java异常
异常概述
java异常就是指java程序不正常的行为或者状态。异常发生的原因有很多,通常包含以下几大类:
- 用户输入了非法数据。
- 要打开的文件不存在。
- 网络通信时连接中断,或者JVM内存溢出。
这些异常有的是因为用户错误引起,有的是程序错误引起的,还有其它一些是因为物理错误引起的。
异常的层次结构
所有的异常类是从 java.lang.Exception 类继承的子类。
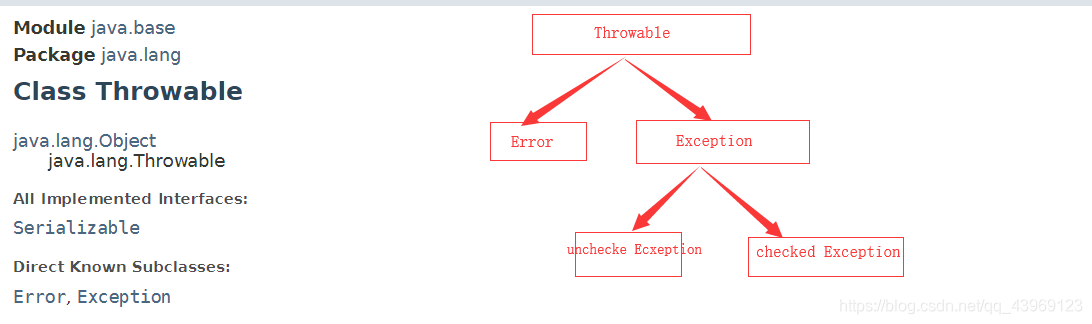
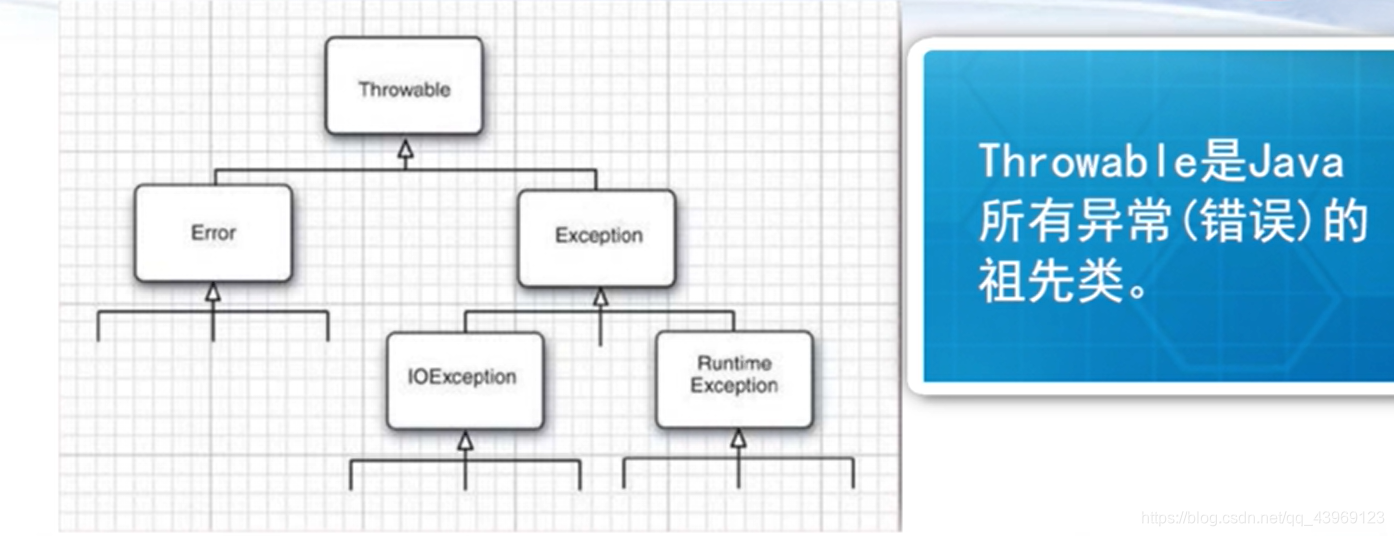
Error
Error一般代表JVM内部出现错误。
Exception
RuntimeException(UncheckedException)
运行时异常,编译器不会辅助去检查,只有在程序运行时才能显示出来。此类异常以预防为主。举个例子:a/b程序不会去帮我们进行辅助检查b是否为0,只有在运行时才会发生异常情况。
CheckedException
该类异常在编译时就需要处理,否则通不过编译。如果程序中有int a = 5/0;这段代码,则必须要异常处理。用户自定义的异常CheckedExcpetion
异常的处理方式
1.捕获异常
捕获异常通过try-catch-finally来处理。当可能发生不止一个异常时,可以通过多个catch来处理,finally无论是否发生异常都要去运行,即使在try和catch块中有return语句也要执行。

注意事项:
- catch块的匹配是从上到下匹配的,所以尽量把范围小的异常放在上面,范围大的异常放在上面。
- try、catch、finally里面可以继续嵌套try-catch-finally代码块
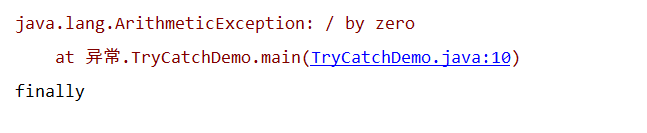
package 异常;
/**
* @author pony
* @date 2020/4/27
*/
public class TryCatchDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
int a = 5/0;
System.out.println("try");
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
System.out.println("finally");
}
}
}
运行结果:
2.声明异常
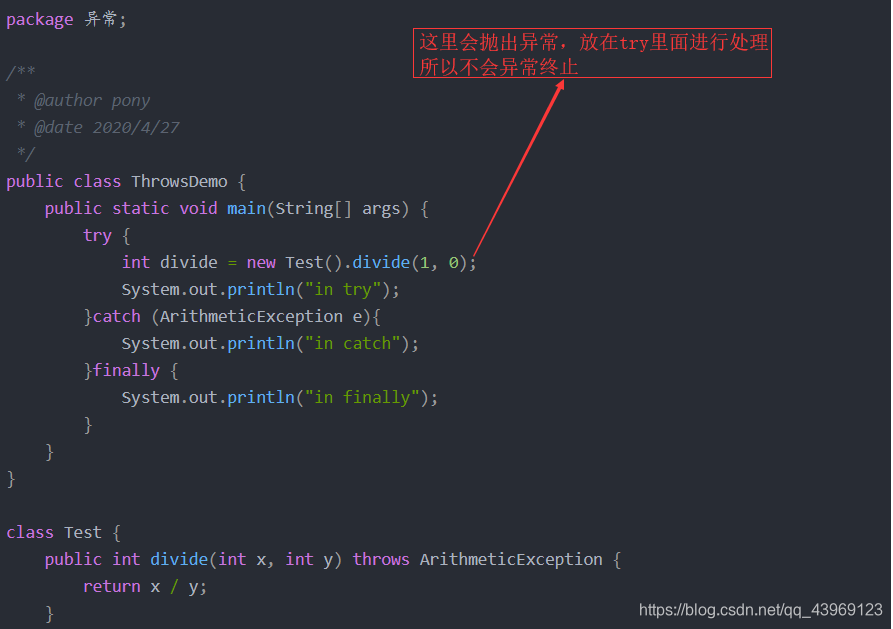
当CheckedException发生时,不一定要立即去处理它,可以通过把异常throws出去。调用带有thorows的方法,要么处理,要么继续throws出去。如果一个方法可能抛出多个已检查异常,则应在方法首部列出所有异常,用逗号隔开。
package 异常;
/**
* @author pony
* @date 2020/4/27
*/
public class ThrowsDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int divide = new Test().divide(1, 0);
System.out.println("in try");
}catch (ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("in catch");
}finally {
System.out.println("in finally");
}
}
}
class Test {
public int divide(int x, int y) throws ArithmeticException {
return x / y;
}
}
运行结果:

异常在继承中的关系
如果父类中的方法抛出了异常,那么它的子类在重写父类的方法时抛出的异常必须是父类抛出的异常的子集。
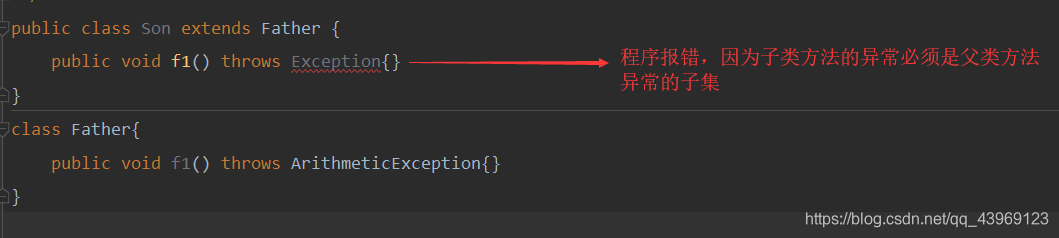
自定义异常
- 自定义异常需要继承Exception类或者其子类
- 继承自Exception类,就成了checkedException
- 继承自RuntimeException,就成了uncheckedException
- 自定义异常重点在构造函数
- 自定义异常通过
throw关键字抛出
package 异常;
/**
* @author pony
* @date 2020/4/27
*/
public class Stu {
public int divide(int x,int y){
return x/y;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws DivideException{
Stu stu = new Stu();
stu.divide5(5,-2);
}
public int divide2(int x,int y){
try{
return x/y;
}catch (ArithmeticException e){
e.printStackTrace();
return 0;
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
return 0;
}
}
public int divide3(int x,int y) throws ArithmeticException{
return x/y;
}
public int divide4(int x,int y){
// return divide3(x,y); //编译器不报错,因为divide3抛出的异常是runtimeException
// return divide5(x,y); //编译器报错,因为自定义的异常继承的是Exception,为checkedException
}
private int divide5(int x, int y) throws DivideException {
try{
if(y<0)
throw new DivideException("除数为负数",y);
return divide3(x,y);
}catch (ArithmeticException e){
e.printStackTrace();
return 0;
}
}
}
class DivideException extends Exception{
int divisor;
public DivideException(String message, int divisor) {
super(message);
this.divisor = divisor;
}
public int getDivisor() {
return divisor;
}
}



