flex 属性
一、flex-direction(元素排列方向)
1、flex-direction:row;//从左到右排列
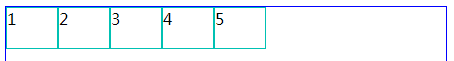
2、flex-direction:column;//从上往下排列

二、flex-wrap(内容一行容不下的时候才有效)
1、flex-wrap:nowrap //超出不换行,很奇怪里面的宽度会变成100%

2、flex-wrap:wrap //超出按父级的高度平分)
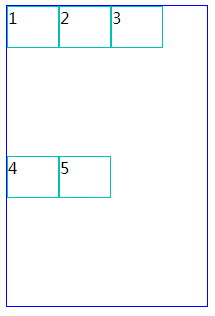
三、justify-content //水平对齐方式
1、justify-content:flex-start; (水平左对齐)
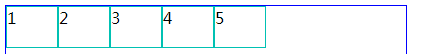
2、justify-content:flex-end; (水平右对齐)
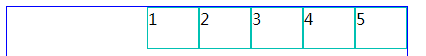
3、justify-content:center; (居中对齐)

4、justify-content:space-between; (两端对齐)

5、justify-content:space-around; (两端对齐,并且两端有间距)
四、align-items (垂直对齐方式)
1、align-items:flex-start; (上对齐,和默认差不多)
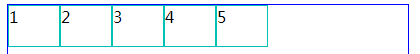
1、align-items:flex-end; (下对齐)
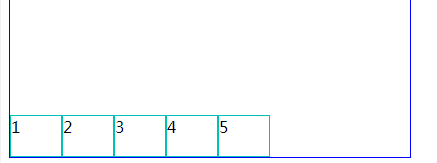
1、align-items:center;(居中对齐)
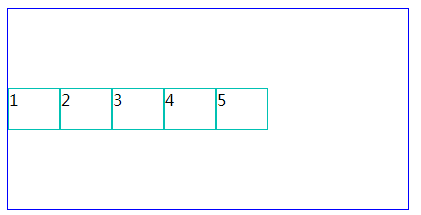
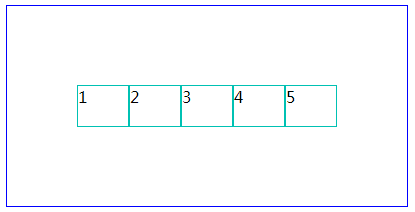
以上是对flex的简单介绍。下面有个小例子,
大家经常用到的,某个div里面水平垂直居中,
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
#box{
display: flex;
display: -webkit-flex;
border: 1px solid #0000FF;
height: 200px;
width: 400px;
align-items:center;
justify-content:center;
}
.item{
width: 50px;
height: 40px;
border: 1px solid #00C1B3;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<div class="item">1</div>
<div class="item">2</div>
<div class="item">3</div>
<div class="item">4</div>
<div class="item">5</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
个人练习::
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box {
height: 600px;
background: #ccc;
display: flex;
-webkit-display: flex;
flex-direction: row; /* 定义子元素排列方向:从左到右(默认) row column */
flex-wrap: wrap; /*元素撑满是否换行:默认是不换行 nowrap */
justify-content: space-around; /*定义子元素在主轴的对齐方式:两端对齐/居中对齐*/
align-items: center; /*定义子元素在辅轴的对齐方式:居中对齐*/
}
.sub {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
font-size: 20px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 200px;
border: 10px solid blue;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="sub">1</div>
<div class="sub">2</div>
<div class="sub">3</div>
<div class="sub" style="order: -1; flex-grow: 1; align-self: end;">4</div>
<!--
order 定义子元素在容器中的排列顺序,数值越小,排列越靠前。
flex-grow 通过一个数值来定义子元素的放大比例
align-self 定义子元素在交叉轴上,自己的对齐方式
-->
</div>
</body>
</html>





