设计模式 - 组合模式
实例
界面控件库
假设一个界面控件库的设计场景,界面控件分为两大类,一类是单元控件,例如按钮、文本框等,一类是容器控件,例如窗体、中间面板等,用户可以根据需要自行搭配使用
初始解决方案
Button.java
/**
* @Description 单元控件:按钮
*/
public class Button {
private final String name;
public Button(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void display() {
System.out.println(this.name);
}
}
TextBox.java
/**
* @Description 单元控件:文本框
*/
public class TextBox {
private final String name;
public TextBox(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void display() {
System.out.println(this.name);
}
}
PopWindow.java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Description 容器控件:弹出窗口
*/
public class PopWindow {
private final List<CenterPanel> centerPanelList = new ArrayList<>();
private final List<Button> buttonList = new ArrayList<>();
private final List<TextBox> textBoxList = new ArrayList<>();
private final String name;
public PopWindow(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void addCenterPanel(CenterPanel centerPanel) {
centerPanelList.add(centerPanel);
}
public void addButton(Button button) {
buttonList.add(button);
}
public void addTextBox(TextBox textBox) {
textBoxList.add(textBox);
}
public void display() {
System.out.println(this.name);
centerPanelList.forEach(CenterPanel::display);
buttonList.forEach(Button::display);
textBoxList.forEach(TextBox::display);
}
}
CenterPanel.java
/**
* @Description 容器控件:中间面板
*/
public class CenterPanel {
private final List<PopWindow> popWindowList = new ArrayList<>();
private final List<Button> buttonList = new ArrayList<>();
private final List<TextBox> textBoxList = new ArrayList<>();
private final String name;
public CenterPanel(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void addPopWindow(PopWindow popWindow) {
popWindowList.add(popWindow);
}
public void addButton(Button button) {
buttonList.add(button);
}
public void addTextBox(TextBox textBox) {
textBoxList.add(textBox);
}
public void display() {
System.out.println(this.name);
popWindowList.forEach(PopWindow::display);
buttonList.forEach(Button::display);
textBoxList.forEach(TextBox::display);
}
}
Test.java
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CenterPanel centerPanel = new CenterPanel("中央面板");
PopWindow popWindow = new PopWindow("弹出窗");
TextBox textBox = new TextBox("文本框");
Button button = new Button("按钮");
popWindow.addTextBox(textBox);
popWindow.addButton(button);
centerPanel.addTextBox(textBox);
centerPanel.addButton(button);
centerPanel.addPopWindow(popWindow);
centerPanel.display();
}
}
- 输出如下:
中央面板
弹出窗
按钮
文本框
按钮
文本框
- 不难看出,该方案存在诸多问题:
组合模式
概念
- 组合模式(
Composite Pattern):组合多个对象形成树形结构以表示具有"整体—部分"关系的层次结构 - 组合模式使客户端对单个对象和组合对象保持一致的方式处理
- 组合模式又称为"整体—部分"(
Part-Whole)模式 - 组合模式是一种对象结构型模式
- 组合模式结构图
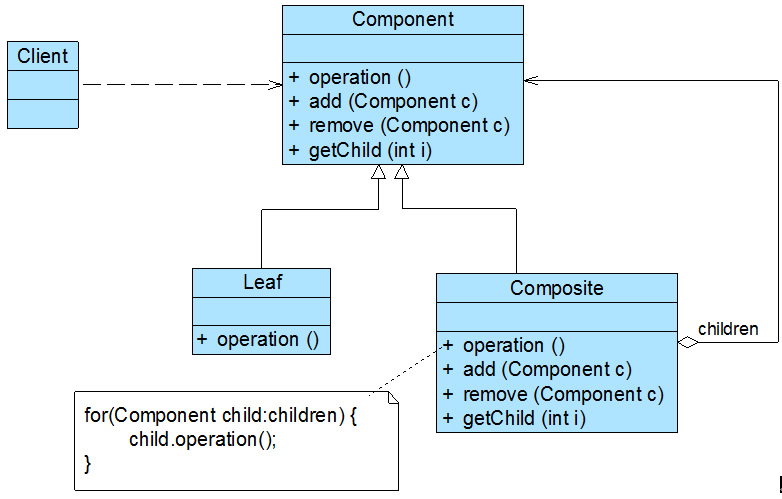
角色定义
| 角色 | 名称 | 释义 |
|---|---|---|
| Component | 抽象构件 | 可以是接口或抽象类,为叶子构件和容器构件对象声明接口,在该角色中可以包含所有子类共有行为的声明和实现。在抽象构件中定义了访问及管理它的子构件的方法,如增加子构件、删除子构件、获取子构件等 |
| Leaf | 叶子构件 | 它在组合结构中表示叶子节点对象,叶子节点没有子节点,它实现了在抽象构件中定义的行为。对于那些访问及管理子构件的方法,可以通过异常等方式进行处理 |
| Composite | 容器构件 | 它在组合结构中表示容器节点对象,容器节点包含子节点,其子节点可以是叶子节点,也可以是容器节点,它提供一个集合用于存储子节点,实现了在抽象构件中定义的行为,包括那些访问及管理子构件的方法,在其业务方法中可以递归调用其子节点的业务方法 |
透明组合模式
Component.java
/**
* @Description 抽象组件
*/
public abstract class Component {
public void add(Component component) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("不支持该操作");
}
public void remove(Component component) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("不支持该操作");
}
public Component getChild(int i) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("不支持该操作");
}
public abstract void display();
}
Button.java
/**
* @Description 按钮:叶子构件
*/
public class Button extends Component {
private final String name;
public Button(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void display() {
System.out.println(this.name);
}
}
TextBox.java
/**
* @Description 文本框:叶子构件
*/
public class TextBox extends Component {
private final String name;
public TextBox(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void display() {
System.out.println(this.name);
}
}
CenterPanel.java
/**
* @Description 中间面板:容器构件
*/
public class CenterPanel extends Component {
private final List<Component> componentList = new ArrayList<>();
private final String name;
private final Integer level;
public CenterPanel(String name, Integer level) {
this.name = name;
this.level = level;
}
@Override
public void add(Component component) {
componentList.add(component);
}
@Override
public void remove(Component component) {
componentList.remove(component);
}
@Override
public Component getChild(int i) {
return componentList.get(i);
}
@Override
public void display() {
System.out.println(this.name);
componentList.forEach(component -> {
for (int i = 0; i < this.level; i++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
component.display();
});
}
}
PopWindow.java
/**
* @Description 弹出窗口:容器构件
*/
public class PopWindow extends Component {
private final List<Component> componentList = new ArrayList<>();
private final String name;
private final Integer level;
public PopWindow(String name, Integer level) {
this.name = name;
this.level = level;
}
@Override
public void add(Component component) {
componentList.add(component);
}
@Override
public void remove(Component component) {
componentList.remove(component);
}
@Override
public Component getChild(int i) {
return componentList.get(i);
}
@Override
public void display() {
System.out.println(this.name);
componentList.forEach(component -> {
for (int i = 0; i < this.level; i++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
component.display();
});
}
}
Test.java
/**
* @Description 透明组合模式测试类
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Component centerPanel = new CenterPanel("中央面板", 1);
Component popWindow = new PopWindow("弹出窗", 2);
Component textBox = new TextBox("文本框");
Component button = new Button("按钮");
popWindow.add(textBox);
popWindow.add(button);
centerPanel.add(textBox);
centerPanel.add(button);
centerPanel.add(popWindow);
centerPanel.display();
}
}
- 输出如下:
中央面板
文本框
按钮
弹出窗
文本框
按钮
- 类图如下:
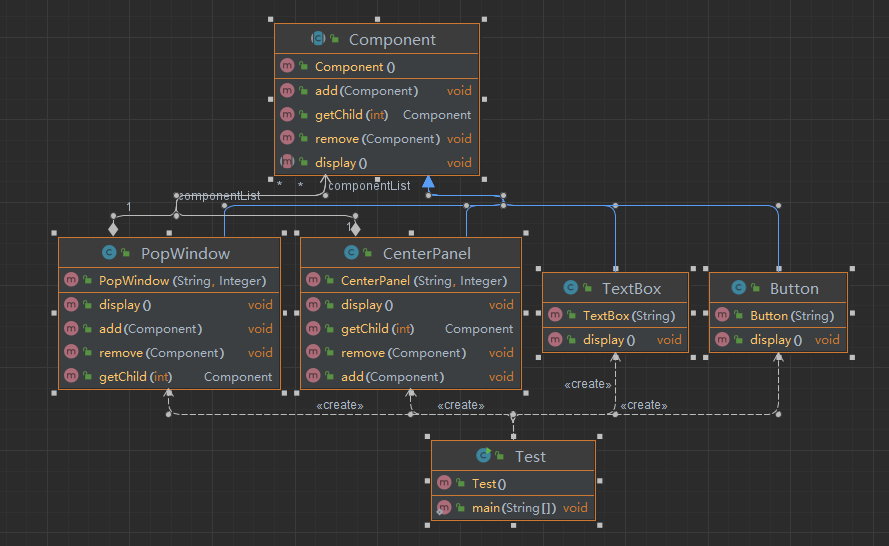
- 透明组合模式:抽象构件
Component中声明了所有用于管理成员对象的方法,包括add()、remove()以及getChild()等方法,这样做的好处是确保所有的构件类都有相同的接口 - 透明组合模式的缺点:不够安全,叶子对象和容器对象是有区别的,叶子对象不可能包含成员对象,为其提供
add()、remove()以及getChild()等方法是没有意义的,在运行阶段调用这些方法可能会出错
安全组合模式
Component.java
/**
* @Description 抽象组件
*/
public abstract class Component {
public abstract void display();
}
Button.java
/**
* @Description 按钮:叶子构件
*/
public class Button extends Component {
private final String name;
public Button(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void display() {
System.out.println(this.name);
}
}
TextBox.java
/**
* @Description 文本框:叶子构件
*/
public class TextBox extends Component {
private final String name;
public TextBox(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void display() {
System.out.println(this.name);
}
}
CenterPanel.java
/**
* @Description 中间面板:容器构件
*/
public class CenterPanel extends Component {
private final List<Component> componentList = new ArrayList<>();
private final String name;
private final Integer level;
public CenterPanel(String name, Integer level) {
this.name = name;
this.level = level;
}
public void add(Component component) {
componentList.add(component);
}
public void remove(Component component) {
componentList.remove(component);
}
public Component getChild(int i) {
return componentList.get(i);
}
@Override
public void display() {
System.out.println(this.name);
componentList.forEach(component -> {
for (int i = 0; i < this.level; i++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
component.display();
});
}
}
PopWindow.java
/**
* @Description 弹出窗口:容器构件
*/
public class PopWindow extends Component {
private final List<Component> componentList = new ArrayList<>();
private final String name;
private final Integer level;
public PopWindow(String name, Integer level) {
this.name = name;
this.level = level;
}
public void add(Component component) {
componentList.add(component);
}
public void remove(Component component) {
componentList.remove(component);
}
public Component getChild(int i) {
return componentList.get(i);
}
@Override
public void display() {
System.out.println(this.name);
componentList.forEach(component -> {
for (int i = 0; i < this.level; i++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
component.display();
});
}
}
Test.java
/**
* @Description 安全组合模式测试类
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CenterPanel centerPanel = new CenterPanel("中央面板", 1);
PopWindow popWindow = new PopWindow("弹出窗", 2);
Component textBox = new TextBox("文本框");
Component button = new Button("按钮");
popWindow.add(textBox);
popWindow.add(button);
centerPanel.add(textBox);
centerPanel.add(button);
centerPanel.add(popWindow);
centerPanel.display();
}
}
- 输出如下:
中央面板
文本框
按钮
弹出窗
文本框
按钮
- 安全组合模式:不在抽象构件
Component中声明任何用于管理成员对象的方法,而是在Composite类中声明并实现这些方法 - 安全组合模式的缺点:不够透明,叶子构件和容器构件具有不同的方法,且容器构件中那些用于管理成员对象的方法没有在抽象构件类中定义,因此客户端不能完全针对抽象编程
总结
- 优点
1.清楚地定义分层次的复杂对象,表示对象的全部或部分层次
2.让客户端忽略了层次的差异,方便对整个层次结构进行控制
3.简化客户端代码,符合开闭原则
- 缺点
1.限制类型时会较为复杂
2.使设计变得更加抽象
- 适用场景
1.希望客户端可以忽略组合对象与单个对象的差异时
2.处理一个树形结构
- 相关设计模式
1.组合模式和访问者模式
- 组合模式源代码
Container(AWT)、HashMap、ArrayList(jdk)、SqlNode(mybatis)



