namespace app\index\controller;
use app\common\model\Articles;
class Index
{
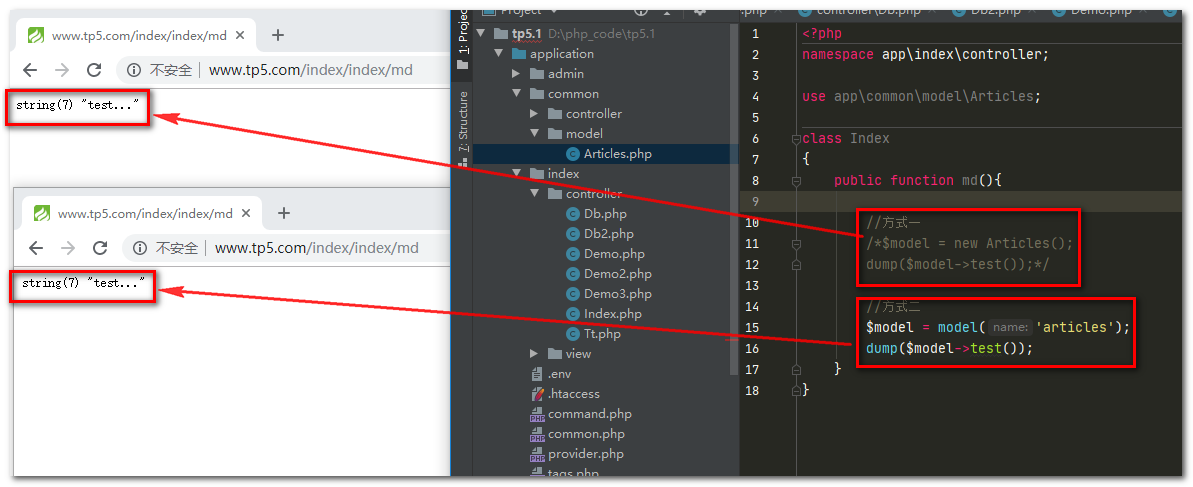
public function md(){
//方式一
/*$model = new Articles();
dump($model->test());*/
//方式二
$model = model('articles');
dump($model->test());
}
}
运行结果
添加模型数据
模型类内容如下:
<?php
namespace app\common\model;
use think\Model;
class Articles extends Model
{
//设置主键
protected $pk = 'id';
//设置表名
protected $table = 'tp_articles';
public function test(){
return 'test...';
}
}
方式一 给模型类单个赋值的方式
官方例子
# 方法1
$user = new User;
$user->name = 'thinkphp';
$user->email = 'thinkphp@qq.com';
$user->save();
例:
<?php
namespace app\index\controller;
use app\common\model\Articles;
class Index
{
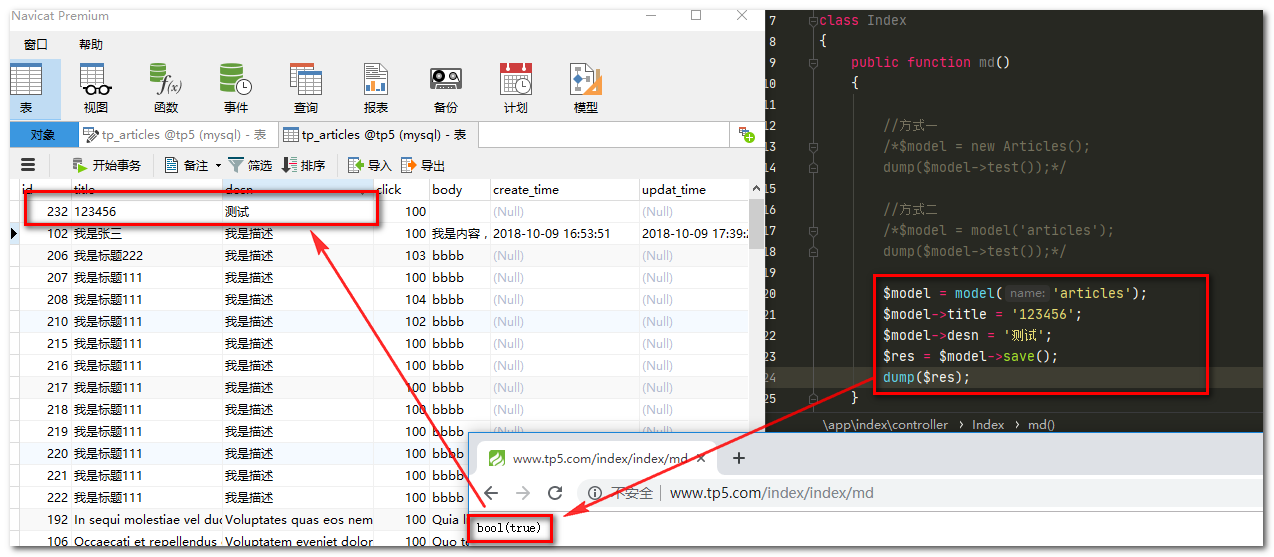
public function md()
{
$model = model('articles');
$model->title = '123456';
$model->desn = '测试';
$res = $model->save();
dump($res);
}
}
运行结果
方式二 创建模型类直接保存关联数组的方式
官方例子
# 方法2
$user = new User;
$user->save([
'name' => 'thinkphp',
'email' => 'thinkphp@qq.com'
]);
例:
<?php
namespace app\index\controller;
use app\common\model\Articles;
class Index
{
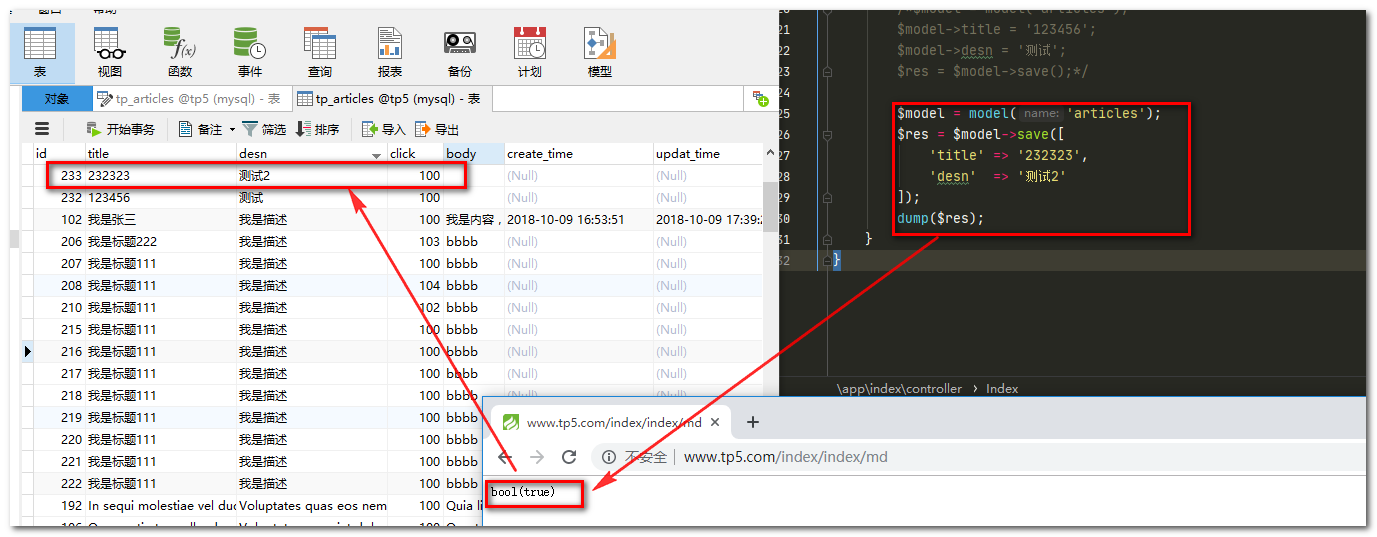
public function md()
{
$model = model('articles');
$res = $model->save([
'title' => '232323',
'desn' => '测试2'
]);
dump($res);
}
}
运行结果
方式三 使用模型类静态方法create[推荐使用]
官方例子
$user = User::create([
'name' => 'thinkphp',
'email' => 'thinkphp@qq.com'
]);
echo $user->name;
echo $user->email;
echo $user->id; // 获取自增ID
例:
<?php
namespace app\index\controller;
use app\common\model\Articles;
class Index
{
public function md()
{
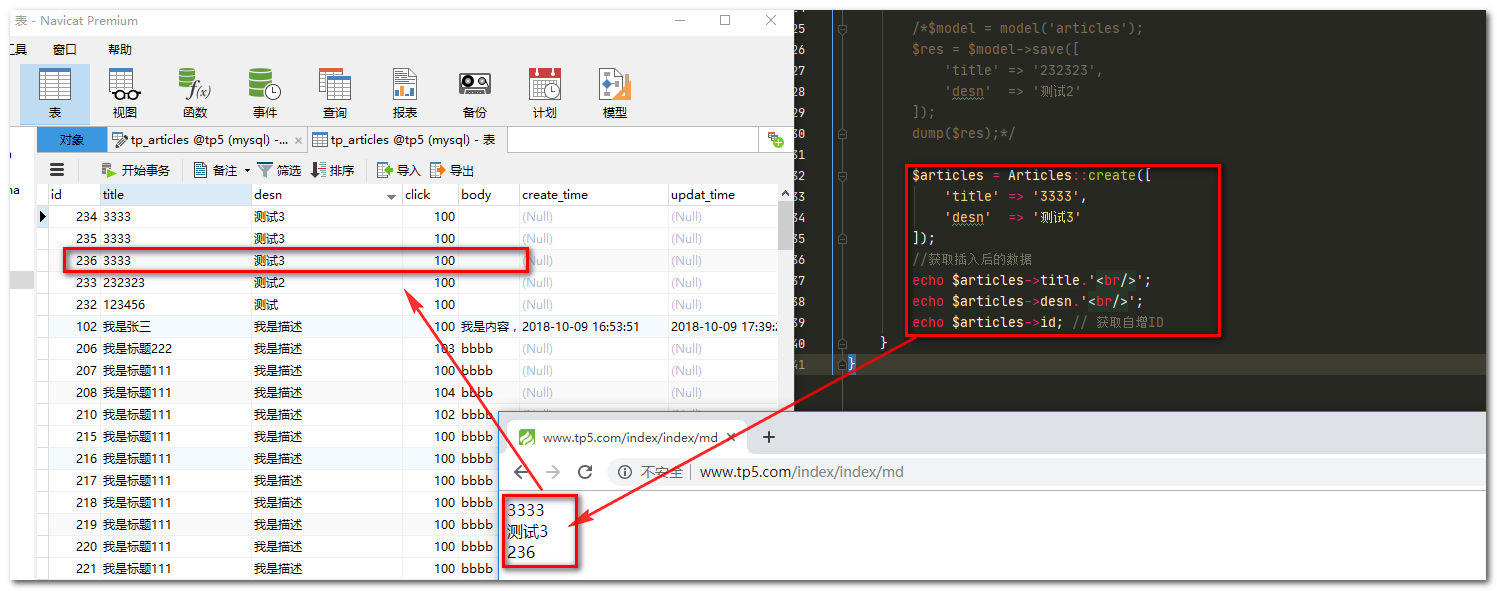
$articles = Articles::create([
'title' => '3333',
'desn' => '测试3'
]);
//获取插入后的数据
echo $articles->title.'<br/>';
echo $articles->desn.'<br/>';
echo $articles->id; // 获取自增ID
}
}
运行结果
添加时过滤非数据表字段的数据
如果需要过滤非数据表字段的数据,可以使用:
$user = new User;
// 过滤post数组中的非数据表字段数据
$user->allowField(true)->save($_POST);
如果你通过外部提交赋值给模型,并且希望指定某些字段写入,可以使用:
$user = new User;
// post数组中只有name和email字段会写入
$user->allowField(['name','email'])->save($_POST);
最佳的建议是模型数据赋值之前就进行数据过滤,例如:
$user = new User;
// 过滤post数组中的非数据表字段数据
$data = Request::only(['name','email']);
$user->save($data);
$user = new User;
$user->name = 'thinkphp';
$user->email = 'thinkphp@qq.com';
$user->save();
// 获取自增ID
echo $user->user_id;
添加多条数据
支持批量新增,可以使用:
$user = new User;
$list = [
['name'=>'thinkphp','email'=>'thinkphp@qq.com'],
['name'=>'onethink','email'=>'onethink@qq.com']
];
$user->saveAll($list);
saveAll方法新增数据返回的是包含新增模型(带自增ID)的数据集对象。
saveAll方法新增数据默认会自动识别数据是需要新增还是更新操作,当数据中存在主键的时候会认为是更新操作,如果你需要带主键数据批量新增,可以使用下面的方式:
$user = new User;
$list = [
['id'=>1, 'name'=>'thinkphp', 'email'=>'thinkphp@qq.com'],
['id'=>2, 'name'=>'onethink', 'email'=>'onethink@qq.com'],
];
$user->saveAll($list, false);
例:
<?php
namespace app\index\controller;
use app\common\model\Articles;
class Index
{
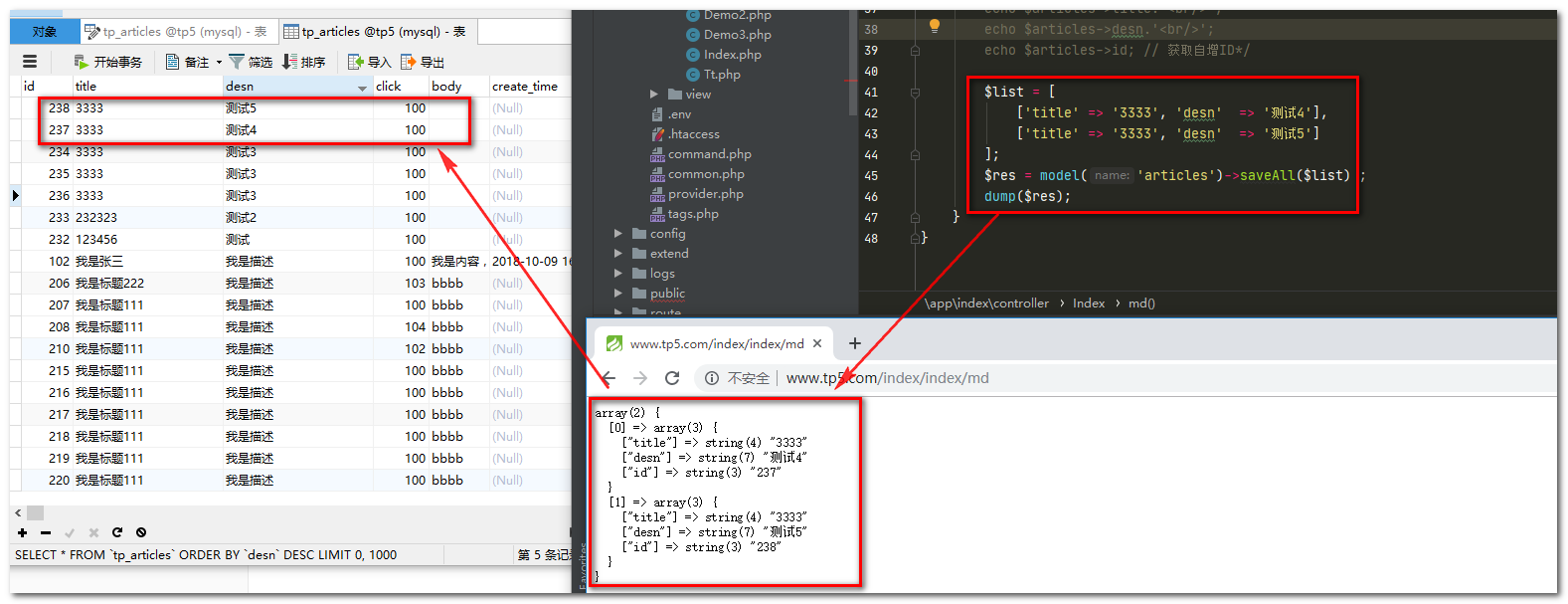
public function md()
{
$list = [
['title' => '3333', 'desn' => '测试4'],
['title' => '3333', 'desn' => '测试5']
];
$res = model('articles')->saveAll($list) ;
dump($res);
}
}
运行结果:
更新模型数据
和模型新增一样,更新操作同样也会经过修改器、自动完成以及模型事件等处理,并不等同于数据库的数据更新,而且更新方法和新增方法使用的是同一个方法,通常系统会自动判断需要新增还是更新数据。
如果需要使用模型事件,那么就先查询后更新,如果不需要使用事件,直接使用静态的Update方法进行条件更新,如非必要,尽量不要使用批量更新。
方式一:查找并更新
在取出数据后,更改字段内容后使用save方法更新数据。这种方式是最佳的更新方式。
$user = User::get(1);
$user->name = 'thinkphp';
$user->email = 'thinkphp@qq.com';
$user->save();
save方法返回影响的记录数
方式二:直接更新,关联数组形式
$user = new User;
// save方法第二个参数为更新条件
$user->save([
'name' => 'thinkphp',
'email' => 'thinkphp@qq.com'
],['id' => 1]);
save方法返回影响的记录数
方式三:静态方法[推荐使用]
User::where('id', 1)->update(['name' => 'thinkphp']);
例:
<?php
namespace app\index\controller;
use app\common\model\Articles;
class Index
{
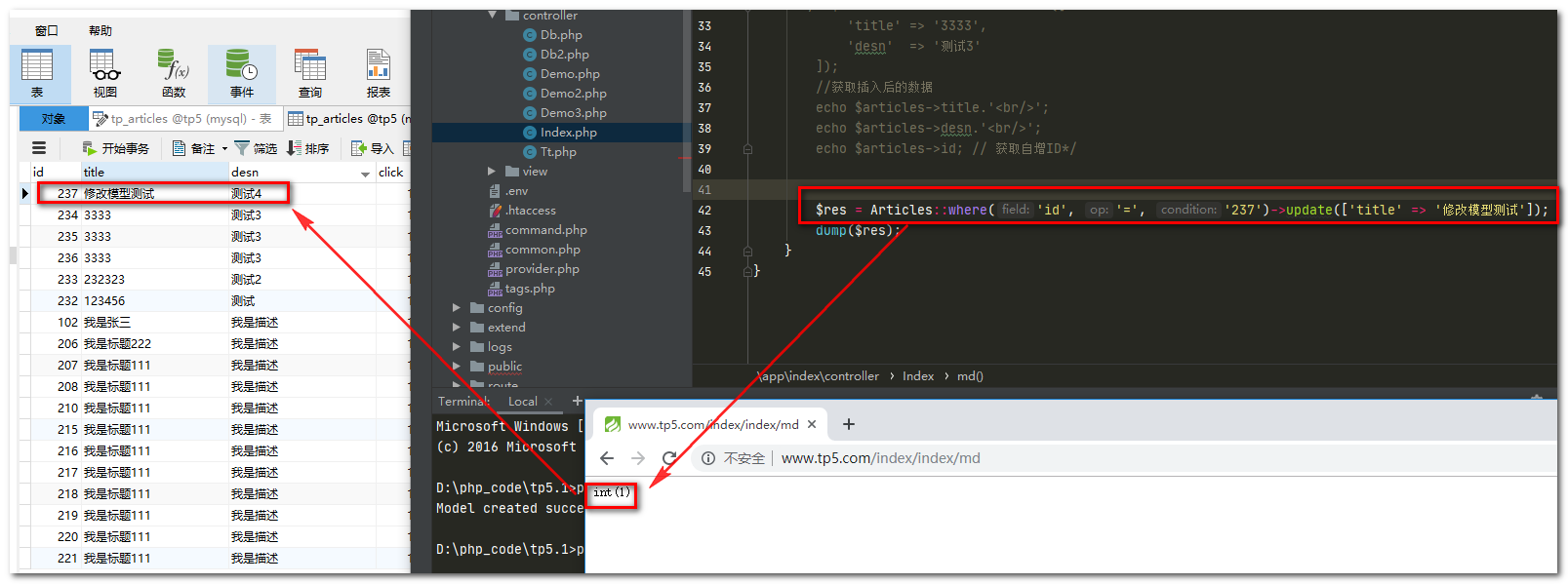
public function md()
{
$res = Articles::where('id', '=', '237')->update(['title' => '修改模型测试']);
dump($res);
}
}
运行结果
过滤非数据表字段的数据更新
如果需要过滤非数据表字段的数据,可以使用:
$user = new User;
// 过滤post数组中的非数据表字段数据
$user->allowField(true)->save($_POST,['id' => 1]);
如果你通过外部提交赋值给模型,并且希望指定某些字段写入,可以使用:
$user = new User();
// post数组中只有name和email字段会写入
$user->allowField(['name','email'])->save($_POST, ['id' => 1]);
最佳建议是在传入模型数据之前就进行过滤,例如:
$user = new User();
// post数组中只有name和email字段会写入
$data = Request::only(['name','email']);
$user->save($data, ['id' => 1]);
批量更新
可以使用saveAll方法批量更新数据,只需要在批量更新的数据中包含主键即可,例如:
$user = new User;
$list = [
['id'=>1, 'name'=>'thinkphp', 'email'=>'thinkphp@qq.com'],
['id'=>2, 'name'=>'onethink', 'email'=>'onethink@qq.com']
];
$user->saveAll($list);
批量更新方法返回的是一个数据集对象。
批量更新仅能根据主键值进行更新,其它情况请自行处理。
save添加还是更新的识别
我们已经看到,模型的新增和更新方法都是save方法,系统有一套默认的规则来识别当前的数据需要更新还是新增。
- 实例化模型后调用
save方法表示新增; - 查询数据后调用
save方法表示更新; save方法传入更新条件后表示更新;
如果你的数据操作比较复杂,可以用isUpdate方法显式的指定当前调用save方法是新增操作还是更新操作。
显式更新数据:
// 实例化模型
$user = new User;
// 显式指定更新数据操作
$user->isUpdate(true)
->save(['id' => 1, 'name' => 'thinkphp']);
显式新增数据:
$user = User::get(1);
$user->name = 'thinkphp';
// 显式指定当前操作为新增操作
$user->isUpdate(false)->save();
不要在一个模型实例里面做多次更新,会导致部分重复数据不再更新,正确的方式应该是先查询后更新或者使用模型类的update方法更新。
如果你调用
save方法进行多次数据写入的时候,需要注意,第二次save方法的时候必须使用isUpdate(false),否则会视为更新数据。
删除模型数据
如果删除当前模型数据,用delete方法,如果需要直接删除数据,使用destroy静态方法。
方式一:查询删除
删除模型数据,可以在查询后调用delete方法。
$user = User::get(1);
$user->delete();
delete方法返回影响的记录数,V5.1.6+版本开始返回布尔值
方式二:根据主键删除(支持多个)
或者直接调用静态方法(根据主键删除)
User::destroy(1);
// 支持批量删除多个数据
User::destroy('1,2,3');
// 或者
User::destroy([1,2,3]);
注意:当destroy方法传入空值(包括空字符串和空数组)的时候不会做任何的数据删除操作,但传入0则是有效的
方式三:条件删除
还支持使用闭包删除,例如:
User::destroy(function($query){
$query->where('id','>',10);
});
或者通过数据库类的查询条件删除
User::where('id','>',10)->delete();
直接调用数据库的
delete方法的话无法调用模型事件。
软删除
在实际项目中,对数据频繁使用删除操作会导致性能问题,软删除的作用就是把数据加上删除标记,而不是真正的删除,同时也便于需要的时候进行数据的恢复。
模型软删除需要进行的设置
1.软删除必须相关的数据表有delete_time字段并且是数值类型如int
2.要使用软删除功能,需要引入SoftDelete trait
use SoftDelete;
3.定义deleteTime属性
protected $deleteTime = 'delete_time';
例如User模型按照下面的定义就可以使用软删除功能:
<?php
namespace app\index\model;
use think\Model;
use think\model\concern\SoftDelete;
class User extends Model
{
use SoftDelete;
protected $deleteTime = 'delete_time';
}
deleteTime属性用于定义你的软删除标记字段,ThinkPHP的软删除功能使用时间戳类型(数据表默认值为Null),用于记录数据的删除时间。
自定义软删除字段的默认值
V5.1.9+版本开始,可以支持defaultSoftDelete属性来定义软删除字段的默认值,在此之前的版本,软删除字段的默认值必须为null。
<?php
namespace app\index\model;
use think\Model;
use think\model\concern\SoftDelete;
class User extends Model
{
use SoftDelete;
protected $deleteTime = 'delete_time';
protected $defaultSoftDelete = 0;
}
可以用类型转换指定软删除字段的类型,建议数据表的所有时间字段统一一种类型。
软删除和真删除的写法区别
定义好模型后,我们就可以使用:
// 软删除
User::destroy(1);
// 真实删除
User::destroy(1,true);
$user = User::get(1);
// 软删除
$user->delete();
// 真实删除
$user->delete(true);
查询软删除的数据和不包含软删除的数据
默认情况下查询的数据不包含软删除数据,如果需要包含软删除的数据,可以使用下面的方式查询:
//包含软删除的
User::withTrashed()->find();
User::withTrashed()->select();
或
//不包含软删除
User::->select();
如果仅仅需要查询软删除的数据,可以使用:
User::onlyTrashed()->find();
User::onlyTrashed()->select();
恢复被软删除的数据
$user = User::onlyTrashed()->find(1);
$user->restore();
软删除仅对模型的删除方法有效,如果直接使用数据库的删除方法则无效,例如下面的方式无效(将不会执行任何操作)。
$user = new User;
$user->where('id',1)->delete();
自测例子
例
模型内容
<?php
namespace app\common\model;
use think\Model;
use think\model\concern\SoftDelete;
class Articles extends Model
{
//引入软删除的操作方法
use SoftDelete;
//设置主键
protected $pk = 'id';
//设置表名
protected $table = 'tp_articles';
//删除的字段名
protected $deleteTime = 'delete_time';
public function test(){
return 'test...';
}
}
控制器内容
<?php
namespace app\index\controller;
use app\common\model\Articles;
class Index
{
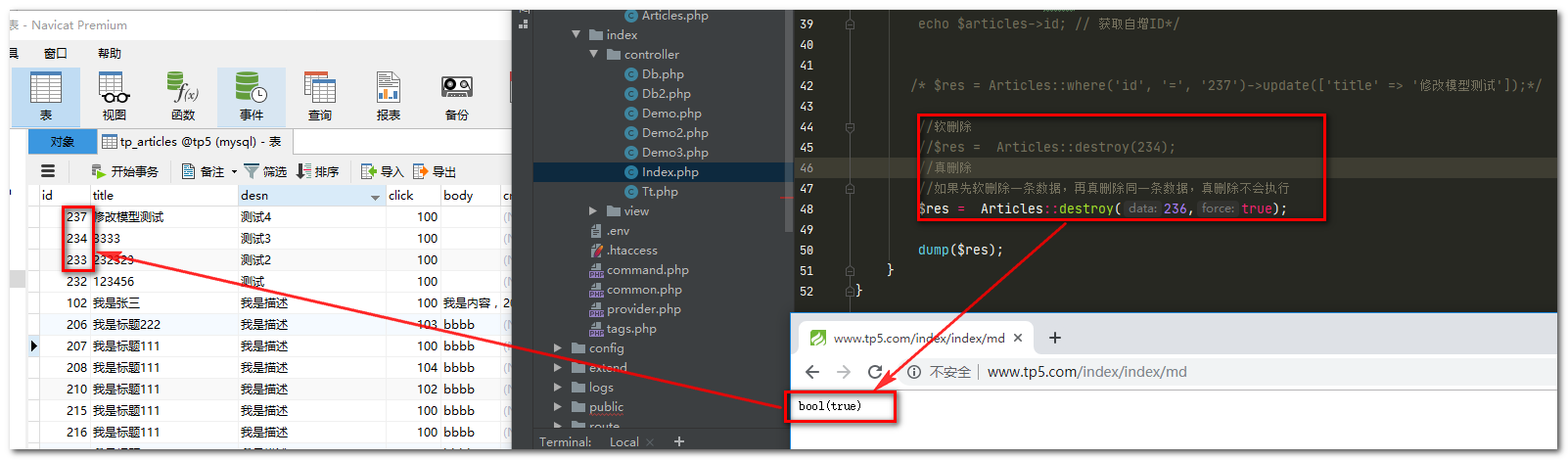
public function md()
{
//软删除
//$res = Articles::destroy(234);
//真删除
//如果先软删除一条数据,再真删除同一条数据,真删除不会执行
$res = Articles::destroy(234,true);
dump($res);
}
}
运行结果
查询模型数据
查询单个记录
# 查询单条记录
$user = User::where('name', 'thinkphp')->find();
例:
<?php
namespace app\index\controller;
use app\common\model\Articles;
class Index
{
public function md()
{
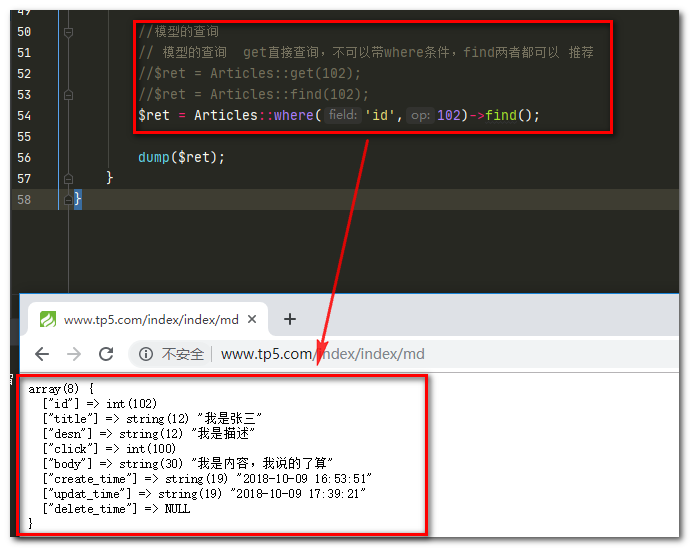
//模型的查询
// 模型的查询 get直接查询,不可以带where条件,find两者都可以 推荐
//$ret = Articles::get(102);
//$ret = Articles::find(102);
$ret = Articles::where('id',102)->find();
dump($ret);
}
}
运行结果
查询多条记录
# 查询多条记录
$list = User::where('status', 1)->limit(3)->order('id', 'asc')->select();
查询条件分组
// 条件分组 where () or ()
$ret = Articles::where(function (Query $query){
#print_r(func_get_args());
$query->where('id','>',200);
})->whereOr(function (Query $query){
$query->where('click','>=',101);
})->select();
例:
<?php
namespace app\index\controller;
use app\common\model\Articles;
//引入
use think\db\Query;
class Index
{
public function md()
{
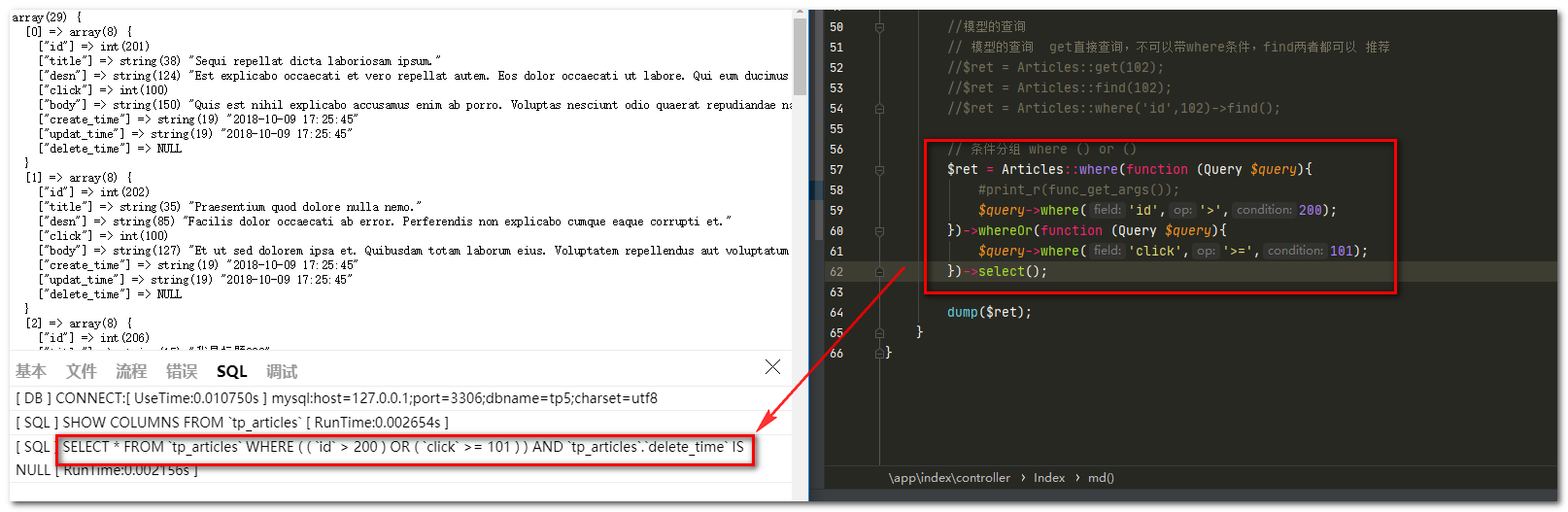
// 条件分组 where () or ()
$ret = Articles::where(function (Query $query){
//打印参数列表
#print_r(func_get_args());
$query->where('id','>',200);
})->whereOr(function (Query $query){
$query->where('click','>=',101);
})->select();
dump($ret);
}
}
运行结果
动态查询
// 查询title字段为"我是张三"的记录
#$ret = Articles::where('title','我是张三')->select();
// 动态查询 getBy固定 字段名,首字母大写,遇到下划线,下划线的后的首字母大写
// 例: title_article getByTitleArticle
$ret = Articles::getByTitle('我是张三');
例:
<?php
namespace app\index\controller;
use app\common\model\Articles;
use think\db\Query;
class Index
{
public function md()
{
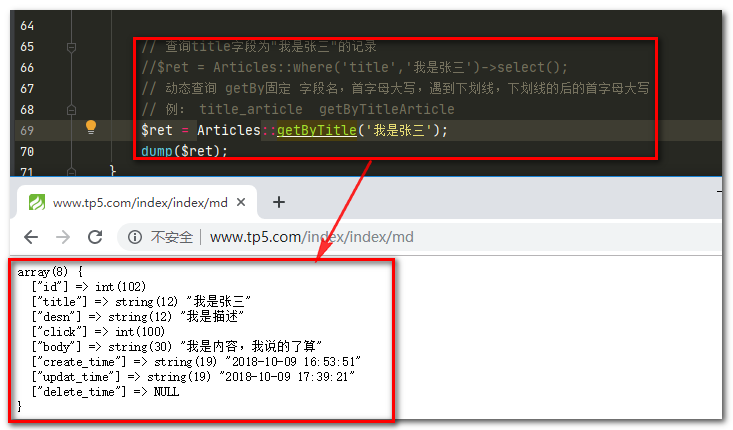
// 查询title字段为"我是张三"的记录
//$ret = Articles::where('title','我是张三')->select();
// 动态查询 getBy固定 字段名,首字母大写,遇到下划线,下划线的后的首字母大写
// 例: title_article getByTitleArticle
$ret = Articles::getByTitle('我是张三');
dump($ret);
}
}
运行结果
获取器
获取器的作用是对模型实例的(原始)数据做出自动处理。
方式一:withAttr方法
例:
<?php
namespace app\index\controller;
use app\common\model\Articles;
use think\db\Query;
class Index
{
public function md()
{
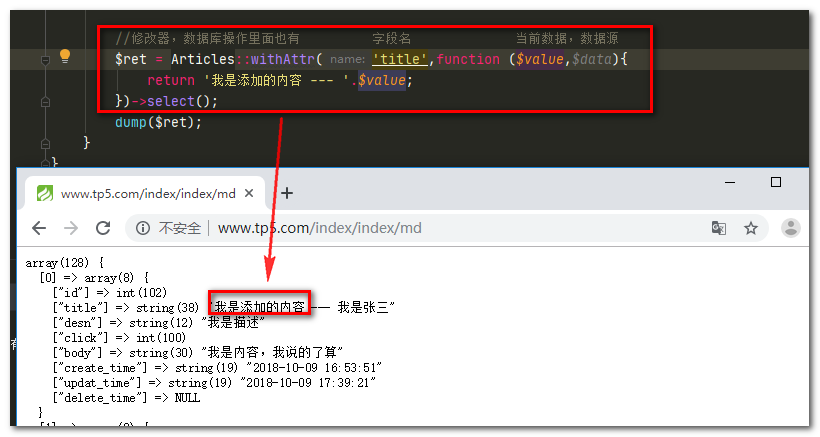
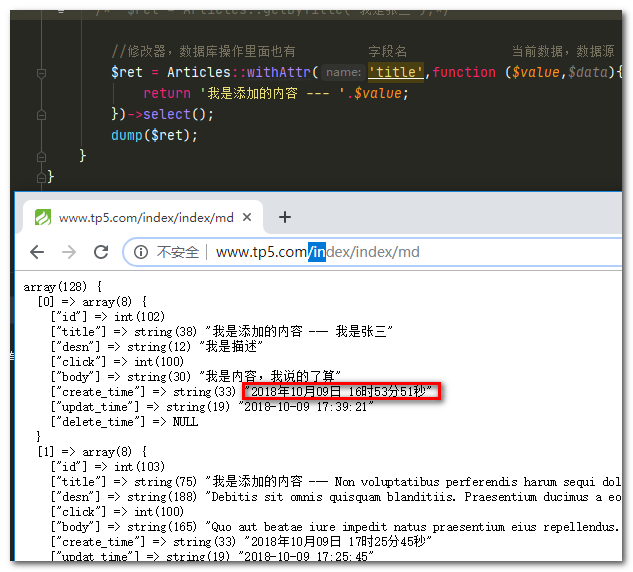
//修改器,数据库操作里面也有 字段名 当前数据,数据源
$ret = Articles::withAttr('title',function ($value,$data){
return '我是添加的内容 --- '.$value;
})->select();
dump($ret);
}
}
运行结果
方式二:模型类里面写获取器
在application\common\model\Articles.php模型类里面,写入如下内容
<?php
namespace app\common\model;
use think\Model;
use think\model\concern\SoftDelete;
class Articles extends Model
{
//引入软删除的操作方法
use SoftDelete;
//设置主键
protected $pk = 'id';
//设置表名
protected $table = 'tp_articles';
//删除的字段名
protected $deleteTime = 'delete_time';
public function test(){
return 'test...';
}
// 获取器
//数据表字段名:create_time
//获取方法名: getCreateTimeAttr
//格式:get字段名(首字母大写)Attr 如果有下划线,下划线的后首字母大写
public function getCreateTimeAttr($value){
//return date('Y年m月d日 H时i分s秒',strtotime($value));
return date('Y年m月d日 H时i分s秒',$value);
}
}
之后查询就正常查询即可,会自动转换
例:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号