Spring MVC:DispatchServlet类
Spring MVC架构
Spring Web MVC是基于Servlet API构建的原始Web框架,从一开始就已包含在Spring框架中。传统的模型层被拆分为了业务层(Service)和数据访问层(DAO,Data Access Object)。 在 Service 下可以通过 Spring 的声明式事务操作数据访问层,而在业务层上还允许我们访问 NoSQL ,这样就能够满足异军突起的 NoSQL 的使用了,它可以大大提高互联网系统的性能。
M 代表 模型(Model),V 代表 视图(View),C 代表 控制器(controller):
-
模型封装了应用程序数据,并且通常它们由 POJO 组成。
-
视图主要用于呈现模型数据,并且通常它生成客户端的浏览器可以解释的 HTML 输出。
- 控制器主要用于处理用户请求,并且构建合适的模型并将其传递到视图呈现。

一些优点:
1.在Spring MVC中,控制器可以处理所有HTTP方法的请求,这是RESTful Web服务的基础。例如,可以处理GET方法来执行读取操作,POST方法来创建资源,PUT方法来更新资源以及DELETE方法来从服务器中删除资源。从Spring 3.2开始,还可以处理PATCH请求。
2.对于REST,数据的表示非常重要,这就是为什么Spring MVC允许您通过使用 @ResponseBody 批注和各种 HttpMessgeConverter 实现方式完全绕过基于View的呈现 。通过使用此功能,您可以直接向客户端发送响应,例如,客户端所需的资源以及客户端所需的格式。
3. Spring 4.0版本添加了专用注释,@RestController使RESTful Web服务的开发更加容易。
如果使用@RestController 而不是 @Controller注释控制器类 ,则 Spring 会将消息对话应用于控制器中的所有处理程序方法。
这意味着您不需要为每个方法添加 @ResponseBody 注释。这也使您的代码更加简洁。
4. REST Web服务和普通Web应用程序之间的主要区别之一是,REST传递资源标识URI本身中的数据,例如 /messages/101, 而Web应用程序通常使用查询参数,例如 /messages?Id=101。
如果您还记得的话,我们使用 @RequestParam 获取这些查询参数的值,但是不用担心,Spring MVC还提供了一个@PathVariable批注,可以从URL提取数据。它允许控制器处理对参数化URL的请求。
5. RESTful Web服务的另一个关键方面是表示,表示同一资源可以以不同的格式表示,例如JSON,XML,HTML等。值得庆幸的是,Spring提供了几种视图实现和视图解析器,以将数据呈现为JSON,XML,和HTML。
例如,ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 可以查看请求的文件扩展名或“接受”标头,以找出客户端资源的正确表示形式。
6.与 @ResponseBody 用于将响应转换为客户端想要的格式(通过使用 HttpMessageConverts)的注释 类似 ,Spring MVC还提供 @RequestBody 注释,该注释使用 HttpMethodConverter 实现将入站HTTP数据转换为传递到控制器的处理程序方法中的Java对象。
7.在 Spring框架还提供了一个模板类,RestTemplate,这是类似的 JdbcTemplate,并且 JmsTemplate,它可以消耗REST资源。您可以使用此类测试RESTful Web服务或开发REST客户端。
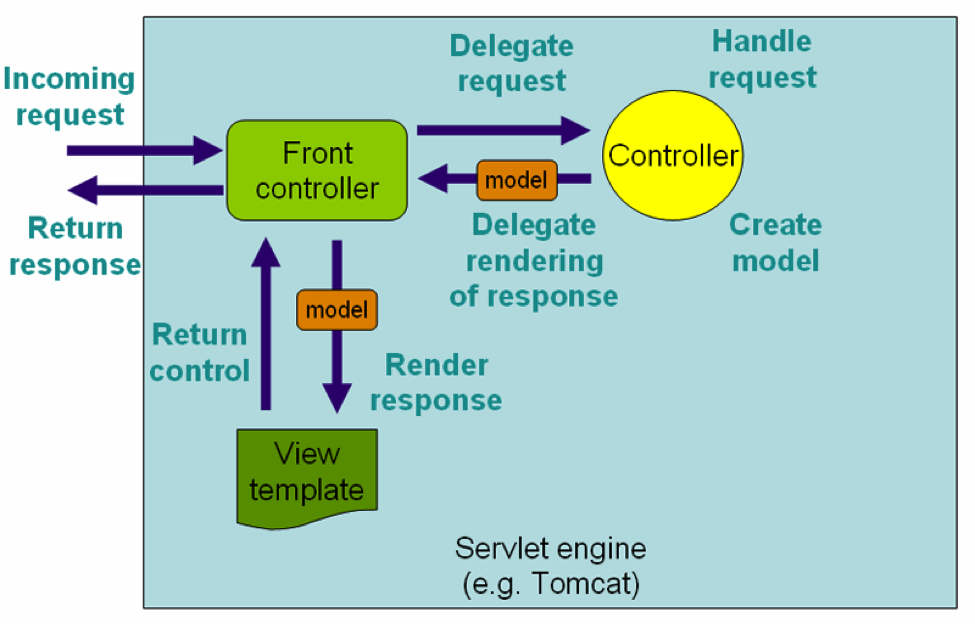
DispatchServlet
DispatchServlet 是 HTTP 请求处理程序/控制器的中央调度程序。Spring Web 模型-视图-控制(MVC)框架是围绕 DispatcherServlet 设计的。

下面是对应于 DispatcherServlet 传入 HTTP 请求的事件序列:
-
收到一个 HTTP 请求后,DispatcherServlet 根据 HandlerMapping 来选择并且调用适当的控制器
-
控制器接受请求(取决于使用@Controller和@RequestMapping注释请求的URL),并基于使用的 GET 或 POST 方法来调用适当的 service 方法。Service 方法将设置基于定义的业务逻辑的模型数据,并返回视图名称到 DispatcherServlet 中。
-
DispatcherServlet 会从视图解析器 ViewResolver 获取帮助,为请求检取定义视图。
- 一旦确定视图,DispatcherServlet 将把模型数据传递给视图,最后呈现在浏览器中。
上面所提到的所有组件,即 HandlerMapping、Controller 和 ViewResolver 是 WebApplicationContext 的一部分,而 WebApplicationContext 是带有一些对 web 应用程序必要的额外特性的 ApplicationContext 的扩展。
DispatcherServlet 初始化流程
DispatcherServlet在MVC子容器初始化时会初始化这9大组件:
-
MultipartResolver:用来处理上传请求的。其处理方式就是将 request 包装成 MultipartHttpServletRequest。然后就可以用 MultipartHttpServletRequest 这个直接调用 getFile 获取的文件了。
-
LocalResolver:作用是从 request 中解析出 local,关于local大多数情况下都是用来做国际化处理的。
-
ThemeResolver:解析主题的,例如配一套properties文件供系统在不同的时候读取切换。
-
HandlerMapping:其作用就是根据 request 找到相应的处理器 Handler 和 Intecepter 拦截器。
-
HandlerAdapter:其接口的 handle 方法就是使用 handler 来处理逻辑的。
-
HandlerExceptionResolver:Spring MVC 中的异常处理组件,根据异常设置 ModelAndView,然后再将处理结果交给
render方法进行渲染。在渲染之前工作的,因此渲染过程中发生异常,HandlerExceptionResolver 是不会处理的。 -
RequestToViewNameTranslator:将request请求转换为视图名称。
-
ViewResolver:作用是将 String 类型的逻辑视图根据 local 解析为 View 视图的。
-
FlashMapManager:在redirect是进行参数传递需要用到。
1 /** 2 * This implementation calls {@link #initStrategies}. 3 */ 4 @Override 5 protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) { 6 initStrategies(context); 7 }
1 /** 2 * Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses. 3 * <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects. 4 */ 5 protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { 6 initMultipartResolver(context); 7 initLocaleResolver(context); 8 initThemeResolver(context); 9 initHandlerMappings(context); 10 initHandlerAdapters(context); 11 initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); 12 initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); 13 initViewResolvers(context); 14 initFlashMapManager(context); 15 }
DispatcherServlet 执行流程
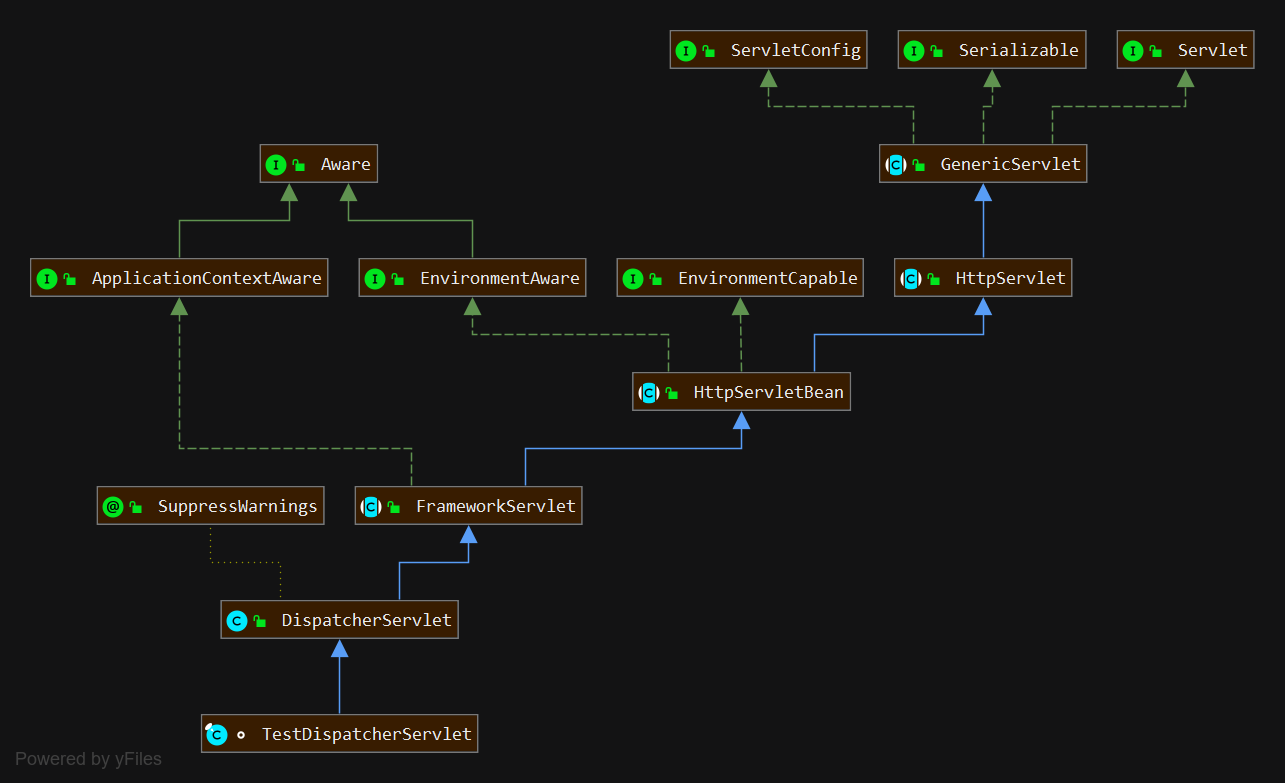
Http请求通过 HttpServlet 读取请求的内容,生成一个 HttpServletRequest 和一个 HttpServletResponse。下面这段方法将客户端请求分派到受保护的 service 方法。
1 @Override 2 public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) 3 throws ServletException, IOException { 4 5 HttpServletRequest request; 6 HttpServletResponse response; 7 8 try { 9 request = (HttpServletRequest) req; 10 response = (HttpServletResponse) res; 11 } catch (ClassCastException e) { 12 throw new ServletException(lStrings.getString("http.non_http")); 13 } 14 service(request, response); 15 }
接着来到 FrameworkServlet 的 service 方法,若是 patch 类型的方法,则单独拿出来进行处理。
1 /** 2 * Override the parent class implementation in order to intercept PATCH requests. 3 */ 4 @Override 5 protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) 6 throws ServletException, IOException { 7 8 HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod()); 9 if (httpMethod == HttpMethod.PATCH || httpMethod == null) { 10 processRequest(request, response); 11 } 12 else { 13 super.service(request, response); 14 } 15 }
最后回到 HttpServlet 的 service 方法中,这里使用到的设计模式是模板方法。
1 protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) 2 throws ServletException, IOException { 3 4 String method = req.getMethod(); 5 6 if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) { 7 long lastModified = getLastModified(req); 8 if (lastModified == -1) { 9 // servlet doesn't support if-modified-since, no reason 10 // to go through further expensive logic 11 doGet(req, resp); 12 } else { 13 long ifModifiedSince; 14 try { 15 ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE); 16 } catch (IllegalArgumentException iae) { 17 // Invalid date header - proceed as if none was set 18 ifModifiedSince = -1; 19 } 20 if (ifModifiedSince < (lastModified / 1000 * 1000)) { 21 // If the servlet mod time is later, call doGet() 22 // Round down to the nearest second for a proper compare 23 // A ifModifiedSince of -1 will always be less 24 maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified); 25 doGet(req, resp); 26 } else { 27 resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED); 28 } 29 } 30 31 } else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) { 32 long lastModified = getLastModified(req); 33 maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified); 34 doHead(req, resp); 35 36 } else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) { 37 doPost(req, resp); 38 39 } else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) { 40 doPut(req, resp); 41 42 } else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) { 43 doDelete(req, resp); 44 45 } else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) { 46 doOptions(req,resp); 47 48 } else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) { 49 doTrace(req,resp); 50 51 } else { 52 // 53 // Note that this means NO servlet supports whatever 54 // method was requested, anywhere on this server. 55 // 56 57 String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented"); 58 Object[] errArgs = new Object[1]; 59 errArgs[0] = method; 60 errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs); 61 62 resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg); 63 } 64 }
然后在跳到 FrameworkServlet 的 doGet 方法中,doGet方法中用到 processRequest 方法,再看看上面对 patch 进行单独处理,可见是把将不同类型的请求合并到了processRequest 这个方法中来处理。
1 @Override 2 protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) 3 throws ServletException, IOException { 4 5 processRequest(request, response); 6 }
processRequest 方法中做了三件事:
-
调用了 doService 模板方法具体处理请求。
-
将当前请求的 LocaleContext 和 ServletRequestAttributes 在处理请求前设置到了 LocaleContextHolder 和 RequestContextHolder,并在请求处理完成后恢复
-
请求处理完后发布了 ServletRequestHandledEvent 消息。
1 protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) 2 throws ServletException, IOException { 3 4 long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); 5 Throwable failureCause = null; 6 7 LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext(); 8 LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request); 9 10 RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes(); 11 ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes); 12 13 WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); 14 asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor()); 15 16 initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes); 17 18 try { 19 doService(request, response); 20 } 21 catch (ServletException | IOException ex) { 22 failureCause = ex; 23 throw ex; 24 } 25 catch (Throwable ex) { 26 failureCause = ex; 27 throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex); 28 } 29 30 finally { 31 resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes); 32 if (requestAttributes != null) { 33 requestAttributes.requestCompleted(); 34 } 35 logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager); 36 publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause); 37 } 38 }
上面这段代码调用了 doService 的模板方法,接着走到了 DispatcherServlet 类中的 doService方法。
1 @Override 2 protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { 3 logRequest(request); 4 5 // Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include, 6 // to be able to restore the original attributes after the include. 7 Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null; 8 if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) { 9 attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>(); 10 Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames(); 11 while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) { 12 String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement(); 13 if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) { 14 attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName)); 15 } 16 } 17 } 18 19 // Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects. 20 request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext()); 21 request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver); 22 request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver); 23 request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource()); 24 25 if (this.flashMapManager != null) { 26 FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response); 27 if (inputFlashMap != null) { 28 request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap)); 29 } 30 request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap()); 31 request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager); 32 } 33 34 try { 35 doDispatch(request, response); 36 } 37 finally { 38 if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { 39 // Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include. 40 if (attributesSnapshot != null) { 41 restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot); 42 } 43 } 44 } 45 }
然后进行请求的分发 DispatcherServlet#doDispatch
1 protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { 2 HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; 3 HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; 4 boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; 5 6 WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); 7 8 try { 9 ModelAndView mv = null; 10 Exception dispatchException = null; 11 12 try { 13 processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); 14 multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); 15 16 // 确定当前请求的handler 17 mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); 18 if (mappedHandler == null) { 19 noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); // 没有找到则执行此方法 20 return; 21 } 22 23 // 确定当前请求的处理程序适配器 24 HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); 25 26 // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. 27 String method = request.getMethod(); 28 boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); 29 if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { 30 long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); 31 if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { 32 return; 33 } 34 } 35 36 if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { 37 return; 38 } 39 40 // 调用对应handler方法 41 mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); 42 43 if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { 44 return; 45 } 46 47 applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); 48 mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); 49 } 50 catch (Exception ex) { 51 dispatchException = ex; 52 } 53 catch (Throwable err) { 54 // As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well, 55 // making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios. 56 dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err); 57 } 58 processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); 59 } 60 catch (Exception ex) { 61 triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); 62 } 63 catch (Throwable err) { 64 triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, 65 new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err)); 66 } 67 finally { 68 if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { 69 // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion 70 if (mappedHandler != null) { 71 mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); 72 } 73 } 74 else { 75 // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. 76 if (multipartRequestParsed) { 77 cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); 78 } 79 } 80 } 81 }
看看 getHandler 方法,遍历所有配置的 HandlerMapping 类,可以看出是支持用户配置多个 HandlerMapping 类的,
1 @Nullable 2 protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { 3 if (this.handlerMappings != null) { 4 for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) { 5 HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request); 6 if (handler != null) { 7 return handler; 8 } 9 } 10 } 11 return null; 12 }
如果没有找到对应的 HandlerExecutionChain 对象,则会执行 noHandlerFound 方法返回异常。
1 protected void noHandlerFound(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { 2 if (pageNotFoundLogger.isWarnEnabled()) { 3 pageNotFoundLogger.warn("No mapping for " + request.getMethod() + " " + getRequestUri(request)); 4 } 5 if (this.throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound) { 6 throw new NoHandlerFoundException(request.getMethod(), getRequestUri(request), 7 new ServletServerHttpRequest(request).getHeaders()); 8 } 9 else { 10 response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND); // 404错误 11 } 12 }
返回到 DispatcherServlet#doDispatch,找到了对应的 handler 后,就去寻找对应的 HandlerAdapter。与 HandlerMapping 类似,查找能够处理具体 Handler 的 HandlerAdapter 时同样会遍历所有配置了的 HandlerAdapter,没有找到对应的 adapter 则会抛出异常。
1 protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException { 2 if (this.handlerAdapters != null) { 3 for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) { 4 if (adapter.supports(handler)) { 5 return adapter; 6 } 7 } 8 } 9 throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler + 10 "]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler"); 11 }
前没有什么问题发生,则按照顺序依次调用 HandlerInterceptor的 preHandle 方法,但当任一 HandlerInterceptor 的 preHandle方法返回了 false 就不再继续执行其他HandlerInterceptor 的 preHandle方法,而是直接跳转执行 triggerAfterCompletion 方法。
1 boolean applyPreHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { 2 HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors(); 3 if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) { 4 for (int i = 0; i < interceptors.length; i++) { 5 HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i]; 6 if (!interceptor.preHandle(request, response, this.handler)) { 7 triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null); 8 return false; 9 } 10 this.interceptorIndex = i; 11 } 12 } 13 return true; 14 }
然后执行 mapperHandler 的 applyPostHandle 方法,应用注册拦截器的 postHandle 方法。
void applyPostHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable ModelAndView mv) throws Exception { HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors(); if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) { for (int i = interceptors.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i]; interceptor.postHandle(request, response, this.handler, mv); } } }
最后执行 processDispatchResult 方法
1 /** 2 * Handle the result of handler selection and handler invocation, which is 3 * either a ModelAndView or an Exception to be resolved to a ModelAndView. 4 */ 5 private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, 6 HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, ModelAndView mv, Exception exception) throws Exception { 7 8 boolean errorView = false; 9 //判断 HandlerMapping、HandlerAdapter 处理时的异常是否有异常,有异常则进行异常处理 10 if (exception != null) { 11 //上述两个组件处理时的异常不为空 12 //如果为 ModelAndViewDefiningException 异常,则获取一个异常视图 13 if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) { 14 logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception); 15 mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView(); 16 } 17 //如果不为 ModelAndViewDefiningException 异常,进行异常视图的获取 18 else { 19 Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null); 20 mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception); 21 errorView = (mv != null); 22 } 23 } 24 25 // Did the handler return a view to render? 26 //判断 mv 是否为空,不管是正常的 ModelAndView 还是异常的 ModelAndView,只要存在 mv 就进行视图渲染 27 if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) { 28 render(mv, request, response); // 交给rander渲染 29 if (errorView) { 30 WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request); 31 } 32 } 33 //否则记录无视图 34 else { 35 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 36 logger.debug("Null ModelAndView returned to DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + 37 "': assuming HandlerAdapter completed request handling"); 38 } 39 } 40 41 if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { 42 // Concurrent handling started during a forward 43 return; 44 } 45 //执行相关HandlerInterceptor的afterCompletion 方法 46 if (mappedHandler != null) { 47 mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null); 48 } 49 }
到这里之后则按着栈帧一步步弹出,DispatcherServlet 处理完 Http 请求的流程。