算法:数字推盘游戏--重排九宫(8-puzzle)
一、数字推盘游戏
数字推盘游戏(n-puzzle)是一种最早的滑块类游戏,常见的类型有十五数字推盘游戏和八数字推盘游戏等。也有以图画代替数字的推盘游戏。可能Noyes Palmer Chapman在1874年发明十五数字推盘,但Sam Loyd则在1891年也宣称为其发明。
八数字推盘(又名重排九宫)则同样是Noyes Palmer Chapman在1870年代发明,并且马丁·加德纳在科学科普杂志上寻求更快的解答。也有人宣称重排九宫是传统中国游戏,来自洛书,并且为华容道的祖先。
二、分支界定法
给定一个具有 8 个图块的 3×3 板(每个图块都有一个 1 到 8 的数字)和一个空白空间(用 0 代表)。目的是将数字放置在图块上,以使用空白的空间匹配最终配置。我们可以将四个相邻的(左,右,上方和下方)图块滑动到空白区域。
通常可以使用 DFS、BFS 搜索算法来进行暴力破解。本文利用分支界定法,来“智能”的排名函数(近似于成本函数)来加快对成本节点的搜索,这里每一个节点都存有当前移动后整个方块的分布,从而避免在找不到最终答案的子树继续搜索。
分支界定法基本上涉及三种类型的节点:
- 存活节点,是已生成但尚未生成其子节点的节点;
- 当前正在扩展的节点,探索它的子节点;
- 死亡节点,死节点是生成的节点,将不再扩展或探索。死节点的所有子节点均已扩展。
成本函数:C(x) = g(x) + h(x)。
g(x) 是当前节点到根节点的成本(即路径长度)。h(x) 是当前除开空白块外与答案节点错位(放错位置)的成本,假设在往上下左右任一方向移动图块的成本为 1。
给定初始状态和目的状态:
 下图显示了上述算法从给定的8-Puzzle初始配置达到最终配置所遵循的路径。注意,仅具有最小成本函数值的节点被扩展。
下图显示了上述算法从给定的8-Puzzle初始配置达到最终配置所遵循的路径。注意,仅具有最小成本函数值的节点被扩展。
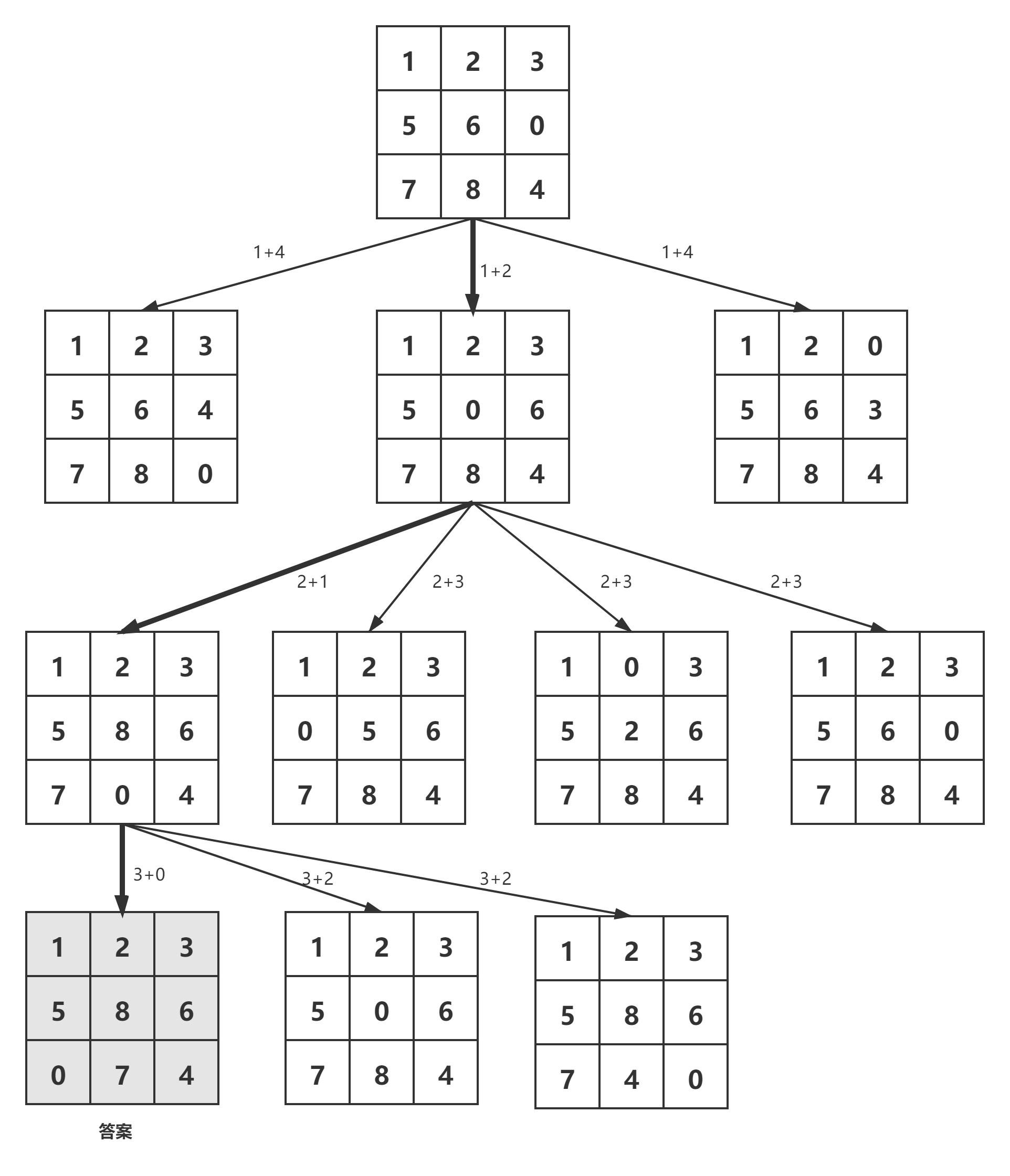
(注意:以上是本算法的流程图)
三、分支界定法的实现
节点的构造:
1 /** 2 * 节点 3 */ 4 private class Node { 5 private Node parent; 6 private int[][] mat; 7 private int x, y; 8 private int cost; 9 private int level; 10 private Node() { 11 mat = new int[N][N]; 12 } 13 }
插入一个新节点:
1 /** 2 * 分配一个新节点 3 * 4 * @param mat 5 * @param x 6 * @param y 7 * @param newX 8 * @param newY 9 * @param level 10 * @param parent 11 * @return 12 */ 13 private Node newNode(int[][] mat, int x, int y, int newX, int newY, int level, Node parent) { 14 Node node = new Node(); 15 node.parent = parent; 16 17 copyMatrix(mat, node.mat); 18 19 swap(node.mat, x, y, newX, newY); 20 21 node.cost = Integer.MAX_VALUE; 22 node.level = level; 23 24 node.x = newX; 25 node.y = newY; 26 27 return node; 28 }
计算错位成本:
1 /** 2 * 计算错位方块的数量, 即不在目标位置的非空白块的数量 3 * 4 * @param initial 5 * @param finals 6 * @return 7 */ 8 private int calculateCost(int[][] initial, int[][] finals) { 9 int count = 0; 10 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) 11 for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) 12 if (initial[i][j] != 0 && initial[i][j] != finals[i][j]) { 13 count++; 14 } 15 return count; 16 }
利用优先队列(PriorityQueue)来实现分支界定法:
1 /** 2 * 分支界定法解决问题 3 * 4 * @param initial 5 * @param x 6 * @param y 7 * @param finals 8 */ 9 private void solve(int[][] initial, int x, int y, int[][] finals) { 10 // 创建优先级队列以存储搜索树的活动节点 11 PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comp()); 12 13 // 创建一个根节点并计算其成本 14 Node root = newNode(initial, x, y, x, y, 0, null); 15 root.cost = calculateCost(initial, finals); 16 17 // 将根添加到活动节点列表中; 18 pq.add(root); 19 20 // 查找成本最低的活动节点, 21 // 将其子级添加到活动节点列表中,并最后将其从列表中删除。 22 while (!pq.isEmpty()) { 23 // 查找估计成本最低的活动节点, 找到的节点将从活动节点列表中删除 24 Node min = pq.poll(); 25 26 // 如果min是一个答案节点 27 if (min.cost == 0) { 28 printPath(min); 29 return; 30 } 31 32 // 为每个min节点的孩子 33 // 一个节点最多4个孩子 34 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { 35 if (isSafe(min.x + row[i], min.y + col[i])) { 36 // 创建一个子节点并计算它的成本 37 Node child = newNode(min.mat, min.x, min.y, 38 min.x + row[i], min.y + col[i], 39 min.level, min); 40 child.cost = calculateCost(child.mat, finals); 41 42 // 将min的孩子添加到活动节点列表 43 pq.add(child); 44 } 45 } 46 } 47 }
分支定界是一种算法设计范例,通常用于解决组合优化问题。 这些问题通常在时间复杂度上呈指数关系(2^N),在最坏的情况下可能需要探索所有可能的排列(扩展完堆中所有可能的节点)。 分支界定相对较快地解决了这些问题。但是在最坏的情况下,我们需要完全计算整个树。充其量,我们只需要完全计算一条穿过树的路径,然后修剪其余路径即可。
本文源代码:

1 package algorithm; 2 3 import java.util.Comparator; 4 import java.util.PriorityQueue; 5 6 /** 7 * 重排九宫,或者称之为八码数问题,或是说数字推盘问题4,使用分支界定法实现 8 */ 9 public class EightPuzzle { 10 // 方阵边长 11 private static final int N = 3; 12 13 // 坐标的行列索引向下、左、上、右 14 private static final int[] row = {1, 0, -1, 0}; 15 private static final int[] col = {0, -1, 0, 1}; 16 17 /** 18 * 节点 19 */ 20 private class Node { 21 private Node parent; 22 private int[][] mat; 23 private int x, y; 24 private int cost; 25 private int level; 26 private Node() { 27 mat = new int[N][N]; 28 } 29 } 30 31 /** 32 * 用于堆排序的比较对象 33 */ 34 class Comp implements Comparator<Node> { 35 @Override 36 public int compare(Node o1, Node o2) { 37 return (o1.cost + o1.level) - (o2.cost + o2.level); 38 } 39 } 40 41 /** 42 * 打印矩阵 43 * 44 * @param mat 45 */ 46 private void printMatrix(int[][] mat) { 47 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { 48 for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) 49 System.out.print(mat[i][j] + " "); 50 System.out.println(); 51 } 52 } 53 54 /** 55 * 交换二维矩阵中的值 56 * 57 * @param mat 58 * @param x 59 * @param y 60 * @param newX 61 * @param newY 62 */ 63 private void swap(int[][] mat, int x, int y, int newX, int newY) { 64 int tmp = mat[x][y]; 65 mat[x][y] = mat[newX][newY]; 66 mat[newX][newY] = tmp; 67 } 68 69 /** 70 * 矩阵复制 71 * 72 * @param arr1 73 * @param arr2 74 */ 75 private static void copyMatrix(int[][] arr1, int[][] arr2) { 76 for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++) 77 System.arraycopy(arr1[i], 0, arr2[i], 0, arr1[0].length); 78 79 } 80 81 /** 82 * 分配一个新节点 83 * 84 * @param mat 85 * @param x 86 * @param y 87 * @param newX 88 * @param newY 89 * @param level 90 * @param parent 91 * @return 92 */ 93 private Node newNode(int[][] mat, int x, int y, int newX, int newY, int level, Node parent) { 94 Node node = new Node(); 95 node.parent = parent; 96 97 copyMatrix(mat, node.mat); 98 99 swap(node.mat, x, y, newX, newY); 100 101 node.cost = Integer.MAX_VALUE; 102 node.level = level; 103 104 node.x = newX; 105 node.y = newY; 106 107 return node; 108 } 109 110 /** 111 * 计算错位方块的数量, 即不在目标位置的非空白块的数量 112 * 113 * @param initial 114 * @param finals 115 * @return 116 */ 117 private int calculateCost(int[][] initial, int[][] finals) { 118 int count = 0; 119 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) 120 for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) 121 if (initial[i][j] != 0 && initial[i][j] != finals[i][j]) { 122 count++; 123 } 124 return count; 125 } 126 127 /** 128 * 检查(x,y)是否为有效矩阵坐标 129 * 130 * @param x 131 * @param y 132 * @return 133 */ 134 private boolean isSafe(int x, int y) { 135 return (x >= 0 && x < N && y >= 0 && y < N); 136 } 137 138 /** 139 * 打印路径 140 * 141 * @param root 142 */ 143 private void printPath(Node root) { 144 if (root == null) 145 return; 146 printPath(root.parent); 147 printMatrix(root.mat); 148 System.out.println(); 149 } 150 151 /** 152 * 分支界定法解决问题 153 * 154 * @param initial 155 * @param x 156 * @param y 157 * @param finals 158 */ 159 private void solve(int[][] initial, int x, int y, int[][] finals) { 160 // 创建优先级队列以存储搜索树的活动节点 161 PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comp()); 162 163 // 创建一个根节点并计算其成本 164 Node root = newNode(initial, x, y, x, y, 0, null); 165 root.cost = calculateCost(initial, finals); 166 167 // 将根添加到活动节点列表中; 168 pq.add(root); 169 170 // 查找成本最低的活动节点, 171 // 将其子级添加到活动节点列表中,并最后将其从列表中删除。 172 while (!pq.isEmpty()) { 173 // 查找估计成本最低的活动节点, 找到的节点将从活动节点列表中删除 174 Node min = pq.poll(); 175 176 // 如果min是一个答案节点 177 if (min.cost == 0) { 178 printPath(min); 179 return; 180 } 181 182 // 为每个min节点的孩子 183 // 一个节点最多4个孩子 184 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { 185 if (isSafe(min.x + row[i], min.y + col[i])) { 186 // 创建一个子节点并计算它的成本 187 Node child = newNode(min.mat, min.x, min.y, 188 min.x + row[i], min.y + col[i], 189 min.level, min); 190 child.cost = calculateCost(child.mat, finals); 191 192 // 将min的孩子添加到活动节点列表 193 pq.add(child); 194 } 195 } 196 } 197 } 198 199 public static void main(String[] args) { 200 int[][] initial = 201 { 202 {1, 2, 3}, 203 {5, 6, 0}, 204 {7, 8, 4} 205 }; 206 207 int[][] finals = 208 { 209 {1, 2, 3}, 210 {5, 8, 6}, 211 {0, 7, 4} 212 }; 213 214 // 0的位置(空白块) 215 int x = 1, y = 2; 216 217 EightPuzzle eightPuzzle = new EightPuzzle(); 218 eightPuzzle.solve(initial, x, y, finals); 219 220 } 221 }




