proverif代码分析(一):SpreadMeNot: A Provably Secure and Privacy-Preserving Contact Tracing Protocol
时间:2022/08/23
一. 协议描述
论文题目:SpreadMeNot: A Provably Secure and Privacy-Preserving Contact Tracing Protocol
这篇论文提出了针对新冠疫情感染的跟踪协议,具体协议流程如下: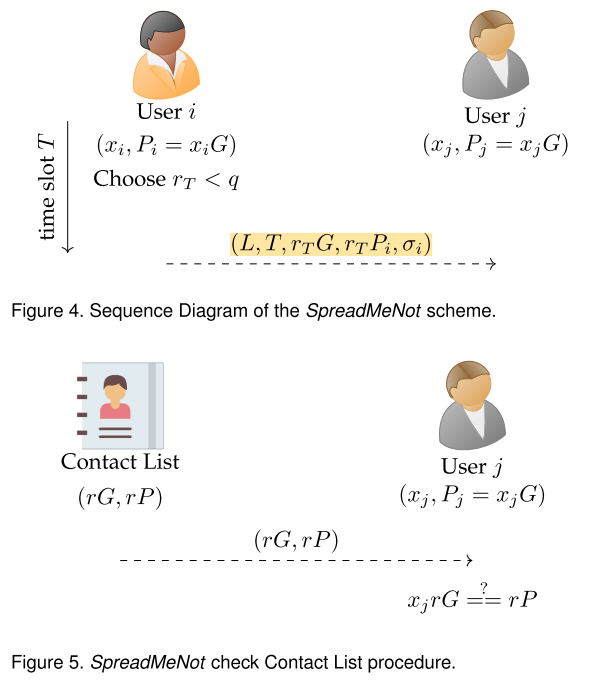
上图中Fig.4描述的是User i将自己的位置L、时间戳T、信标<rTG, rTPi>和签名值σi广播给周围的用户;Fig.5描述的是User j从下载新冠感染者的联系人列表,并从中比对是否自己的信标也在其中,从而确定自己是否是密接。
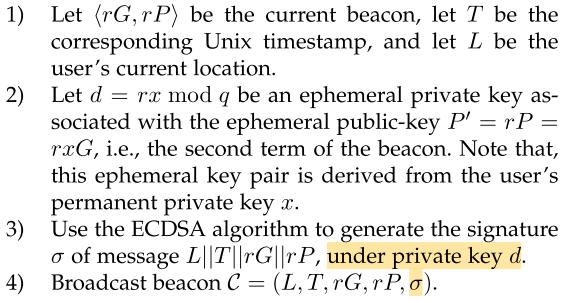
对于上面签名值的产生过程可以参考下图:
二. 代码分析
代码地址:https://github.com/pietrotedeschi/spreadmenot
协议代码:
1 (* 2 SpreadMeNot: A Provably Secure andPrivacy-Preserving Contact Tracing Protocol (Formal Security Proof with Proverif) 3 Authors: Pietro Tedeschi, Spiridon Bakiras and Roberto Di Pietro 4 Division of Information and Computing Technology (ICT) 5 College of Science and Engineering (CSE) 6 Hamad Bin Khalifa University (HBKU), Doha, Qatar 7 {ptedeschi, sbakiras, rdipietro}@hbku.edu.qa 8 *) 9 10 (*--Dolev-Yao model Open Channels--*) 11 free c:channel. (*Broadcasting Channel*) 12 13 type device. 14 type scalar. 15 type point. 16 type lon. 17 type lat. 18 type ts. 19 type id. 20 21 (*Elliptic Curve Generator Point and Cyrptographic Functions*) 22 const G: point [data]. 23 fun hash(bitstring):bitstring. 24 fun mult(scalar, point): point. (* 这里scalar对应私钥,生成的point对应公钥 *) 25 fun mul(scalar, scalar): scalar. 26 27 (*--Check timestamp freshness operation--*) 28 fun freshness(ts, bool): bool 29 reduc forall T: ts; freshness(T, true) = true 30 otherwise forall T: ts; freshness(T, false) = false. 31 32 (*--Check distance operation--*) 33 fun distance(lat,lon,bool): bool 34 reduc forall c_lat: lat, c_lon:lon; distance(c_lat, c_lon, true) = true 35 otherwise forall c_lat: lat, c_lon:lon; distance(c_lat,c_lon, false) = false. 36 37 (*--Digital Signatures--*) 38 fun sign(bitstring, scalar): bitstring. 39 reduc forall m: bitstring, k: scalar; getmess(sign(m, k)) = m. 40 reduc forall m: bitstring, k: scalar, p:point; checksign(sign(m, k), mult(k,p)) = m. 41 42 (*Events*) 43 event releaseBeacon(bitstring). 44 event acceptBeacon(bitstring). 45 46 (* Authentication *) 47 query beacon: bitstring; event(acceptBeacon(beacon)) ==> event(releaseBeacon(beacon)). 48 49 let smnA = 50 new xi: scalar; (* 私钥 *) 51 new rk: scalar; 52 new lonc: lon; 53 new latc: lat; 54 new t: ts; 55 56 let rx = mul(rk,xi) in (* d=rx *) 57 let xG = mult(xi, G) in (* 公钥 *) 58 let rG = mult(rk, G) in (*Beacon 1st Component*) 59 let rxG = mult(rk, xG) in (*Beacon 2nd Component --- rP*) 60 61 let h = hash((latc,lonc,t,rG,rxG)) in 62 let ro = sign(h, rx) in 63 64 event releaseBeacon((latc,lonc,t,rG,rxG,ro)); 65 66 out(c, ((latc,lonc,t,rG,rxG,ro), freshness(t, true), distance(latc,lonc,true))). 67 68 (* A generic Receiver *) 69 let smnB = 70 new xj: scalar; 71 let xjG = mult(xj, G) in 72 in(c, ((latc:lat,lonc:lon,t:ts,rG:point,rxG:point,ro:bitstring), checkT:bool, checkL:bool)); 73 74 let xrG = mult(xj, rG) in 75 76 if checkT = true then 77 if checkL = true then 78 let roA = checksign(ro, xrG) in 79 event acceptBeacon((latc,lonc,t,rG,rxG,ro)). 80 81 82 process ((!smnA) | (!smnB))
下图是对上面事件的描述:

针对上面的代码,由于代码量比较少,理解起来是比较容易的,process smnA模拟了Fig.4的过程,process smnB模拟了Fig.5的过程。总的来说,上面的代码对于ECC的建模是比较好的,但是对于上面代码的可执行性存在疑惑。
疑惑:从建模的角度来说,上面的代码其实省略了很多中间过程,主要的疑惑点在于process smnB中由于xj这个私钥是new产生的,相当于是一个随机值,这意味着该值产生的xrG永远无法等于收到rxG,所以签名检查永远无法通过,相当于B永远不在感染者列表中(也就是A≠B)。由于签名永远无法通过,所以事件acceptBeacon永远也不会出现,最终导致query永远通过。
(不知道我上面的理解是否正确,如有错误,欢迎指正)
努力,向上,自律


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号