31.下一个排列
实现获取下一个排列的函数,算法需要将给定数字序列重新排列成字典序中下一个更大的排列。
如果不存在下一个更大的排列,则将数字重新排列成最小的排列(即升序排列)。
必须原地修改,只允许使用额外常数空间。
以下是一些例子,输入位于左侧列,其相应输出位于右侧列。
1,2,3 → 1,3,2
3,2,1 → 1,2,3
1,1,5 → 1,5,1
又是一道没写出来的
每次都是看了题解区的思路,然后豁然开朗
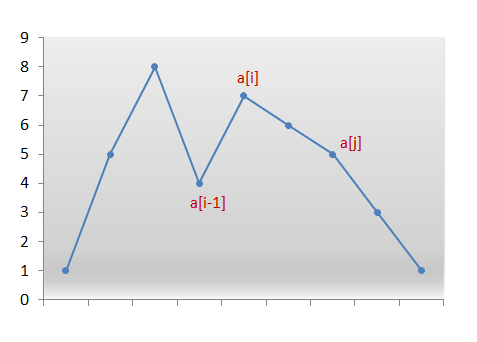
这个是官方的方法,交换一下a[i-1]和a[j],然后对右侧序列降序排列
c++复现版本如下:
class Solution {
public:
void nextPermutation(vector<int>& nums) {
int i,j;
for(i = nums.size()-1; i>0; i--)
if(nums[i-1] < nums[i])
for(j = nums.size()-1; j > i-1; j--)
if(nums[j] > nums[i-1]){
swap(nums[j], nums[i-1]);
sort(nums.begin()+i, nums.end());
return ;
}
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
}
};
Debugging is twice as hard as writing the code in the first place. Therefore, if you write the code as cleverly as possible, you are, by definition, not smart enough to debug it.