了解Oracle内核代码层的作用
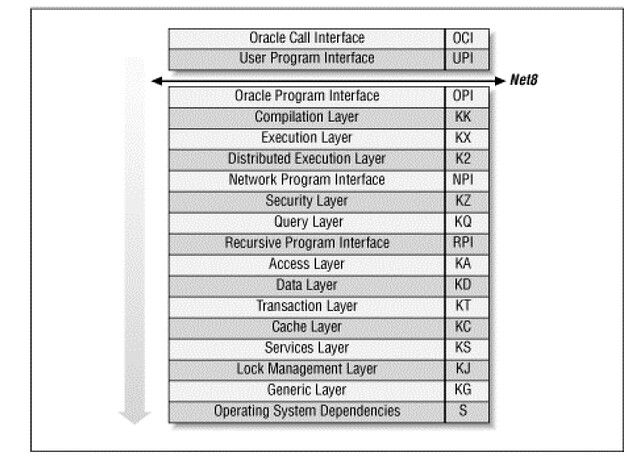 其中部分代码层的作用:
The cache layer (KC)
其中部分代码层的作用:
The cache layer (KC)
The cache layer manages the database buffer cache. It uses operating system dependent facilities for data file I/O, provides concurrency control facilities for local access to the cache buffers, and provides parallel cache management (PCM) instance locking facilities for Oracle parallel server. The other main responsibility of the cache layer is the control of redo generation into the log buffer, and the writing of redo to the log files. The cache layer also caches control file information.
- To read blocks.
- To update blocks in redo only mode.
This layer is responsible for the allocation of transactions to rollback segments, interested transaction list changes within data blocks, changes to rollback segment blocks for undo generation, transaction control facilities such as savepoints, and read consistency. The transaction layer is also responsible for space management, both at the level of segment free lists and at the level of tablespace extent allocation.
- To update blocks with undo.
- To check with the status of the transaction.
- To manage recursive transactions for nested space operations.
The recursive program interface is used to populate the dictionary cache from the data dictionary. Row cache recursive SQL statements are executed in a separate call context, but are not parsed and optimized in the compilation layer.
Row Cache Layer
- To read/update space dictionary information, where acutal updates happens by callbacks when row cache is flushed.
Recursive SQL
- To read/update dictionary information.
- To create/drop/alter files in tablespace.
posted on 2013-03-19 00:47 Oracle和MySQL 阅读(165) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报




 2群基础群 适合刚入门的同学,会共享最佳入门实践和资料 QQ群 # QQ群号:171092051 # 已经升级到 500人的超级群,空位多多,无需面试
2群基础群 适合刚入门的同学,会共享最佳入门实践和资料 QQ群 # QQ群号:171092051 # 已经升级到 500人的超级群,空位多多,无需面试


